George Washington's presidency shaped the American government in several key ways:
1) It saw the growth of the Supreme Court and establishment of the federal court system through the Judiciary Act of 1789.
2) Washington helped develop the structure of the executive branch by creating the first Presidential Cabinet comprised of department heads and advisors.
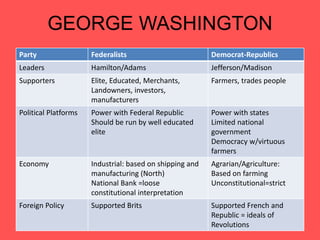
3) During his tenure, the first political parties - the Federalist and Democratic-Republican parties - arose, delineating the philosophical divisions within the government over states' rights and federal power.