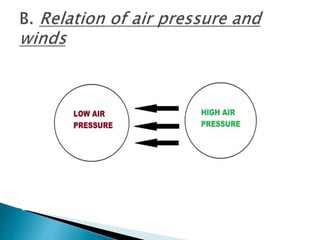
Climate refers to the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time, usually 30 years or more. It is influenced by temperature, air pressure, winds, humidity, cloudiness, and precipitation. Weather describes the short term state of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. Climate is determined by a chain of elements including temperature, winds, humidity, cloud formation, and different types of precipitation which are influenced by factors like air pressure changes, vertical and horizontal air movement, topography, and proximity to bodies of water and the equator. India's climate is considered a monsoon climate which is marked by a seasonal reversal of wind direction.