This document discusses verificationism and positivism. Some key points:
- Verificationism uses the verification principle as a criterion for meaningful statements - a statement is meaningful if it is potentially verifiable through experiences or observations.
- Verificationism connects the meaning of statements to epistemology by linking meaning to what can be verified. However, not all language functions are determined by verifiability.
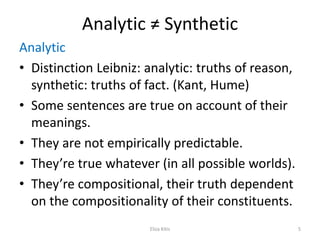
- Analytic statements are true by definition of their terms, while synthetic statements are empirically verified. Verificationism has difficulty accounting for non-descriptive language uses.
- Quine later launched an attack on the analytic-synthetic distinction, arguing that the whole of language and science determines meaning.