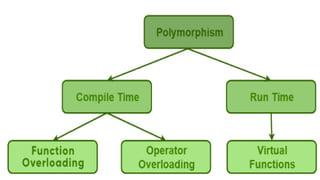
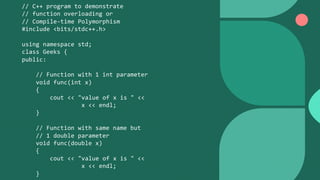
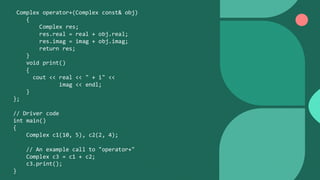
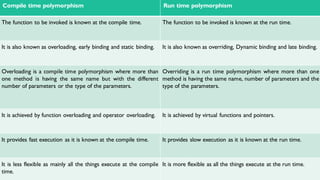
Polymorphism refers to having many forms. There are two types of polymorphism: compile-time polymorphism and runtime polymorphism. Compile-time polymorphism includes function overloading and operator overloading, where functions with the same name but different parameters are resolved at compile-time. Runtime polymorphism is achieved through method overriding using virtual functions, where the function called is resolved at runtime based on the object type. This allows a base class pointer to call derived class functions.