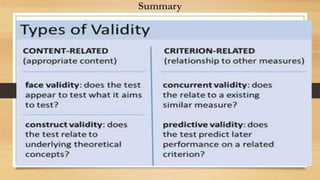
This document discusses different types of validity that are important for evaluating quantitative instruments. It defines validity as the degree to which an instrument measures what it is intended to measure. The main types of validity discussed are: face validity, content validity, criterion validity (which includes concurrent and predictive validity), and construct validity. Content validity refers to how well the instrument covers all aspects of the construct being measured. Construct validity assesses if the instrument actually measures the intended abstract concept. It is broken into convergence validity and divergence validity.