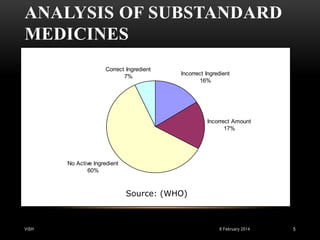
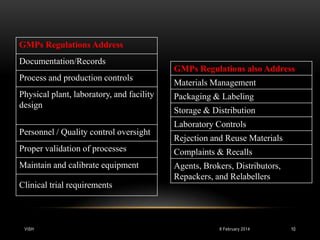
This document is a report on Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) prepared by Vishal H. Parikh for his M.Pharm QARA program. It was guided by Mr. Darshil Shah of the QA department at L.J. Institute of Pharmacy. The report defines GMP, discusses its history and principles, and covers key aspects of GMP including documentation, production processes, facilities, personnel, validation, equipment maintenance, and calibration. GMP regulations are designed to minimize risks in pharmaceutical production that cannot be eliminated through final testing alone.