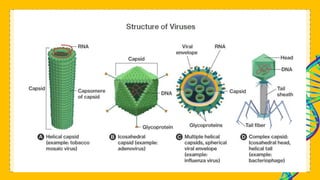
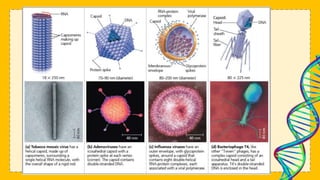
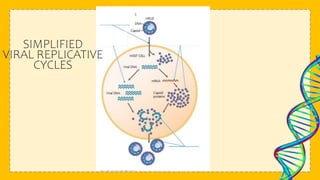
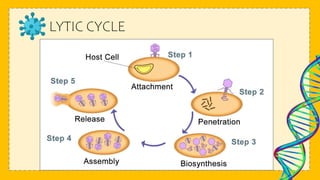
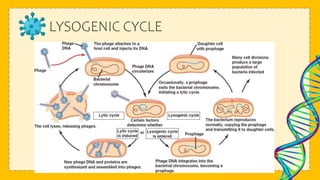
This document discusses viruses and provides information about their structure and life cycle. It defines viruses as non-cellular infectious particles composed of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat. Viruses are described as non-living because they contain no organelles and must use a host cell's machinery to replicate, but are also considered living because they can reproduce and mutate. The document outlines the differences between DNA and RNA viruses and describes viral capsids and envelopes. It explains the lytic and lysogenic replication cycles viruses use to infect host cells and how they are specific to certain kingdoms but not always specific species.