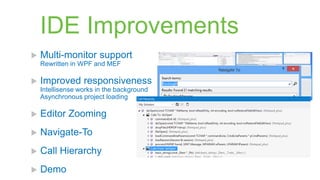
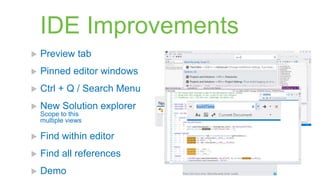
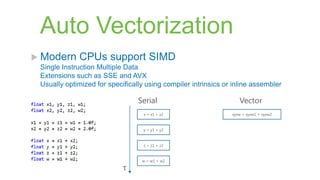
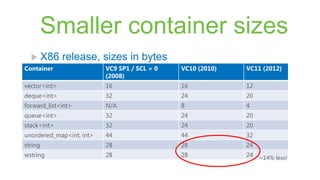
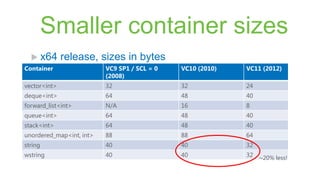
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the enhancements in Visual Studio 2012 over its predecessor, including IDE improvements, support for C++11 features, and new capabilities for unit testing and code analysis. Key highlights include better IntelliSense, improved debugging experiences with customizable data representation, and significant changes in C++ language features like auto, lambdas, and move semantics. The author emphasizes the evolving landscape of C++ development and the importance of these updates for modern software engineering practices.















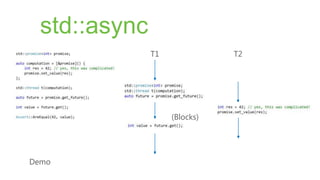
->return-type{body}
represent by type std::function<>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vcpp2012fullstyled-130325020553-phpapp01/85/Whats-New-in-Visual-Studio-2012-for-C-Developers-19-320.jpg)


















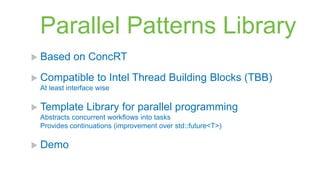





![Code Analysis
What does it check ?
Uninitialized Reads
HRESULT verification checks
Concurrency Warnings
Format string checks
Correct destructor calls (delete[] vs delete)
Redundant code checks
Many more: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/a5b9aa09.aspx
Custom code can be annotated to aid code analysis
See http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms182032.aspx
Demo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vcpp2012fullstyled-130325020553-phpapp01/85/Whats-New-in-Visual-Studio-2012-for-C-Developers-48-320.jpg)