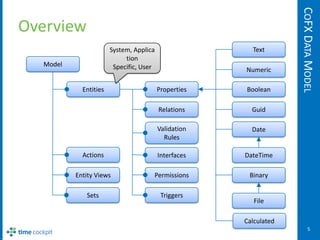
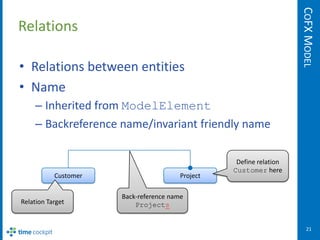
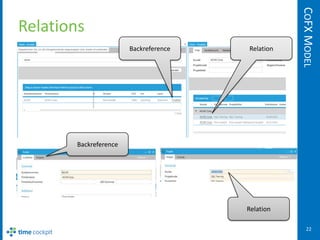
The document describes the CoFX data model, which is the data model for the Cockpit Framework (CoFX). It provides an overview of the key elements of the model including entities, properties, relations, validation rules, permissions, actions, entity views, sets, and triggers. The model uses a TCQL expression language to define things like calculated properties, validation rules, and permissions.









![COFX MODEL
Properties
• Binary properties
– Used to store blobs
– Storage types (BinaryProperty.StorageType)
• Database
• Windows Azure Blob Storage (only in the cloud)
– Content processing
(BinaryProperty.ContentProcessing)
• None, compress, encrypt, compress & encrypt
– Blob in DB (VARBINARY in SQL Server)
– Byte[] in .NET
– MaxStorageSize = length in bytes
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20121001cofxdatamodel-121001014935-phpapp02/85/The-CoFX-Data-Model-12-320.jpg)


![COFX MODEL
TCQL Expression Language
<expression> ::=
( <expression> )
| <expression> [ Or | And ] <expression>
| <expression> [ = | <> | < | <= | > | >= ] <expression>
| <expression> In ( <expression> [, <expression>...] )
| <expression> In Set( "<expressionName>" [, "<propertyName>" ] )
| <expression> In <parameterAccess>
| <expression> [Not] Like <expression>
| <expression> [ + | - | * | / | % ] <expression>
| Not <expression>
| <functionCall>
| <aggregationFunctionCall>
| <memberAccess>
| <literal>
| <parameterAccess>
| <nestedStatement>
| <EnvironmentVariable>
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20121001cofxdatamodel-121001014935-phpapp02/85/The-CoFX-Data-Model-15-320.jpg)

![COFX MODEL
TCQL String Functions
:Len( string-expression )
:Substring( string-expression, start-index, length )
:Replace( string-expression, string-to-find, replacing-string )
:FormatDate( date-expression, format-string )
(see MSDN Library for details about format string)
:FormatNumber( numeric-expression, format-string )
(see MSDN Library for details about format strings)
:FormatDateCanonical( date-expression [, boolean-expression] )
(see MSDN Library for SQL Server's canonical date format)
:FormatDateAsPeriod( date-expression )
(returns YYYY/MM)
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20121001cofxdatamodel-121001014935-phpapp02/85/The-CoFX-Data-Model-17-320.jpg)











![TRIGGERS
Trigger Example
[ModelEntityTrigger]
public static class User
{
[TriggerMethod]
public static void AddUser(ExecutionContext context)
{
…
}
[TriggerMethod]
public static void UpdateUser(ExecutionContext context)
{
…
}
…
}
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20121001cofxdatamodel-121001014935-phpapp02/85/The-CoFX-Data-Model-33-320.jpg)

