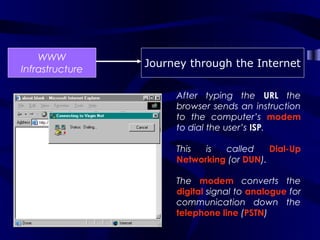
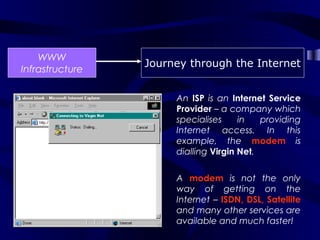
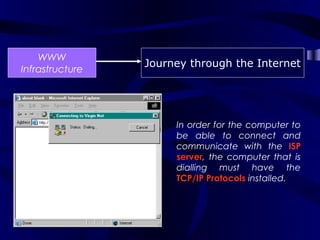
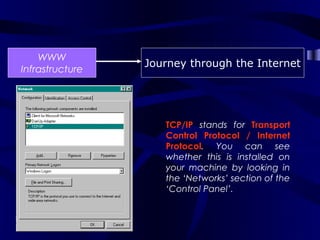
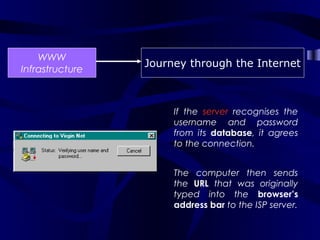
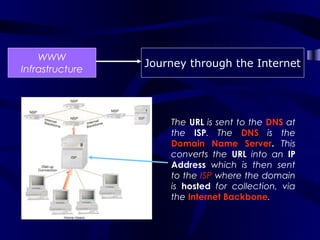
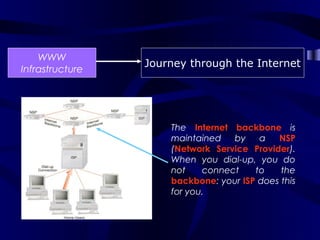
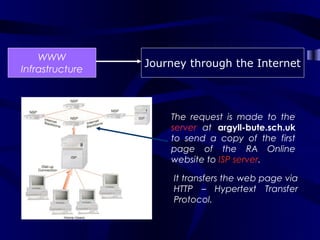
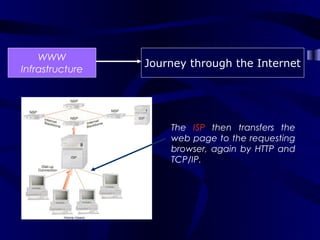
The document describes the journey a request takes from a web browser through the internet to a web server and back. It begins with the user entering a URL in their browser. Their computer then connects to their Internet Service Provider who directs the request to the appropriate DNS server to convert the URL to an IP address. The IP address is used to retrieve the requested page from the web server, which is then sent back to the user's browser to be displayed.