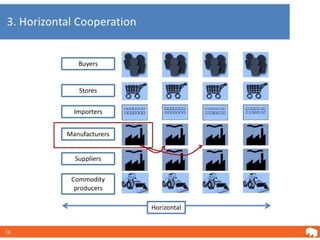
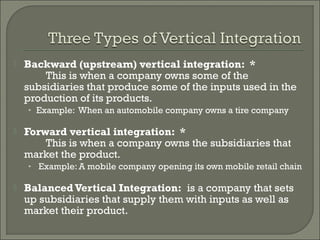
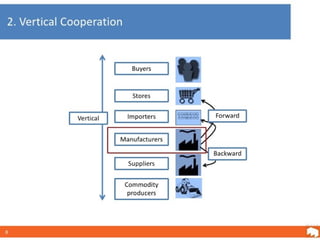
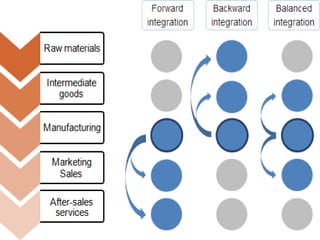
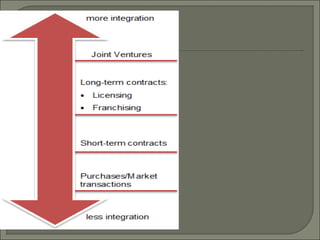
This document defines and compares horizontal and vertical integration strategies. Horizontal integration involves combining businesses that operate at the same stage of production, such as when an automobile manufacturer acquires a sport utility vehicle maker. The main advantages are economies of scale and market power, while disadvantages include increased costs and potential antitrust issues. Vertical integration combines businesses at different stages of production, such as a tire company owned by an automaker. Upstream integration involves owning suppliers, while downstream integration means owning distributors. Vertical integration can reduce costs and entry barriers but also limits flexibility and increases bureaucracy. The best strategy depends on a company's resources, and alternatives like contracts may offer more benefits than full integration in some cases.