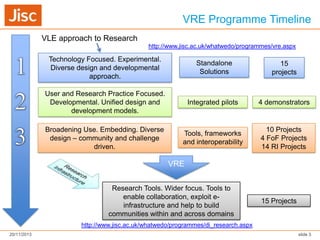
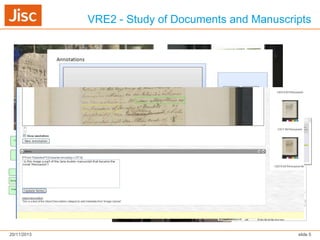
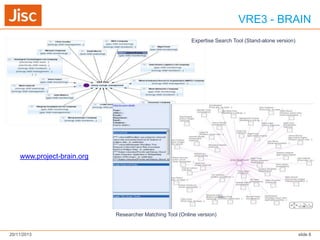
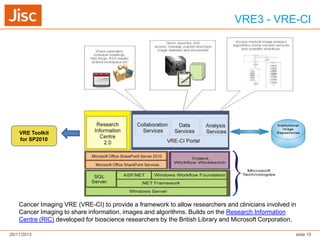
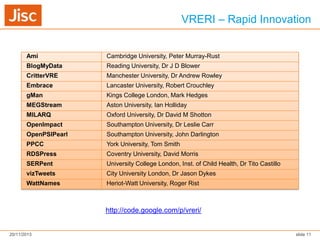
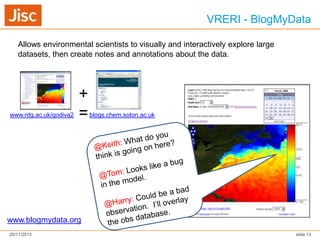
The document discusses Virtual Research Environments (VREs), which consist of online tools and resources that promote collaboration among researchers. It outlines various projects, tools, and frameworks designed to facilitate collaborative research across institutions, focusing on user needs and interoperability. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of embedding these tools in institutions and improving usability for diverse user expertise levels.