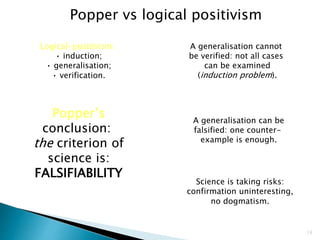
Positivism is a philosophical system rooted in science and empiricism that rejects metaphysics and holds that knowledge is only derived from logical reasoning and sensory experience. It views society and the physical world as operating according to general laws that can be observed and measured scientifically. Some key aspects of positivism include its rejection of introspection and intuition, focus on observation and experimentation to verify phenomena, and belief that anything beyond direct observation cannot be known. Logical positivism refined these ideas, proposing that philosophy should only consider statements that are verifiable or confirmable through observation or experiment.







![A.J. Ayer
One of the most important Logical Positivists was A. J. Ayer who,
in 1936, released his groundbreaking book, ‘Language, Truth and Logic’.
– The main tenet of logical positivism is that language causes many illusions. When we
properly analyze a proposition, we find that some are literally nonsense.
They can be neither true nor false, and are thus grammatical trickery.
This too applies to questions: some are meaningless (e.g. “Does God exist?”)
Language, Truth and Logic (1936)
– Ayer begins his book by accusing metaphysicians of making sentences which have no
meaning.
– He says that for a sentence to be literally significant, meaningful, it must conform to
certain criteria.
Ayer goes on to formulate this criteria, he calls it the criterion of verifiability:
– ‘We say that a sentence is factually significant [meaningful] … if, and only if, he knows
how to verify the proposition which it purports to express – that is, if he knows what
observations would lead him, under certain conditions, to accept the proposition as being
true, or reject it as being false.’ (p.16)
i.e. a sentence only has meaning if it can be proved true or false by observation.
– Thus, a question is genuine only if it can be observed true or false.
– It is important to note that a sentence’s observation should at least be possible in
principle. This gives it genuiness: verifiable in principle.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/logicalpositivism-171206080309/85/Logical-positivism-8-320.jpg)


![ A forerunner to logical positivism:
Mach held that scientific laws are summaries of experimental
events, constructed for the purpose of human comprehension of
complex data. Thus scientific laws have more to do with the mind
than with reality as it exists apart from the mind.
”The goal which it
[physical science] has set
itself is the simplest and
most economical abstract
expression of facts” (from
the Essay ”The economical
nature of physical inquiry” ).
Ernst Mach (1838-1916)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/logicalpositivism-171206080309/85/Logical-positivism-11-320.jpg)