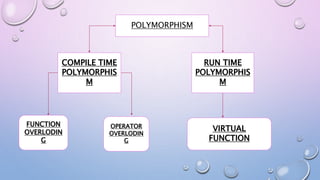
This document discusses polymorphism and its types. It defines polymorphism as representing one form in multiple forms. There are two types of polymorphism: compile-time polymorphism and run-time polymorphism. Compile-time polymorphism includes function overloading and operator overloading, which provide fast execution but are less flexible since binding occurs at compile-time. Run-time polymorphism includes virtual functions and uses dynamic binding via pointers, making it more flexible but slower since binding is determined at runtime. Virtual functions can be overridden in derived classes to change behavior when called through a base class pointer.