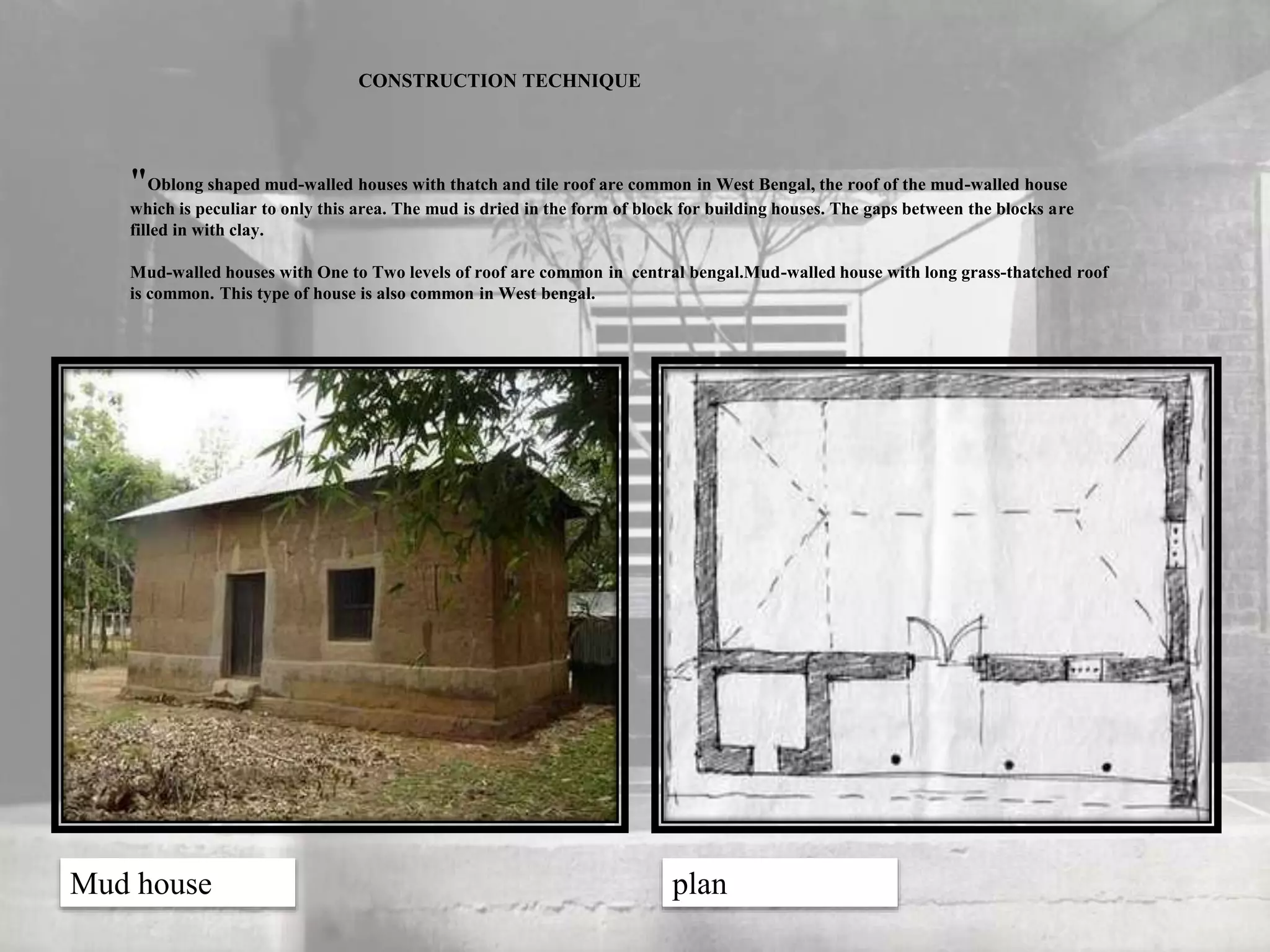
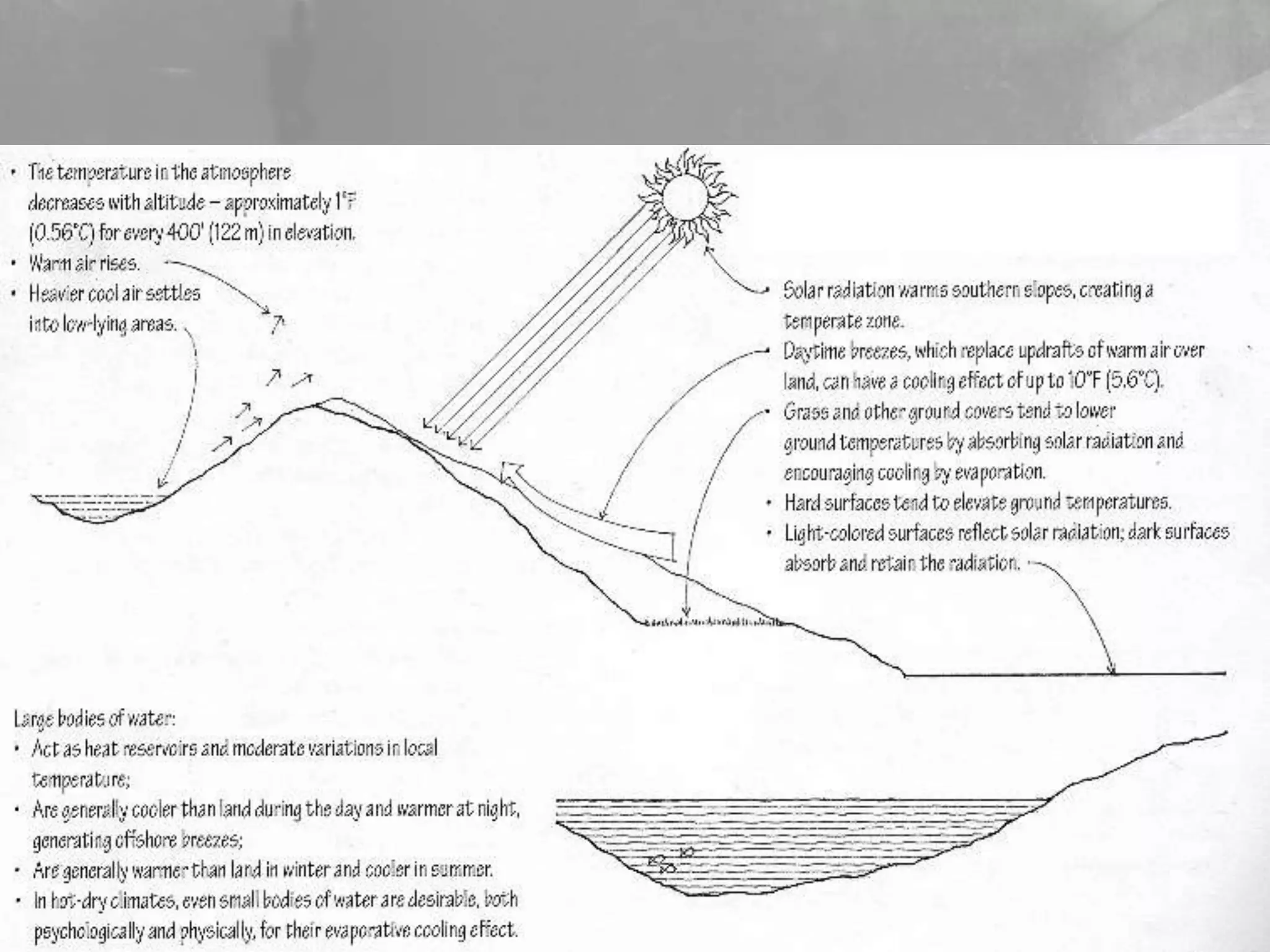
Vernacular architecture reflects local traditions, materials, and environmental contexts, evolving over time to meet community needs. This document discusses the significance of vernacular architecture in contrasting with polite architecture, emphasizing the economic, cultural, and technological aspects influencing regional building practices, particularly in India. Various construction methods and materials, such as bamboo, mud, and thatch, are highlighted, alongside their adaptation to local climates and innovations.