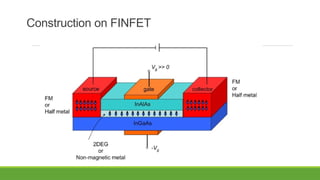
The presentation speak more about explaining a very vital category or section from transistor set as a part of Final year Electronics Engineering Assignments or Tutorials. It includes the introduction to transistors and what are the types of transistors, followed by Construction and working of spin FINFET. Advantages over other FETs are explained including applications and elaborating future of FINFETs.