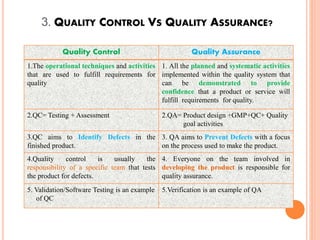
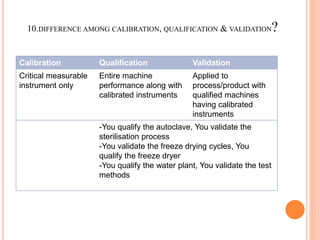
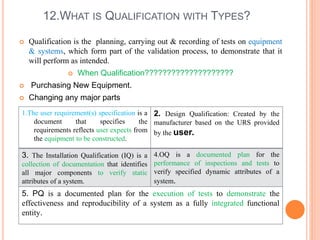
The document discusses quality assurance activities in the pharmaceutical industry. It defines key terms like quality control, quality assurance, calibration, qualification and validation. It explains the importance of complying with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure product quality and safety. GMP guidelines require validating processes, maintaining facilities and equipment, training staff, and performing regular audits and quality checks. The document compares techniques like cleaning, sanitization, sterilization and disinfection. It also outlines the differences between calibration, qualification and validation activities.