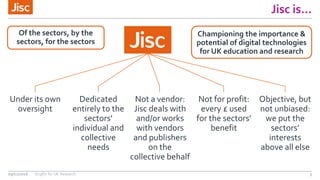
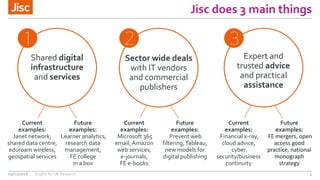
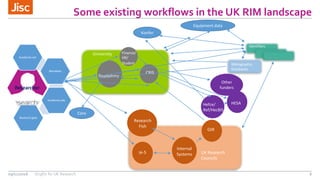
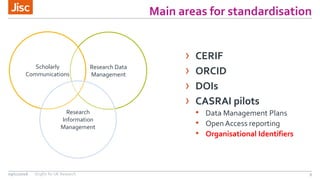
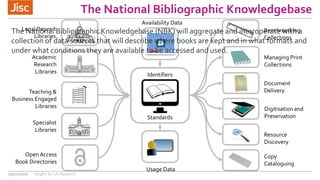
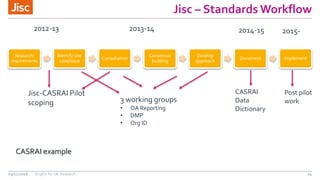
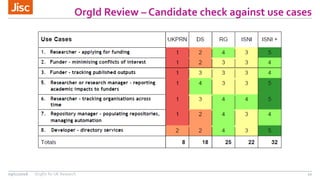
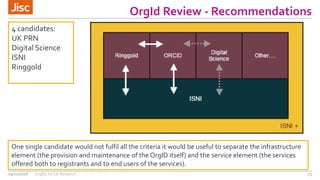
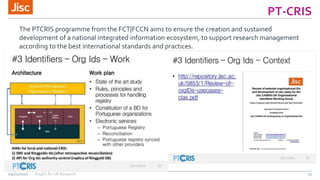
This document summarizes an event about organizational identifiers (OrgIDs) for UK research. It discusses Jisc's role in supporting the UK research sector through shared digital infrastructure and services. It also outlines Jisc's work with CASRAI to pilot the use of OrgIDs and other research data standards through several working groups. One such working group examined key OrgID candidates and produced recommendations for a hybrid approach relying on ISNI as the backbone standard. The document provides context on related areas like funder reporting requirements and the need for better integration across research systems in the UK.