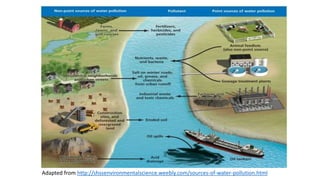
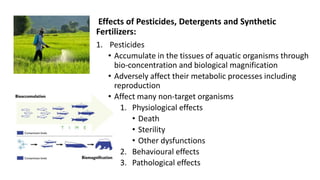
This document discusses various sources and effects of water pollution. It identifies key sources of water pollution as domestic/municipal, agricultural, industrial, oil spills, marine dumping, and burning fossil fuels. Water pollution can have serious negative impacts on human health, ecosystems, animals, and economies. It discusses specific pollutants like sewage, nutrients, pesticides, toxic chemicals, and their adverse effects. The document also outlines some methods to control water pollution, including implementing laws and regulations, international conventions, and practices like reducing chemical usage, organic farming, and reforestation.