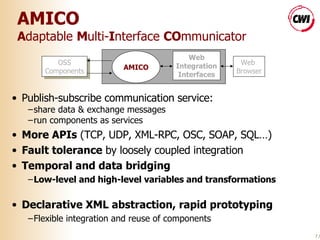
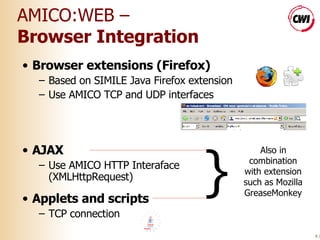
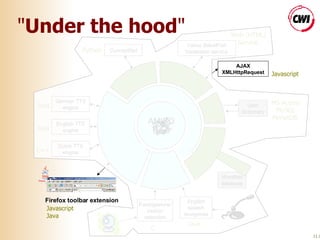
The document discusses building accessible web browsers using open-source software. It proposes a solution called AMICO:WEB that uses a service-based architecture to loosely couple and integrate various open-source components like speech recognition and text-to-speech engines. This allows novel interaction modalities to be supported beyond just screen, keyboard and mouse. AMICO:WEB acts as an adapter between web browsers and open-source components running as local or remote services. Examples of using translation and camera-based modalities are provided.
![Web Browser Accessibility using Open-Source Software http:// amico.sourceforge.net Željko Obrenović Jacco van Ossenbruggen Semantic Media Interfaces CWI, Amsterdam [email_address] http:// www.cwi.nl/~obrenovi /](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-browser-accessibility-using-opensource-software-29550/75/Web-Browser-Accessibility-using-Open-Source-Software-1-2048.jpg)