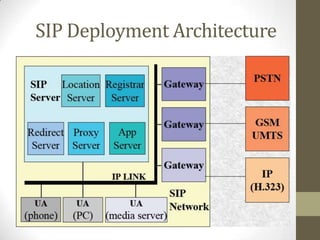
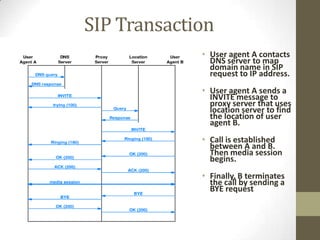
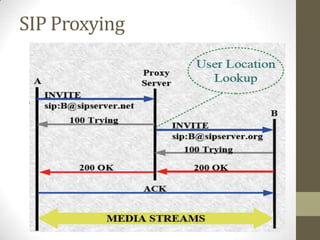
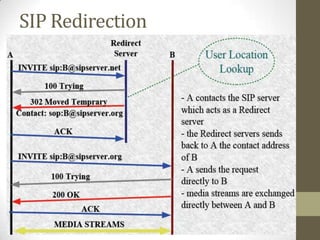
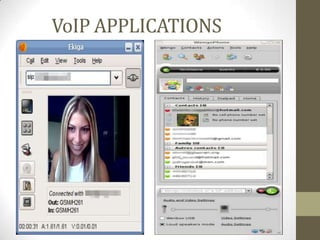
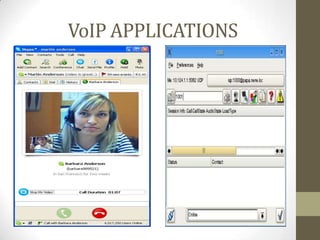
SIP is a signaling protocol used to set up multimedia communication sessions between endpoints over IP networks. It allows for user location, capabilities, availability, call setup and handling. SIP uses client-server architecture with user agents, proxies, registrars, and other entities. Common SIP methods include INVITE, ACK, BYE, and REGISTER. Responses are categorized by class with 1xx for provisional, 2xx for success, 3xx for redirect, 4xx for client error, 5xx for server error, and 6xx for global errors. The Via header tracks the path of SIP requests. SIP supports voice and video calls as well as instant messaging through extensions like SIMPLE.