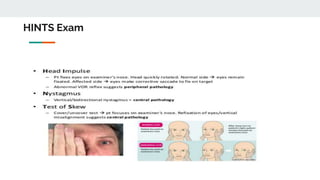
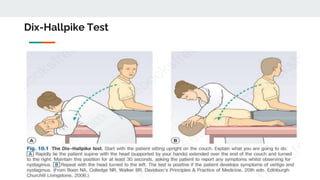
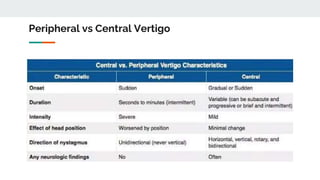
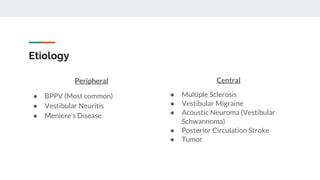
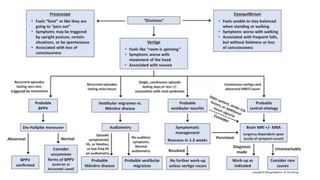
This document discusses an approach to vertigo. It begins by distinguishing vertigo, dizziness, and presyncope. A thorough history is important, including descriptions of symptoms, triggers, and associated symptoms. The physical exam includes ear, neurological, HINTS, and Dix-Hallpike tests to differentiate peripheral and central causes. Peripheral causes include BPPV, vestibular neuritis, and Meniere's disease. Central causes are multiple sclerosis, vestibular migraine, acoustic neuroma, posterior circulation stroke, and tumors. Red flags help identify more serious conditions. Symptomatic treatments are discussed.