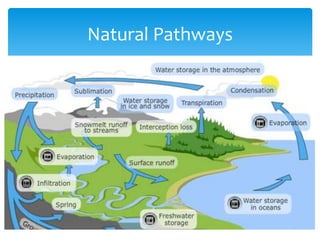
The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. It is powered by the sun and includes processes such as evaporation, transpiration, precipitation, and runoff. Water is stored in natural reservoirs including ice/snow, lakes, aquifers, and oceans. The water cycle is essential for life but is impacted by human activities like overpumping aquifers, water pollution, and increased surface runoff. More developed countries have advanced water filtration systems but also high industrial pollution, while less developed countries have less sanitation but lower overall pollution levels.