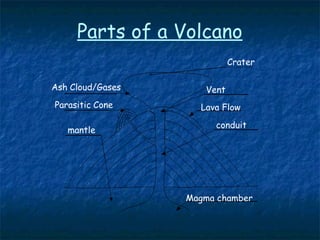
This document provides an introduction to volcanology. It defines a volcano as an opening in the Earth's surface through which lava, gases, and rock fragments erupt. It describes how magma rises from deep underground to form a magma chamber near the surface, which then erupts through a vent to form a volcano. Key parts of a volcano include the vent, crater, lava flows, and sometimes parasitic cones. Volcanoes are often located along tectonic plate boundaries like the Ring of Fire around the Pacific. Earthquakes can provide information about volcanic structures and pathways. Volcanology studies volcanoes and related phenomena, while volcanism describes the geological process of material emerging from the Earth's interior.