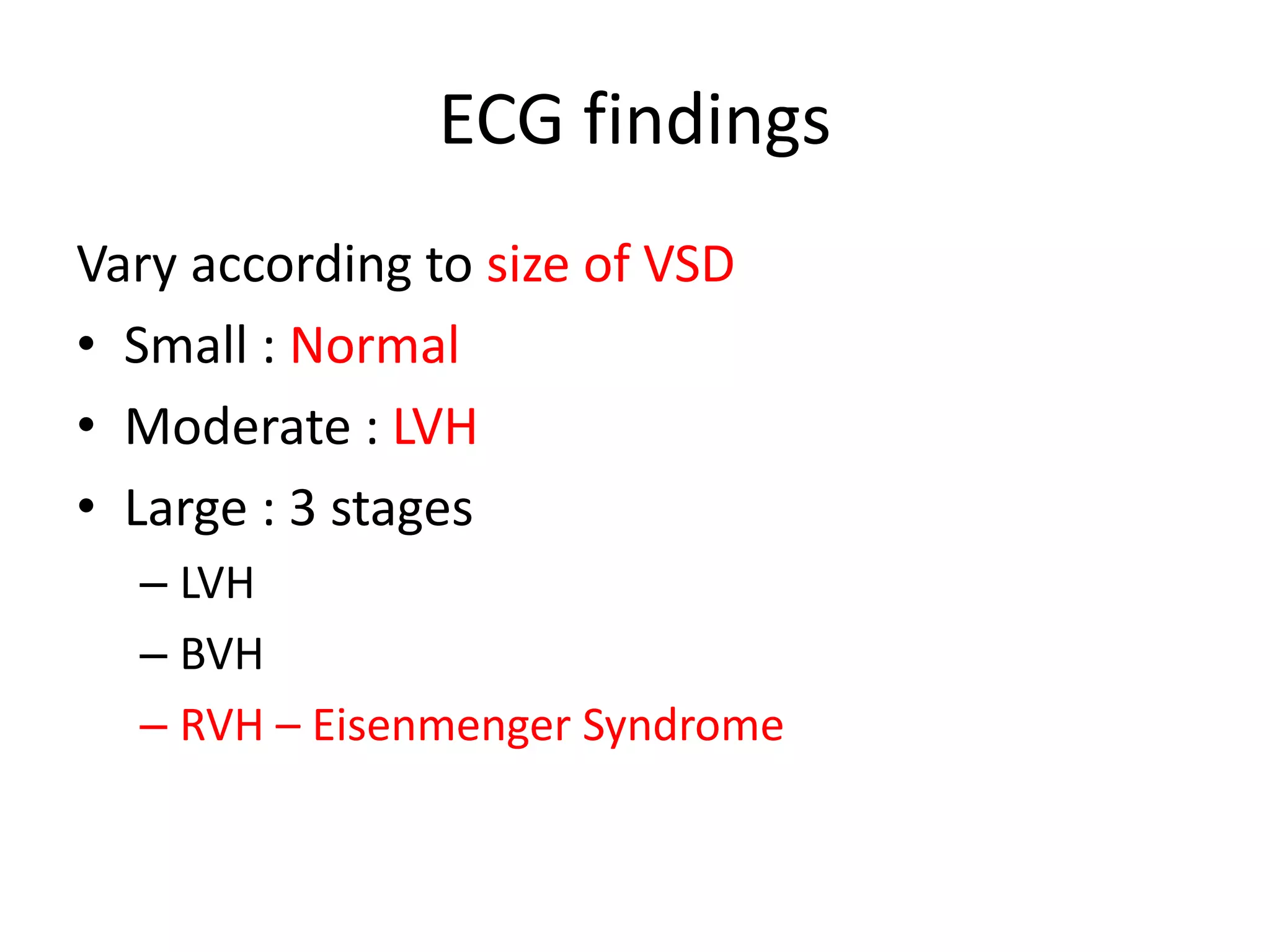
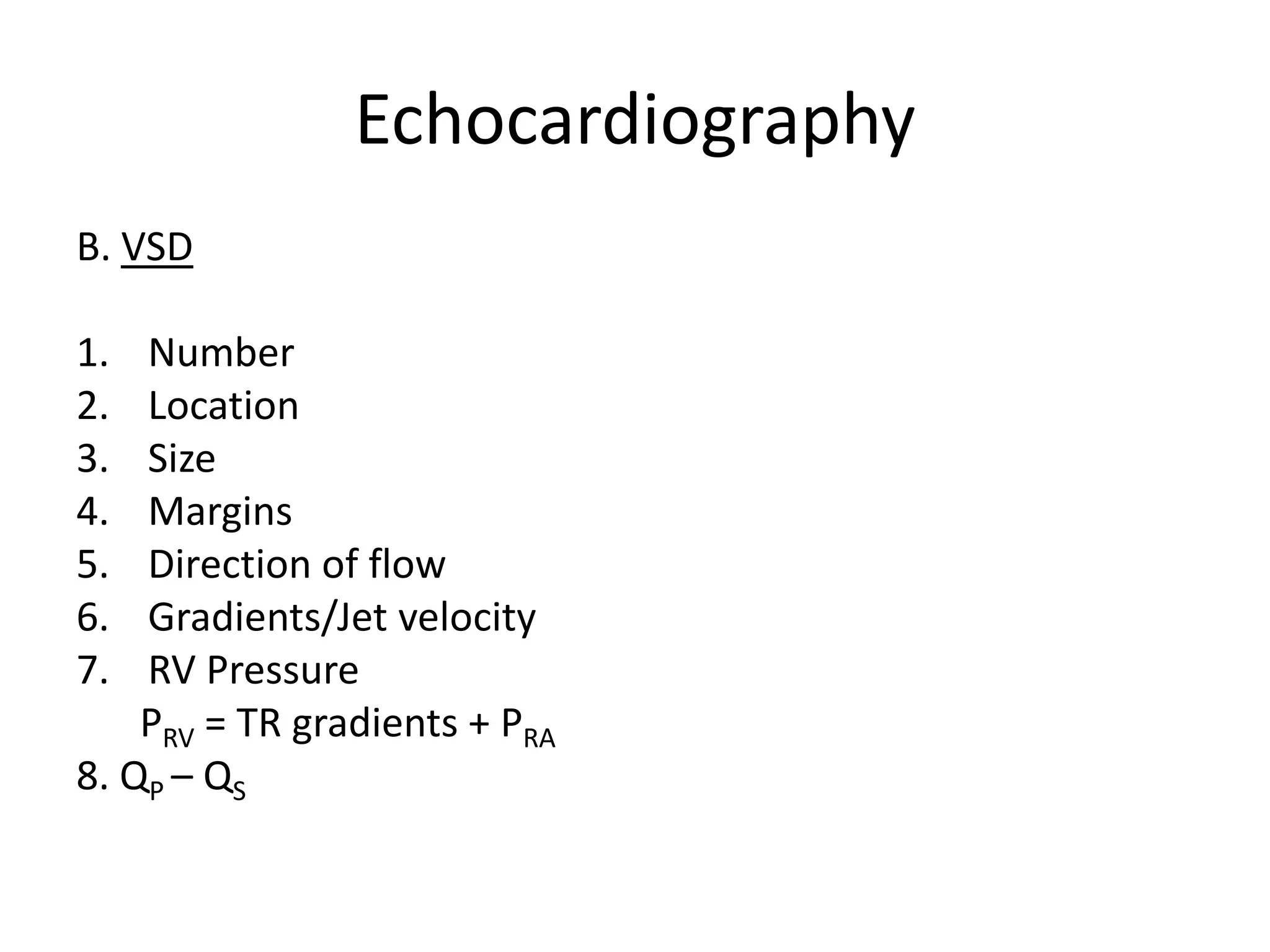
Surgical management of ventricular septal defects (VSDs) involves evaluation using echocardiography and cardiac catheterization to determine the size, location, and hemodynamics of the defect. Indications for surgical intervention include symptoms, large defect size, and pulmonary vascular disease. Approaches include transatrial, transventricular, and transarterial depending on defect location. Complications include heart block, residual defects, and pulmonary hypertensive crisis. Long-term outcomes are generally good with surgical cure, though late complications like endocarditis can occur. Device closure is now an option for certain midmuscular and anterior muscular VSDs.