Embed presentation
Downloaded 70 times


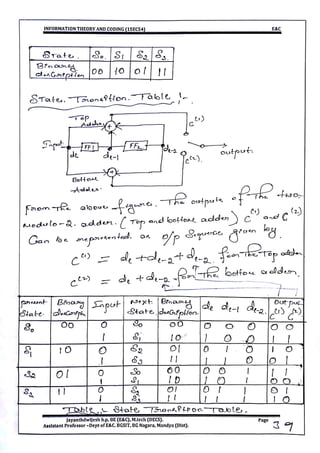
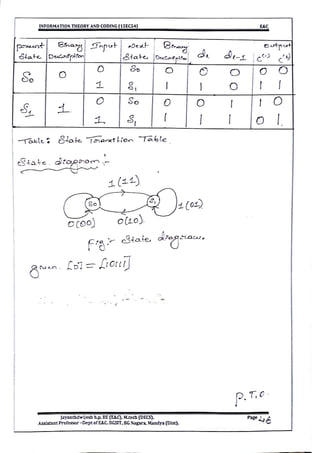
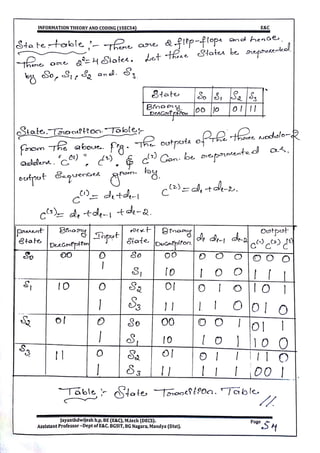
![ Number of rows in [G] =L (one input)
Number of rows in [G] =2L (two inputs)
Number of columns in [G]= n(L+M)
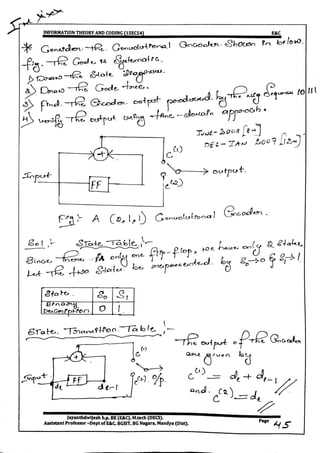
The output of the encoder is given by
[C] = [d][G]
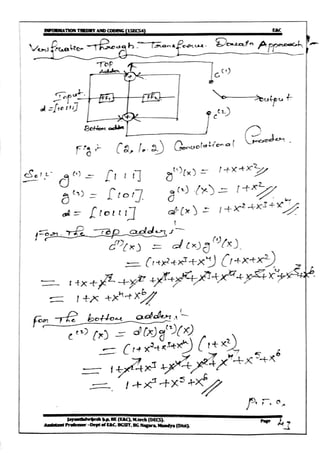
Transform domain approach
The output polynomials for the j(j=1,2,3…) adders are given by
𝑪𝒋
(x)= d(x) 𝒈𝒋
(x) for j=1, 2, 3….
The output of the encoder is given by
C(X) = 𝑪(𝟏)
(𝑿 𝒏
) +X 𝑪(𝟐)
(𝑿 𝒏
) + 𝑿 𝟐
𝑪(𝟑)
(𝑿 𝒏
) +……………+𝑿 𝒏−𝟏
𝑪(𝒏)
(𝑿 𝒏
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module5-171119064827/85/VTU-CBCS-E-C-5th-sem-Information-theory-and-coding-15EC54-Module-5-notes-3-320.jpg)















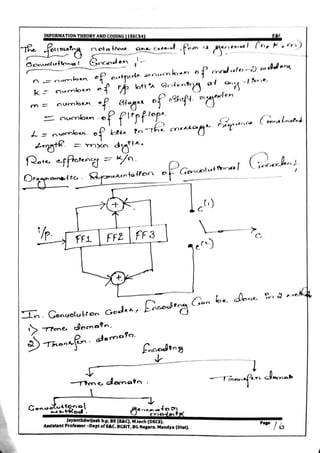
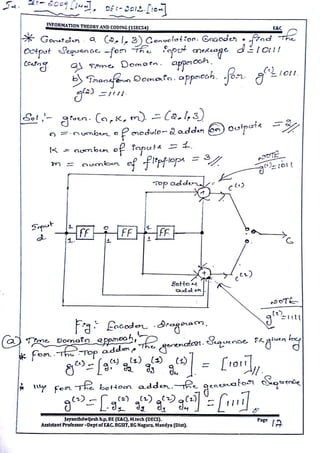



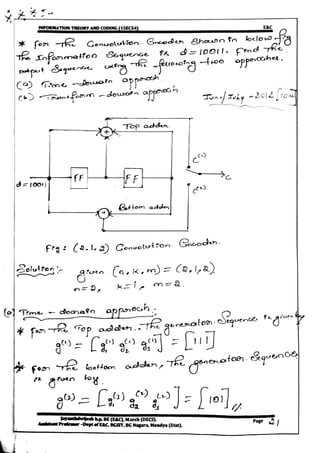
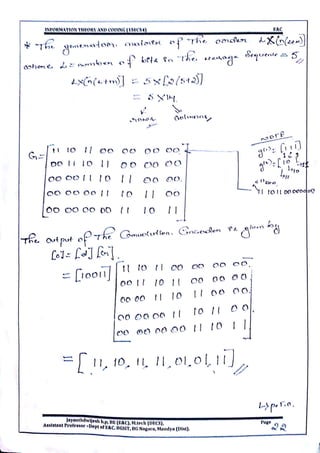


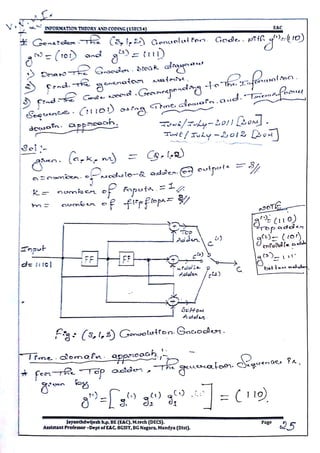



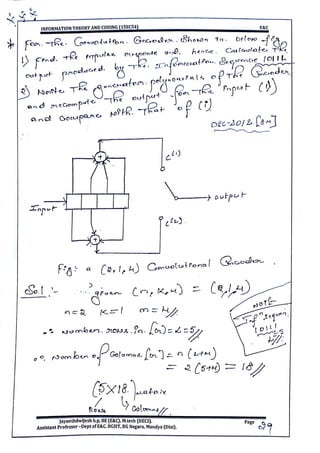


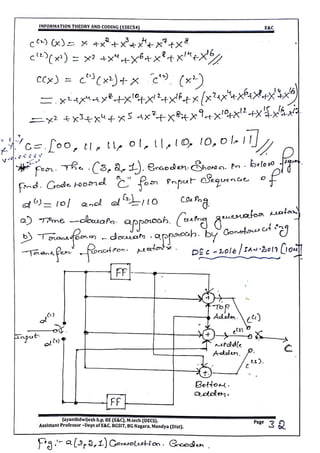





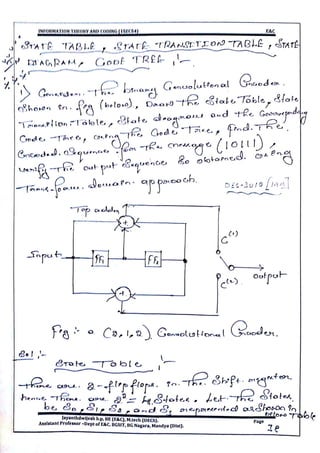
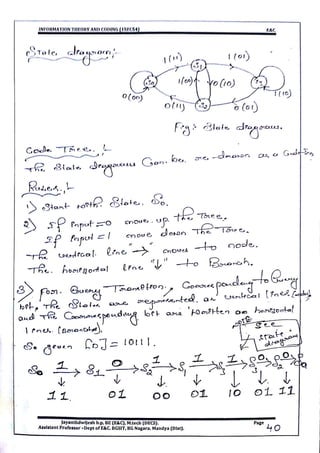

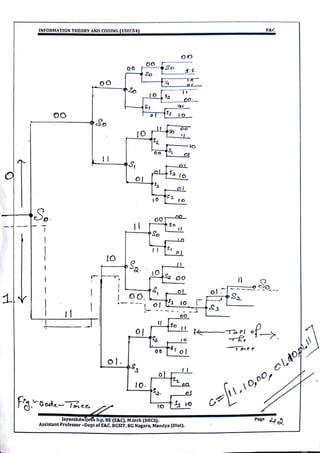

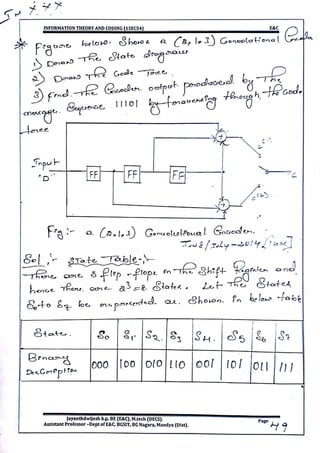
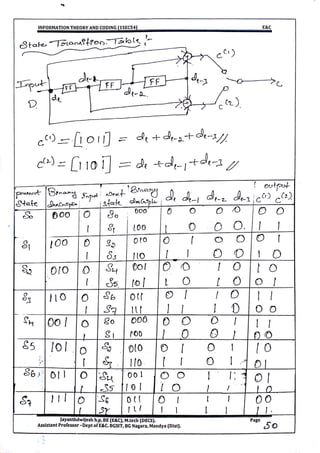
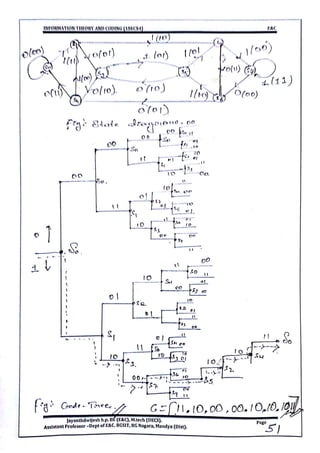

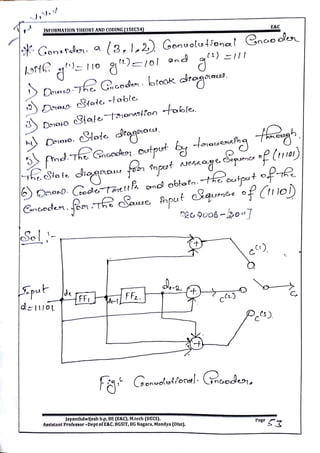
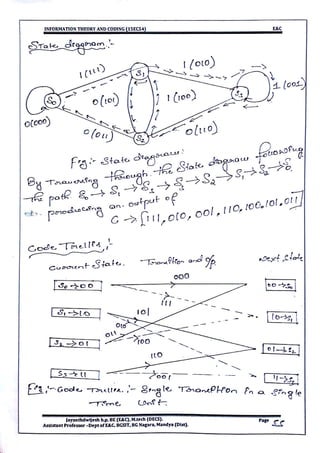

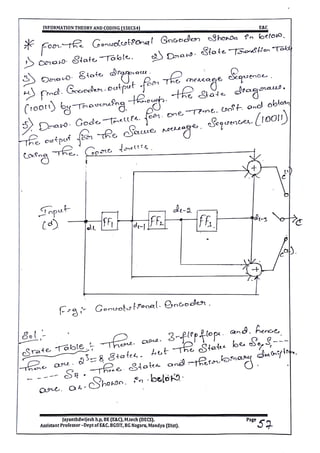
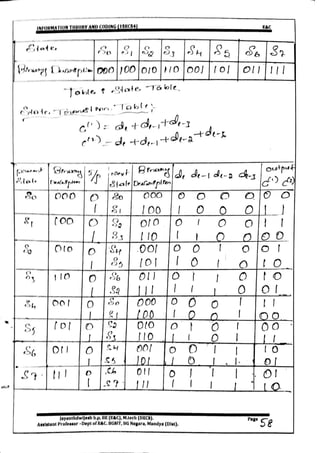
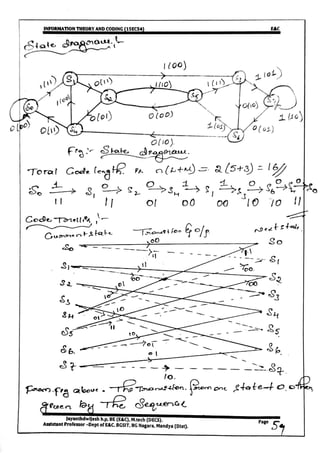


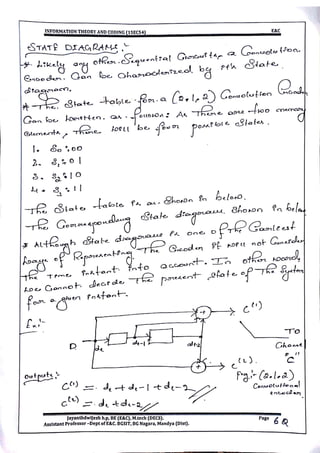
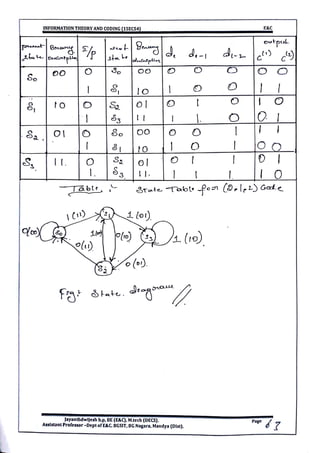



This document provides information and formulas related to information theory and coding. It discusses important cyclic codes like Reed-Solomon codes and convolution codes. For convolution codes, it provides the generator matrix formulas in the time and transform domains, showing how the output of the encoder is calculated from the input and generator matrix. It also gives the formulas for calculating the output polynomials from the input polynomial and generator polynomials in the transform domain approach.


![ Number of rows in [G] =L (one input)
Number of rows in [G] =2L (two inputs)
Number of columns in [G]= n(L+M)
The output of the encoder is given by
[C] = [d][G]
Transform domain approach
The output polynomials for the j(j=1,2,3…) adders are given by
𝑪𝒋
(x)= d(x) 𝒈𝒋
(x) for j=1, 2, 3….
The output of the encoder is given by
C(X) = 𝑪(𝟏)
(𝑿 𝒏
) +X 𝑪(𝟐)
(𝑿 𝒏
) + 𝑿 𝟐
𝑪(𝟑)
(𝑿 𝒏
) +……………+𝑿 𝒏−𝟏
𝑪(𝒏)
(𝑿 𝒏
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module5-171119064827/85/VTU-CBCS-E-C-5th-sem-Information-theory-and-coding-15EC54-Module-5-notes-3-320.jpg)
































































