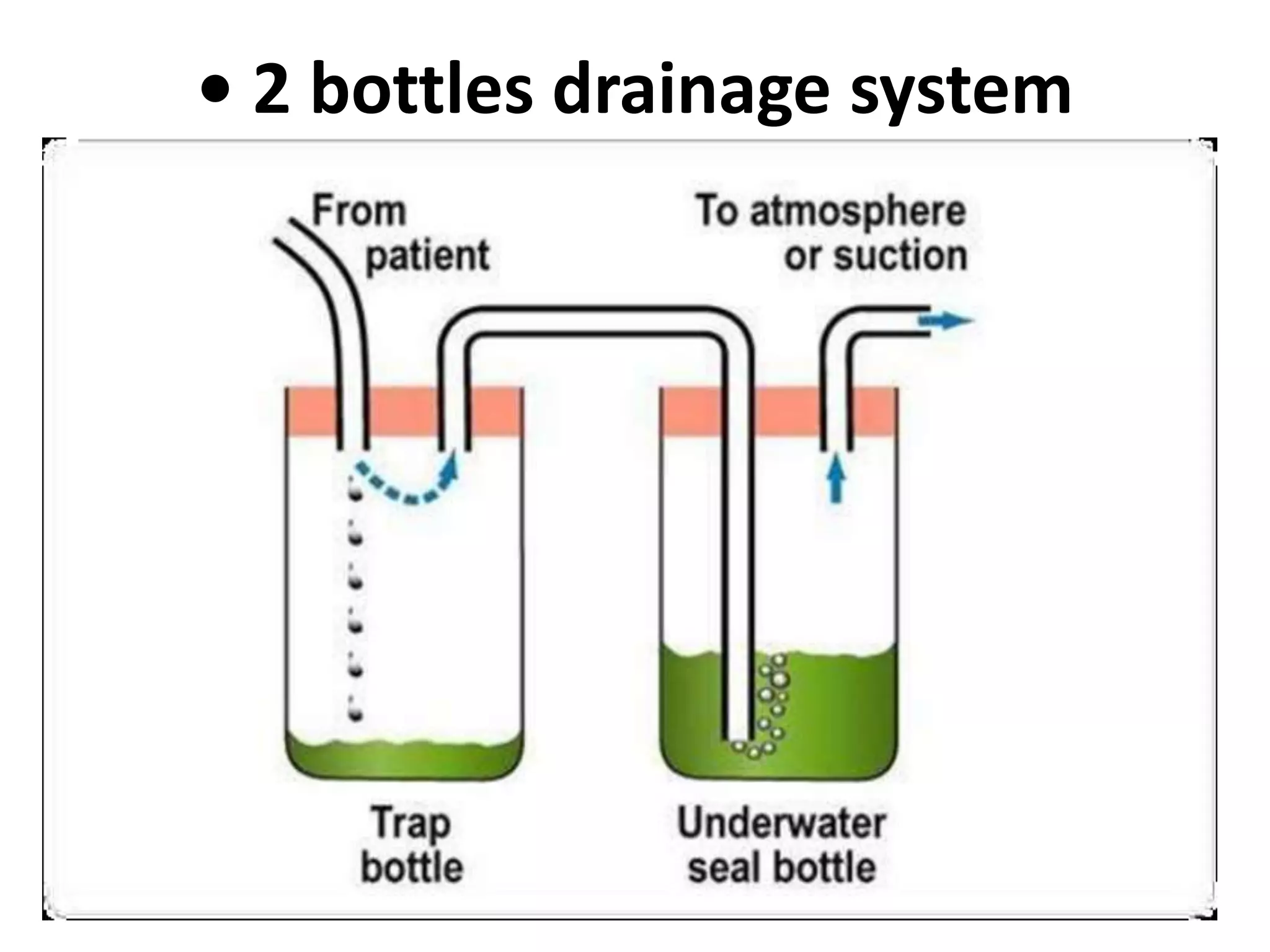
Water seal drainage is a closed chest drainage system used to drain air and fluid from the pleural space during exhalation while preventing backflow during inhalation. It is indicated for conditions causing pneumothorax or pleural effusions. The system uses gravity and a water seal to establish negative pressure and allow for lung expansion while continuously draining the pleural space. Proper placement and maintenance of the drainage system and tubes is important to ensure effective drainage and prevent complications.