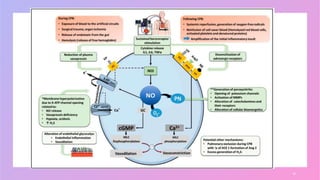
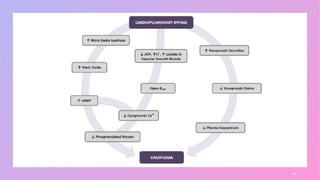
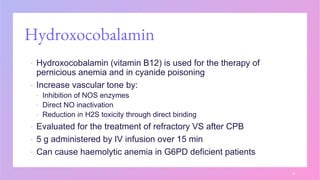
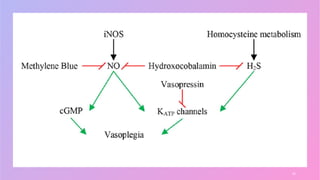
Vasoplegia is a low systemic vascular resistance state that can occur after cardiopulmonary bypass and is characterized by hypotension resistant to fluid resuscitation. It increases morbidity and mortality through organ dysfunction. Treatment aims to restore blood pressure through vasopressor drugs like norepinephrine and vasopressin. Norepinephrine is usually first-line but vasopressin may be added for its vasoconstriction and sympathomimetic effects. Non-conventional vasopressors like methylene blue and angiotensin II are second-line options. Corticosteroids and cytokine filters have not proven effective for preventing or treating vasoplegia.





![Leads to
▪ Activation of the complement cascade
▪ Expression of pro-inflammatory mediators, such as (il-1β),(il-6) and (tnfα).
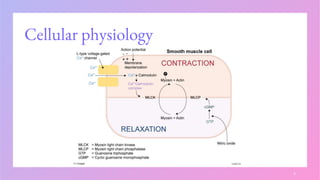
▪ Il-6 increases the synthesis of camp, which promotes vasodilation by reducing
myoplasmic [ca++].
▪ Accordingly, higher circulating levels of il-6 have been associated with an
increased incidence of vs
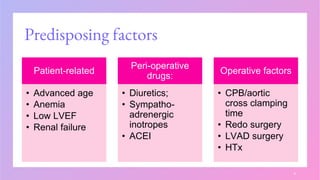
▪ Longer cpb and aortic cross-clamping durations, combined surgery and redo
intervention all predispose to a more intense inflammatory response.
▪ Following the discontinuation of cpb, systemic reperfusion promotes the
generation of oxygen-free radicals and the amplification of the initial
inflammation.
▪ The reinfusion of cell saver blood containing hemolyzed red blood cells,
activated platelets and denatured proteins, may also contribute to this response
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vasoplegiaaftercpb-230205141420-4a3268c7/85/Vasoplegia-after-CPB-pptx-8-320.jpg)