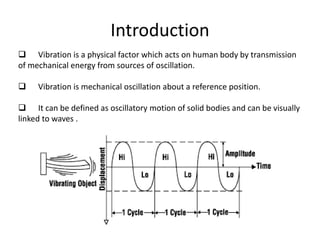
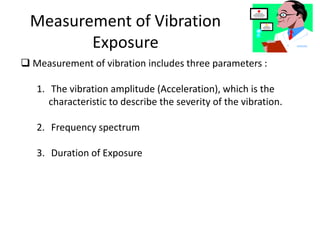
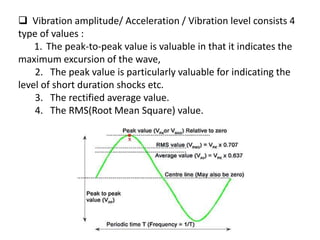
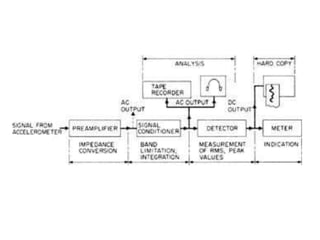
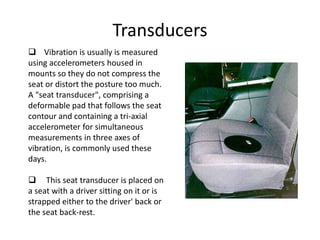
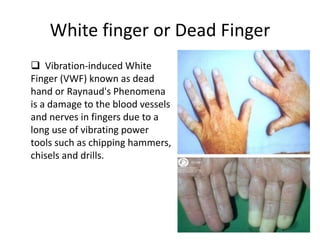
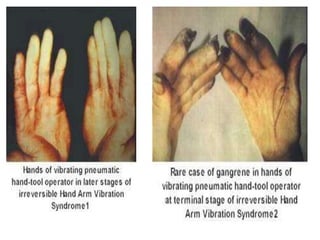
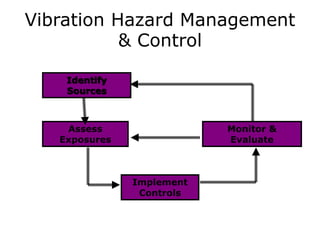
The document discusses vibration hazards and their effects on human health, emphasizing that vibration exposure can occur from contact with vibrating machines, significantly affecting specific organs due to resonant frequencies. It outlines measurement techniques for vibration exposure, the standards for safe limits, and control measures to mitigate risks, such as using anti-vibration tools and proper work practices. Additionally, the effects of vibration on machinery and structures are examined, highlighting the importance of managing and controlling vibration hazards in occupational settings.