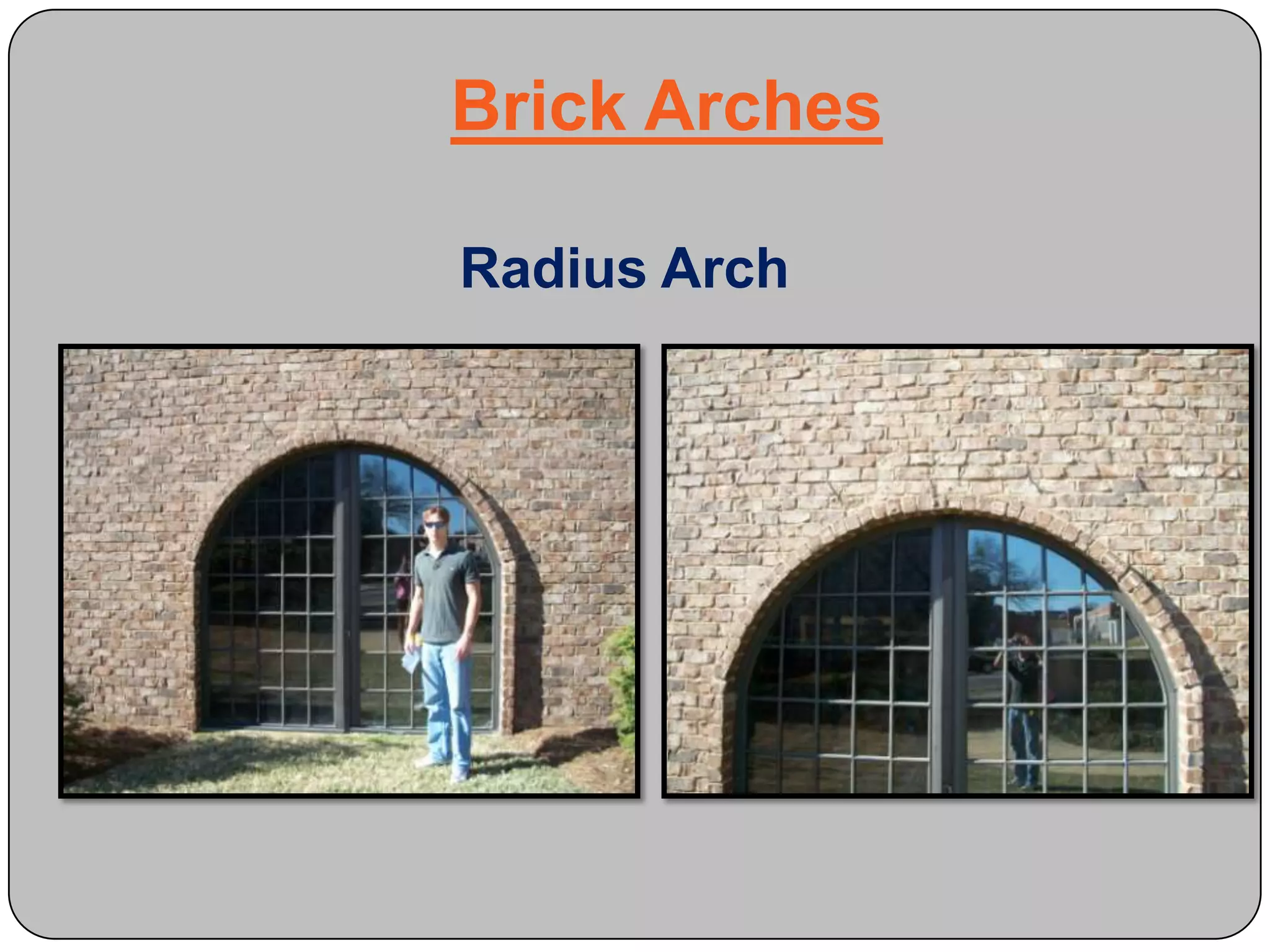
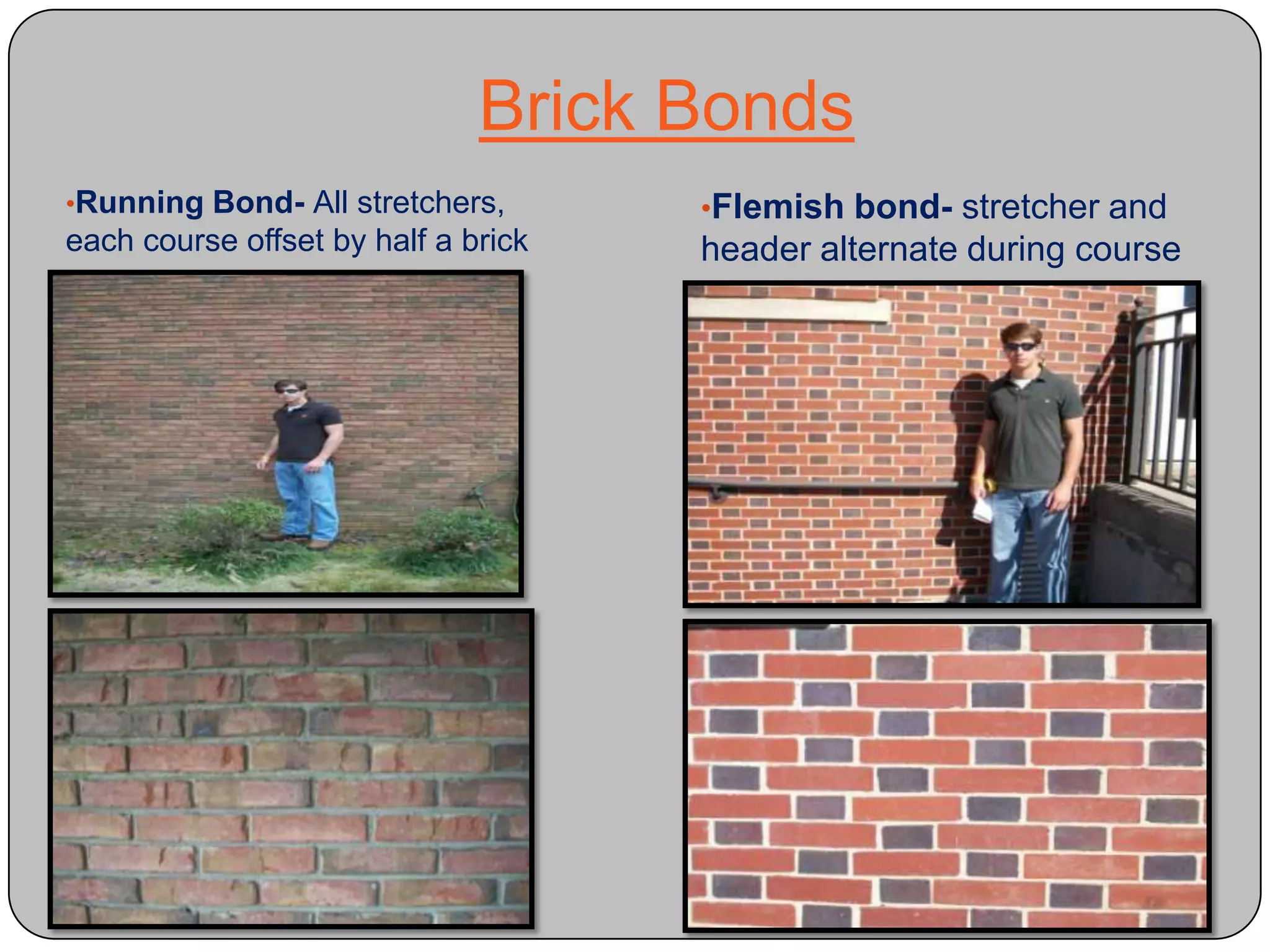
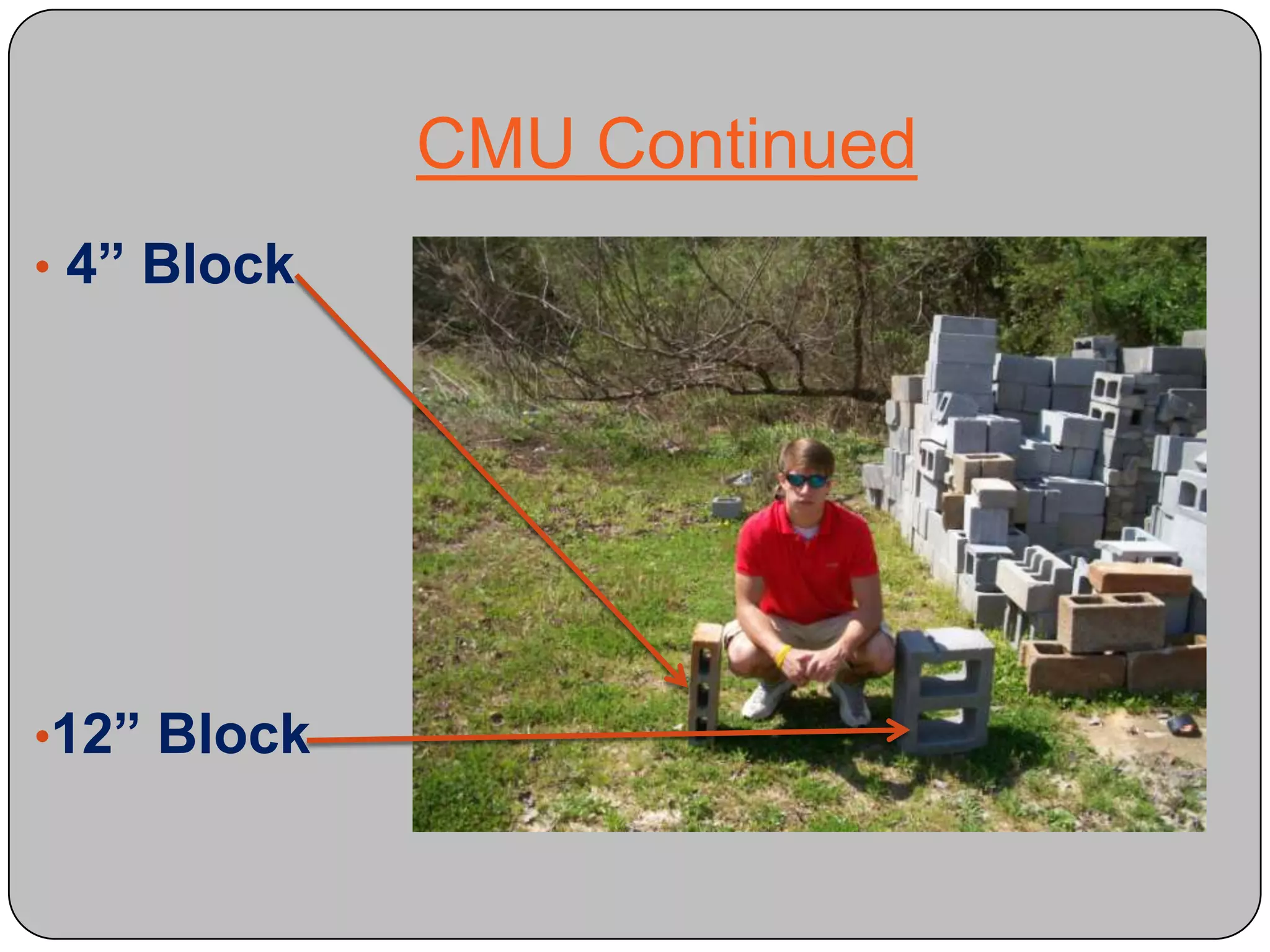
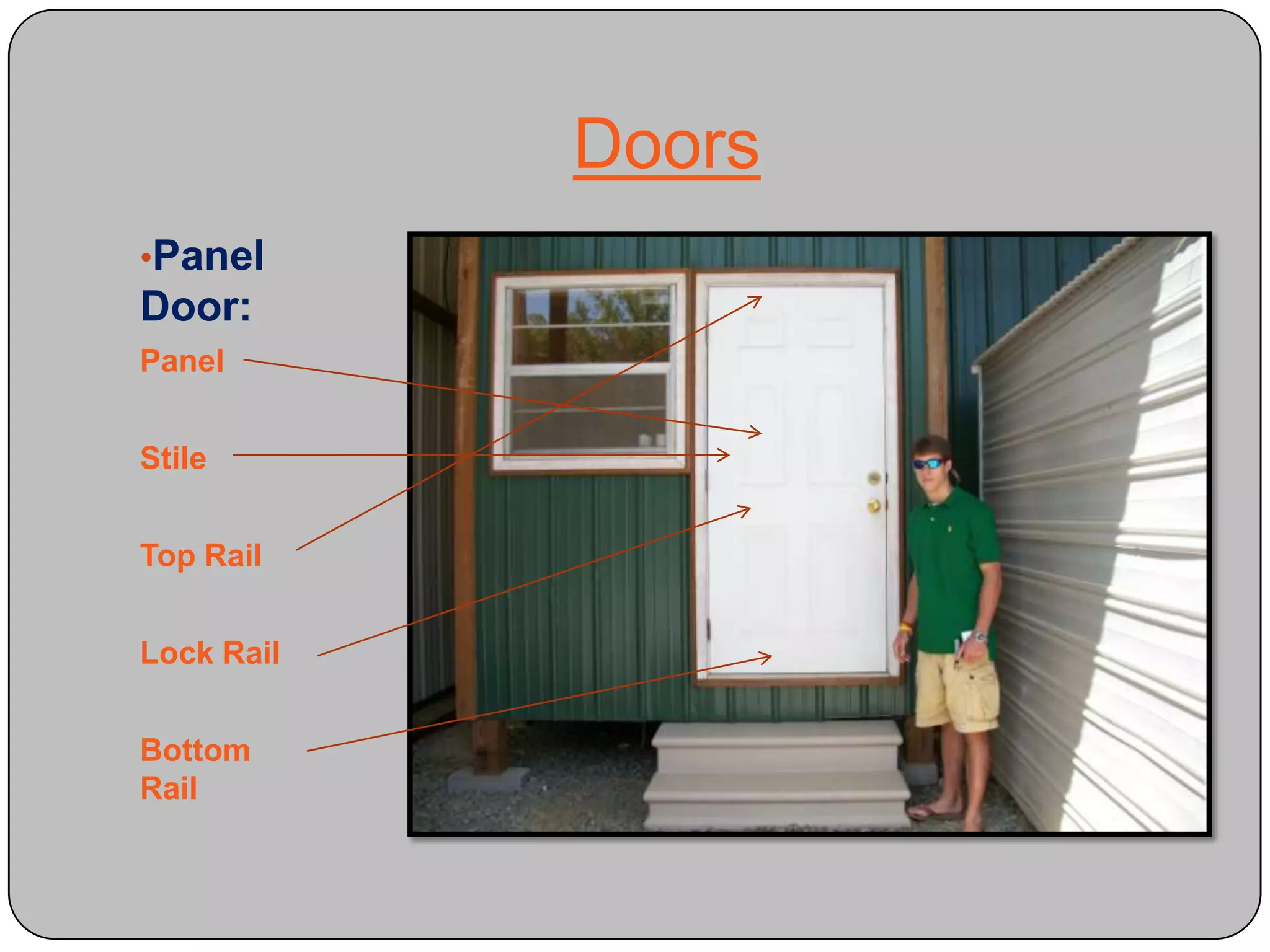
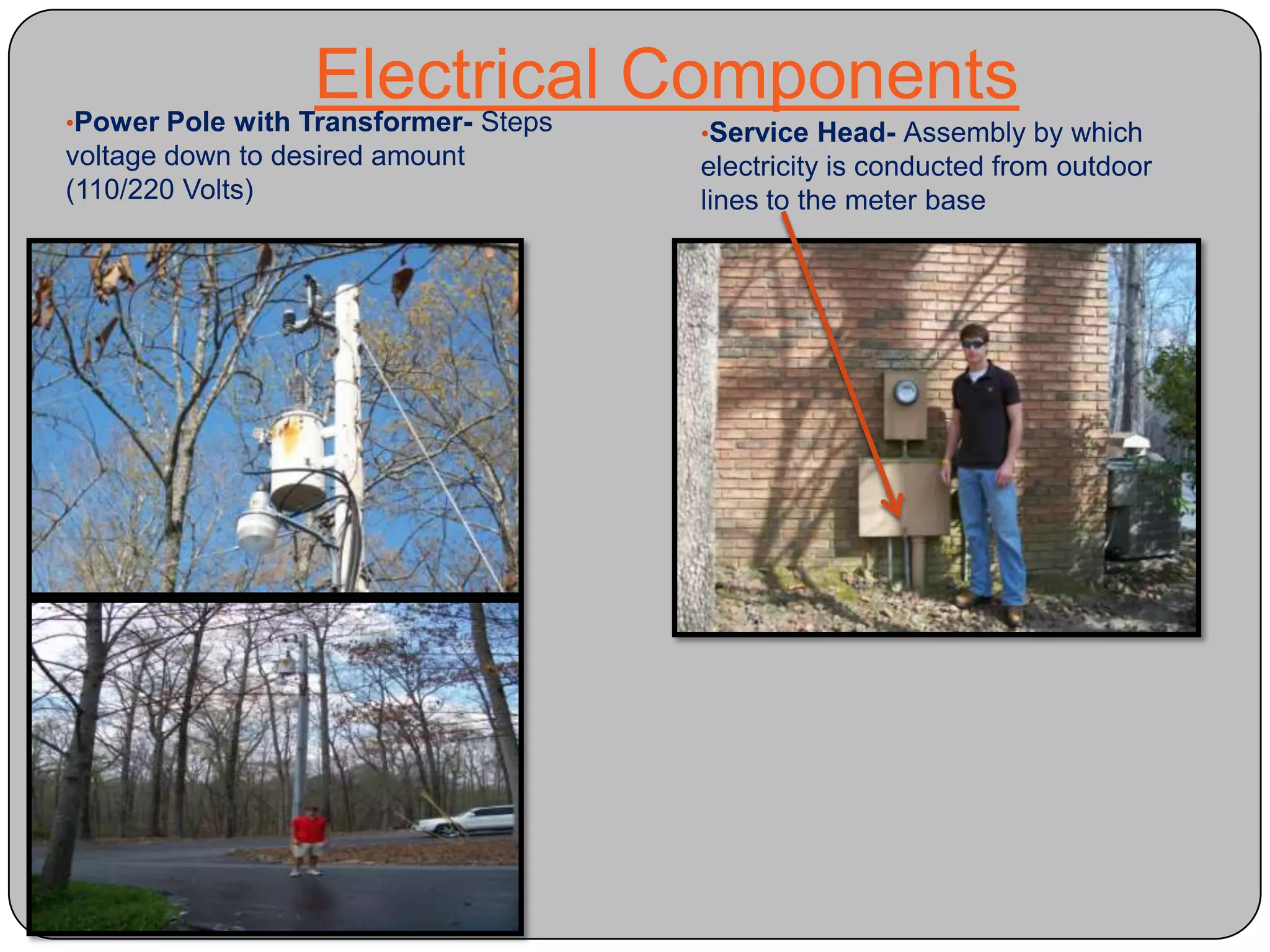
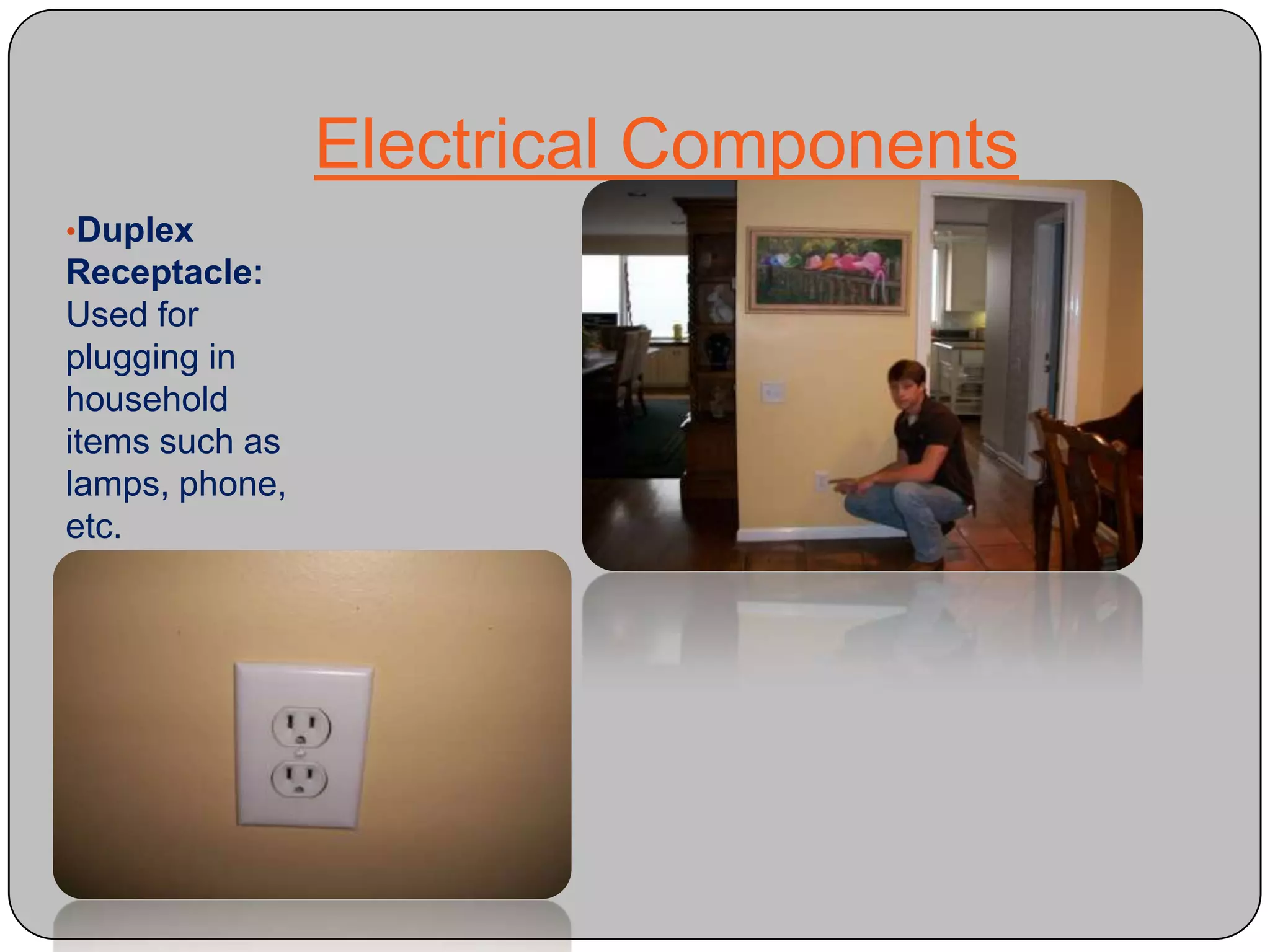
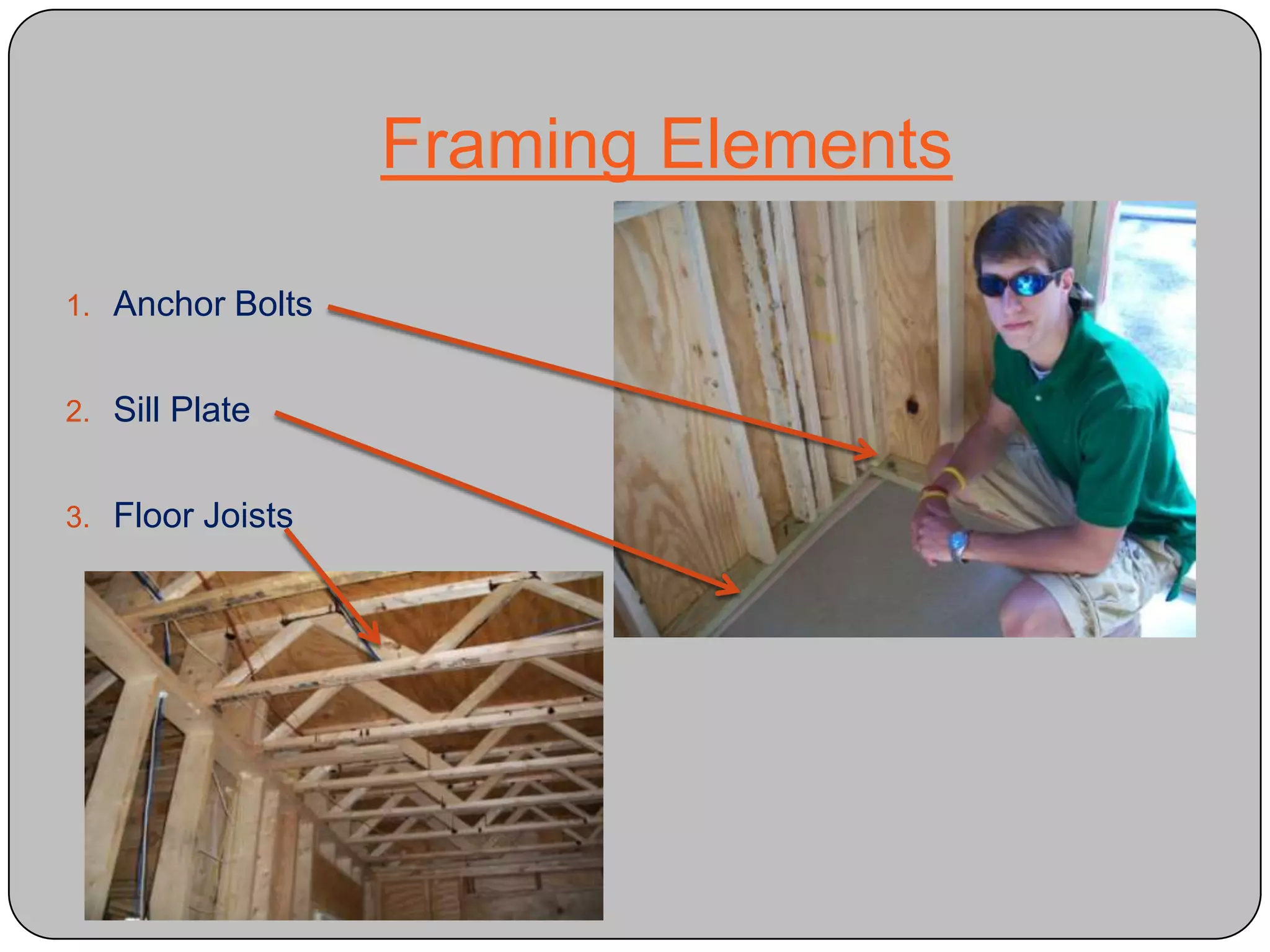
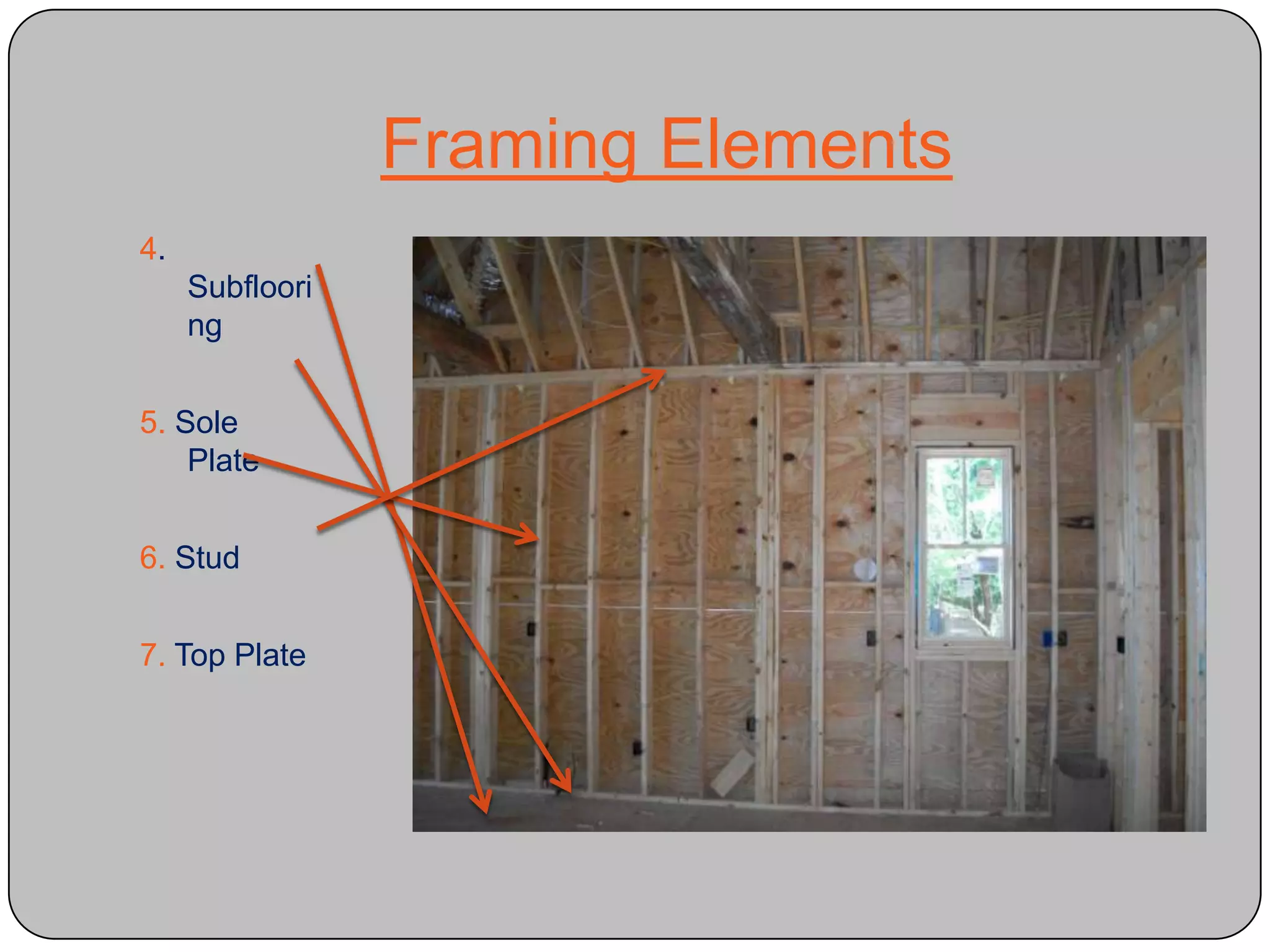
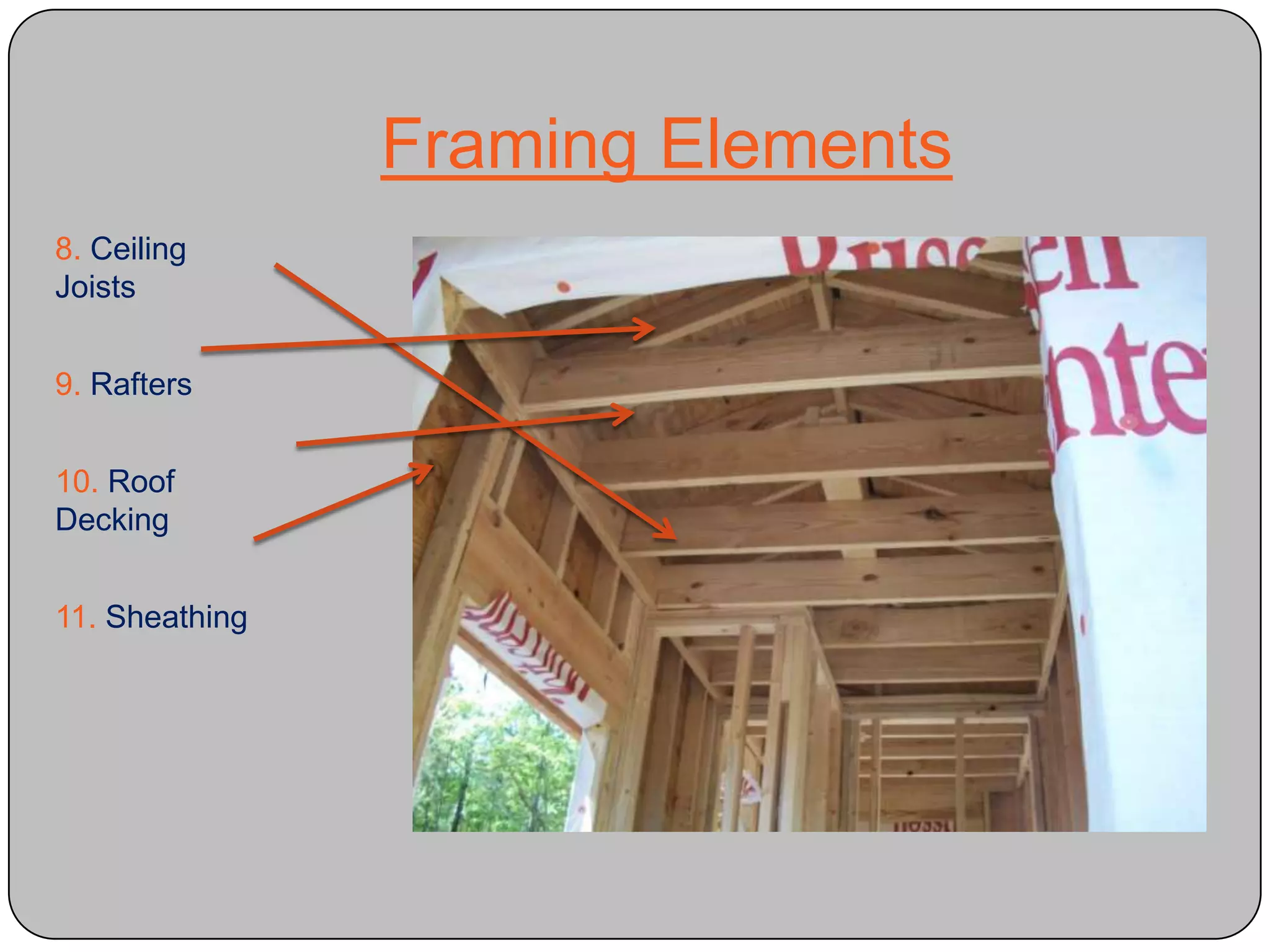
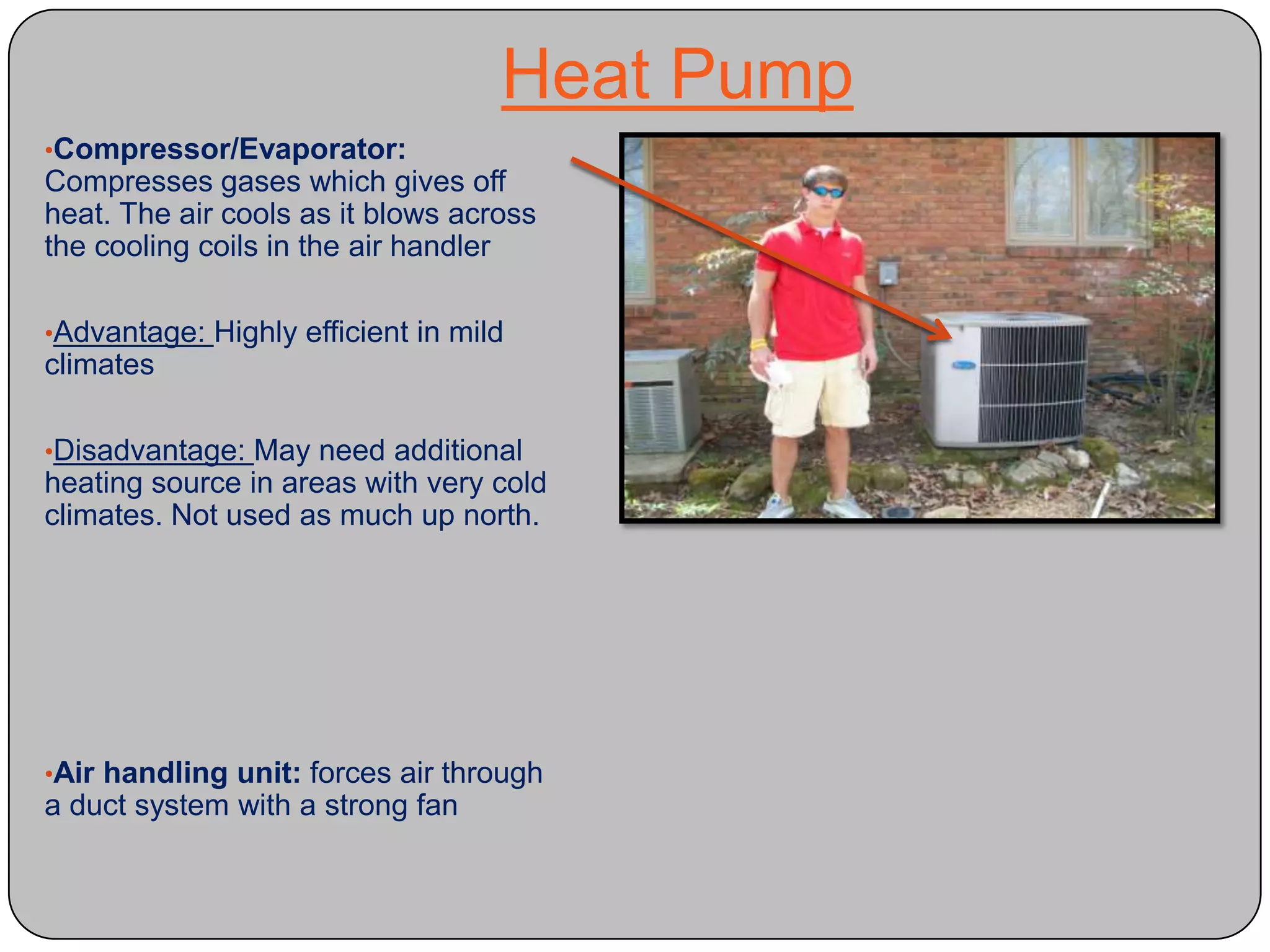
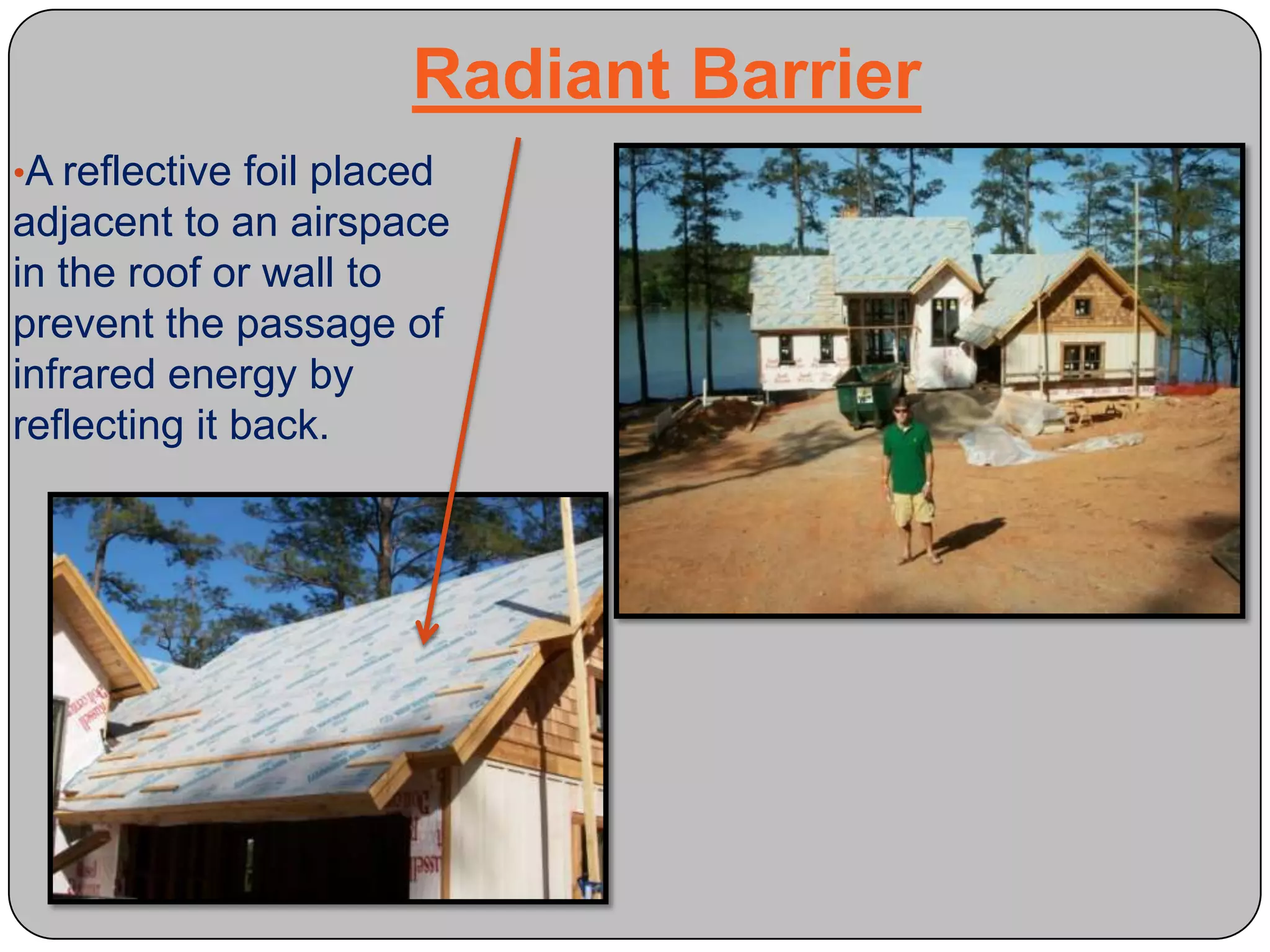
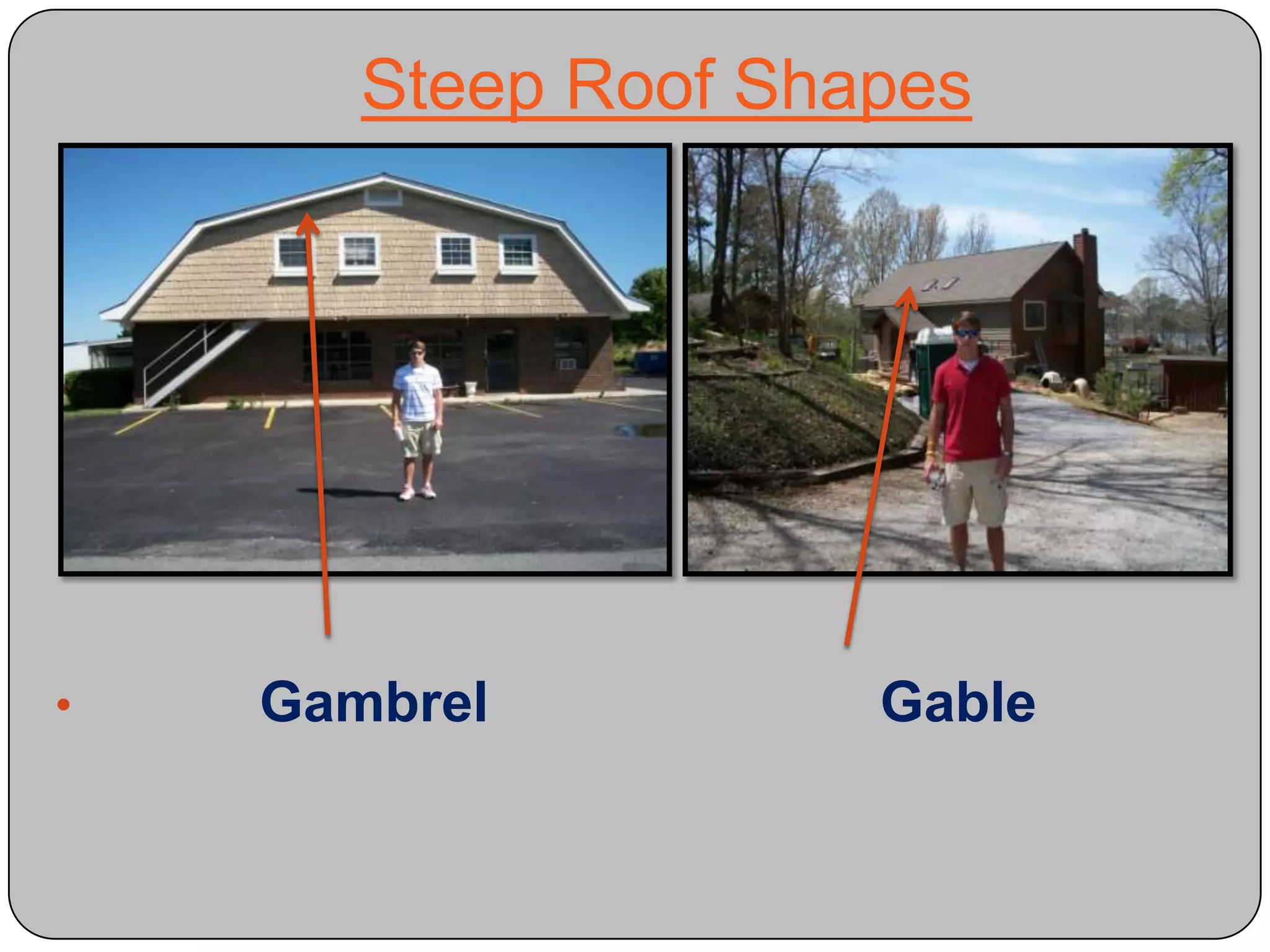
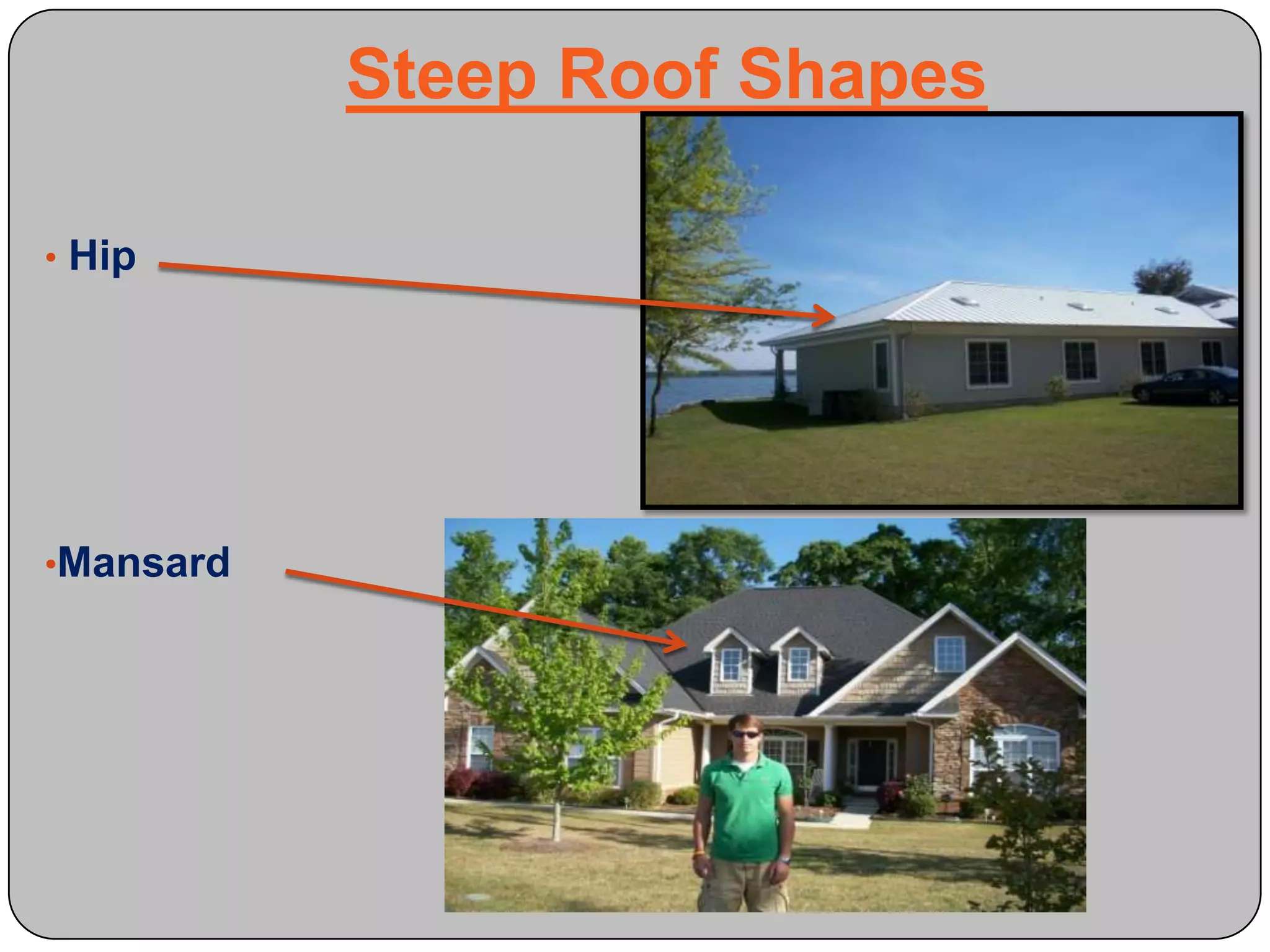
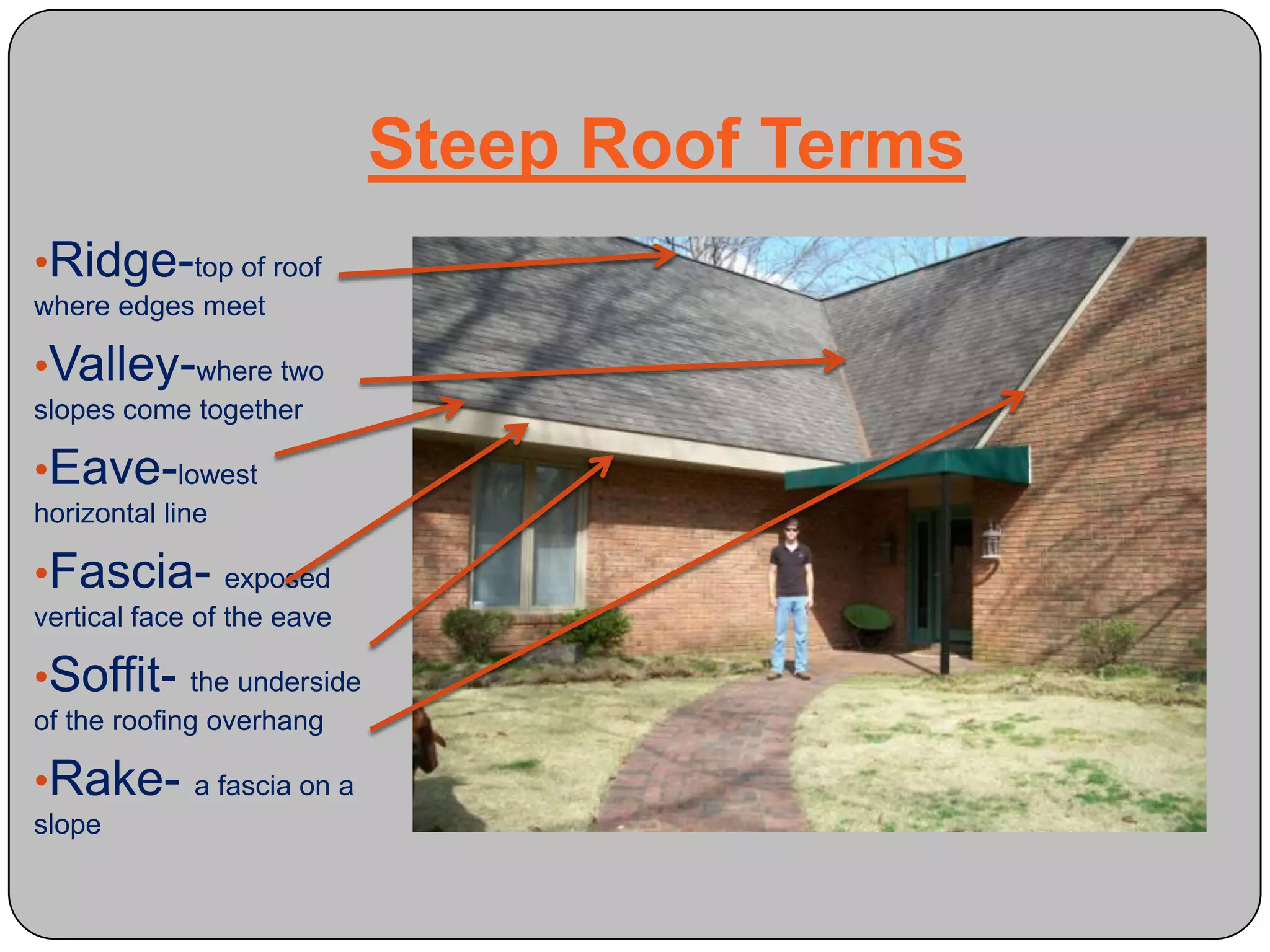
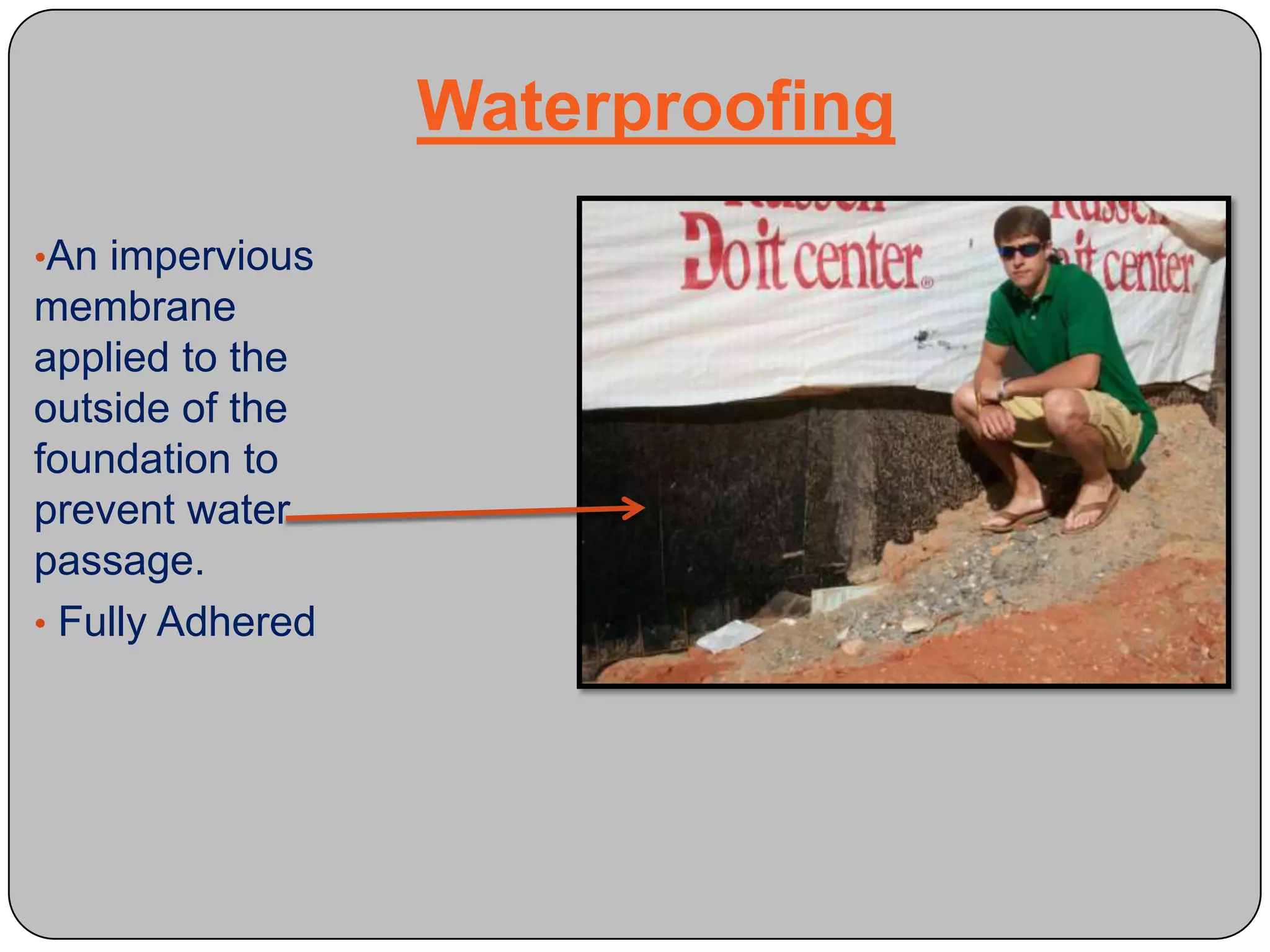
This document provides definitions and descriptions of various construction terms and materials. It discusses components of building framing, roofing, masonry, plumbing, electrical systems, windows, doors, insulation, vapor barriers, and other elements. Definitions include air barriers, batt insulation, brick bonds, cladding types, concrete joints, framing elements, gypsum board, mortar types, rebar, roof drainage components, siding, steep roof materials, stone types, vapor retarders, waterproofing, weep holes, and welded wire fabric. Dimensions and purposes are provided for many items.