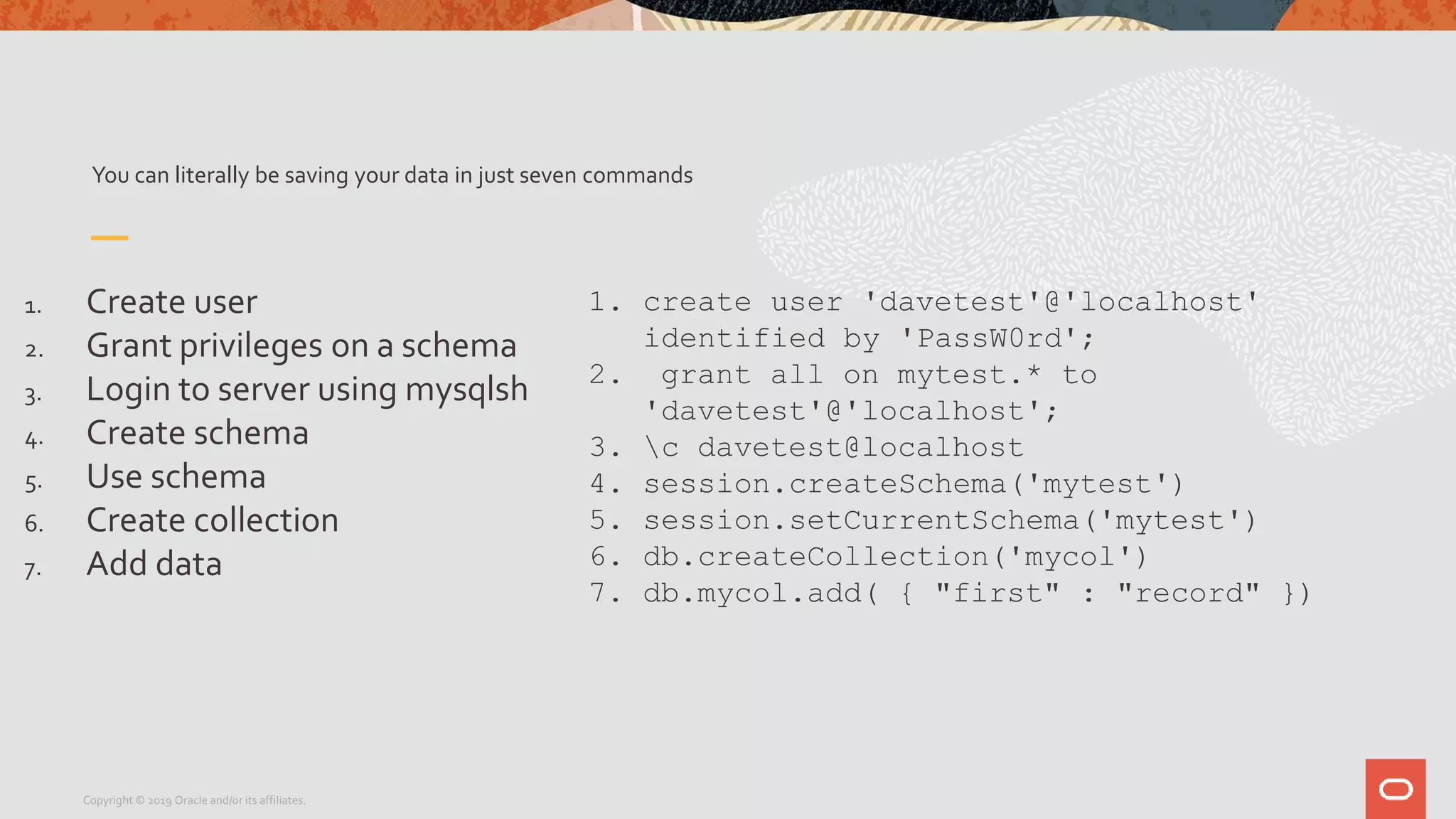
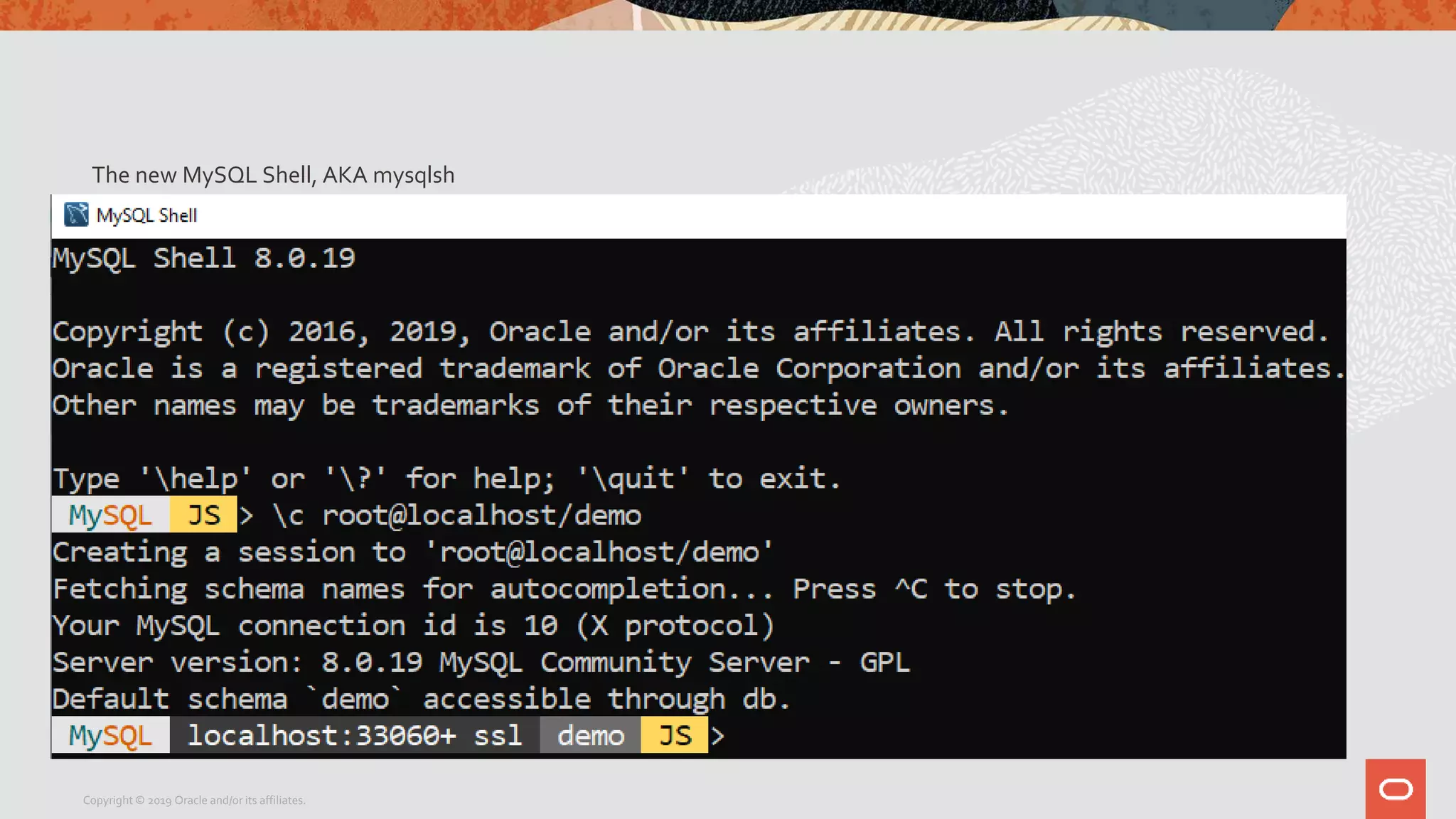
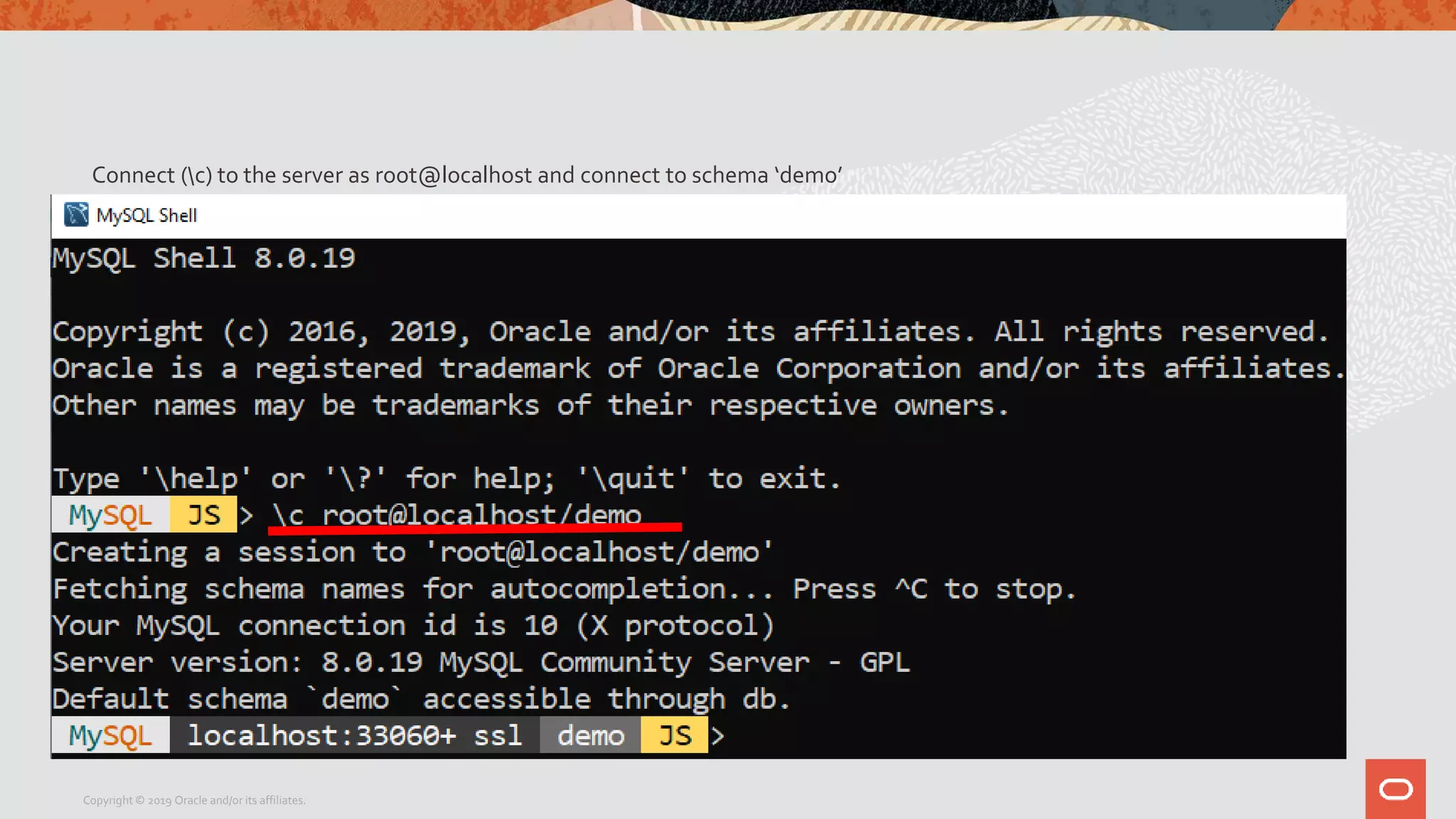
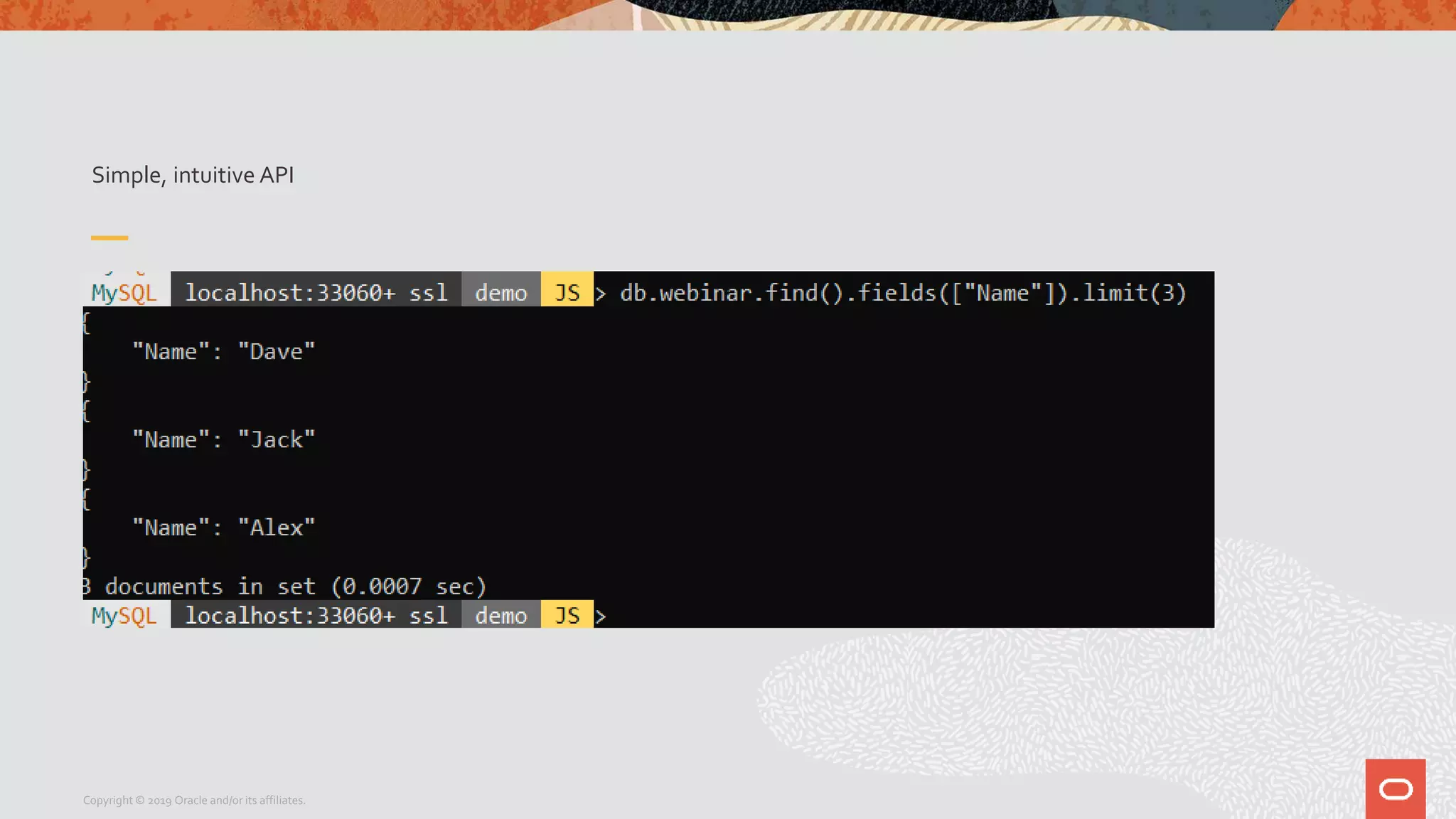
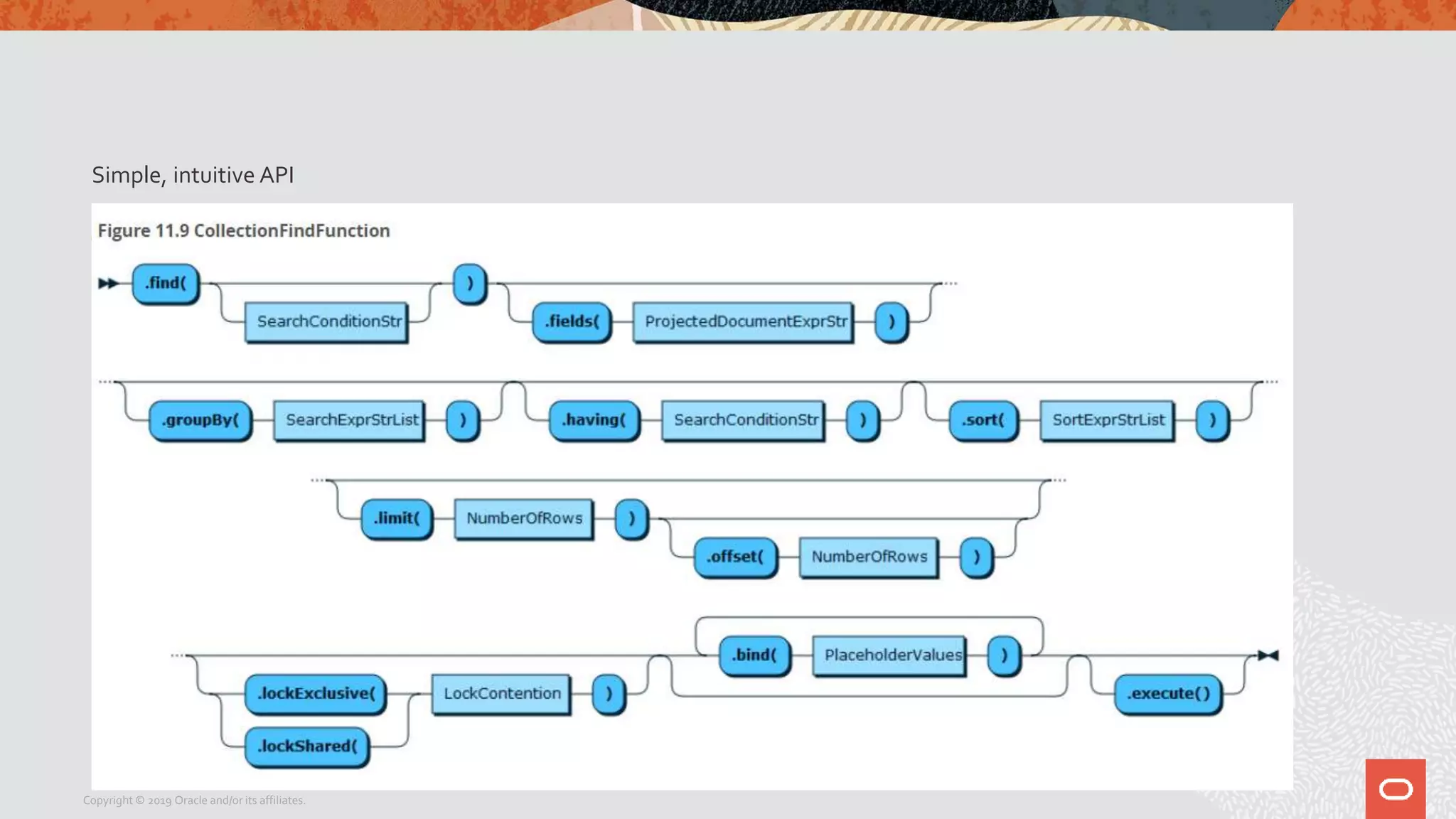
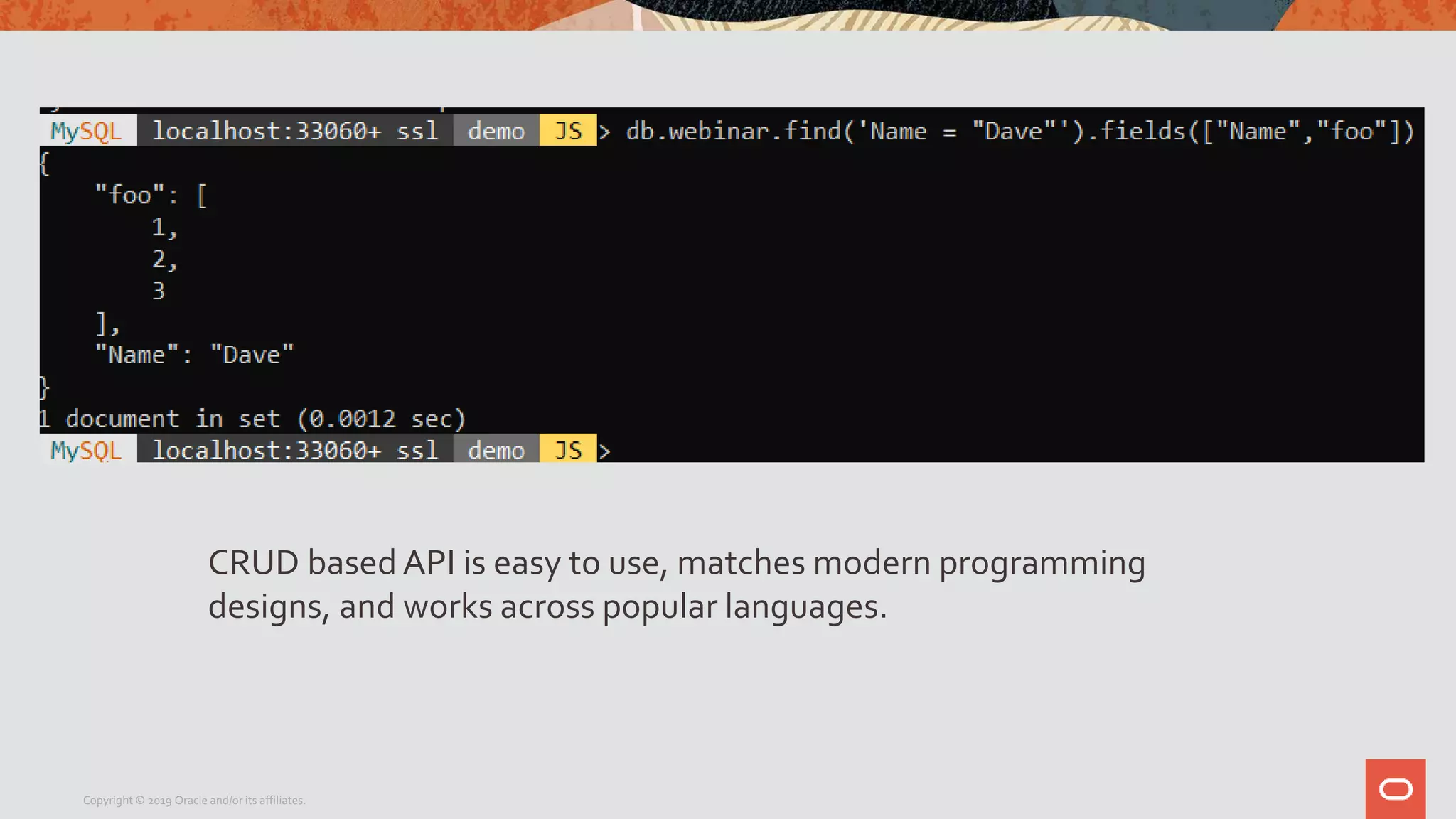
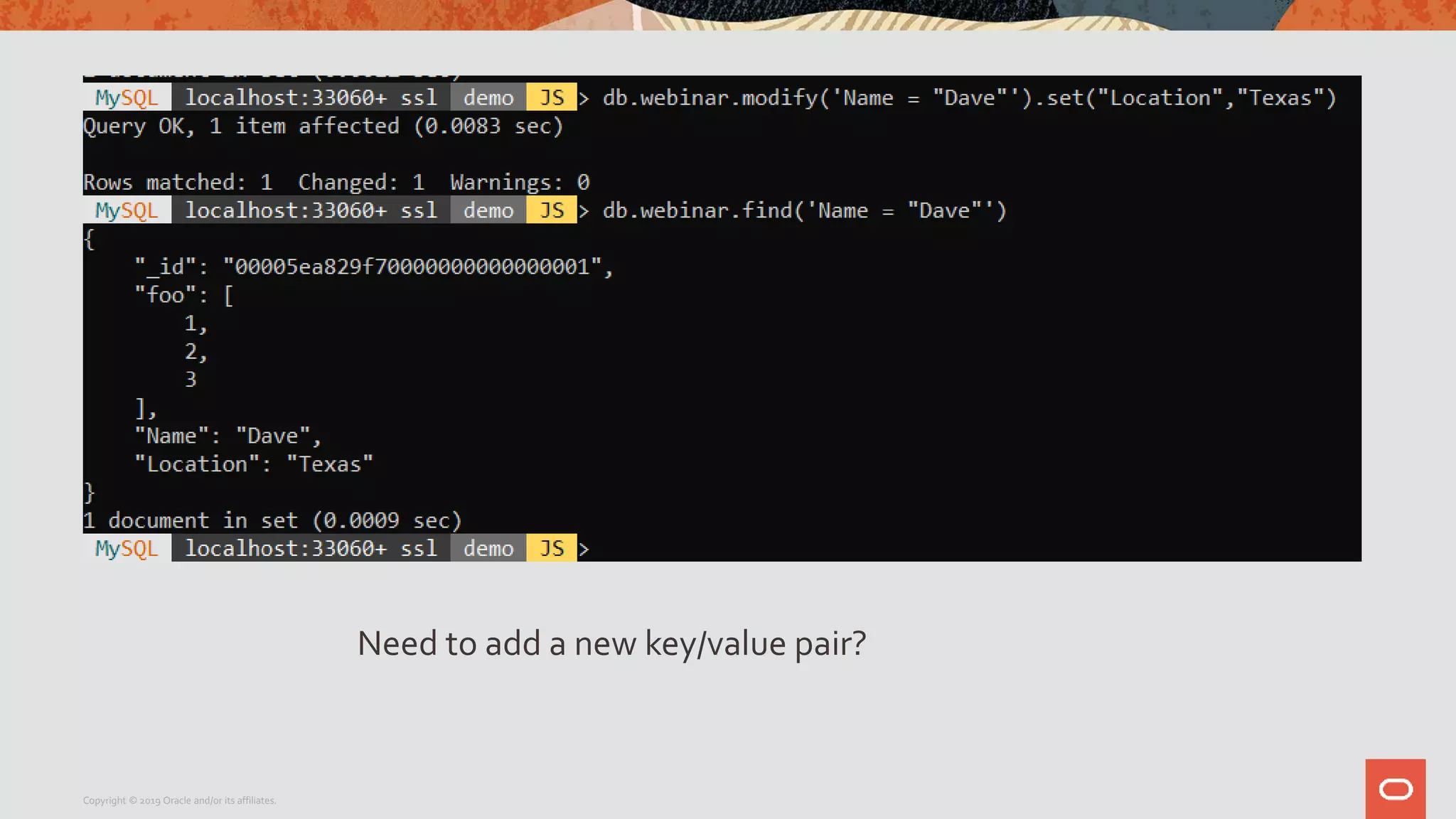
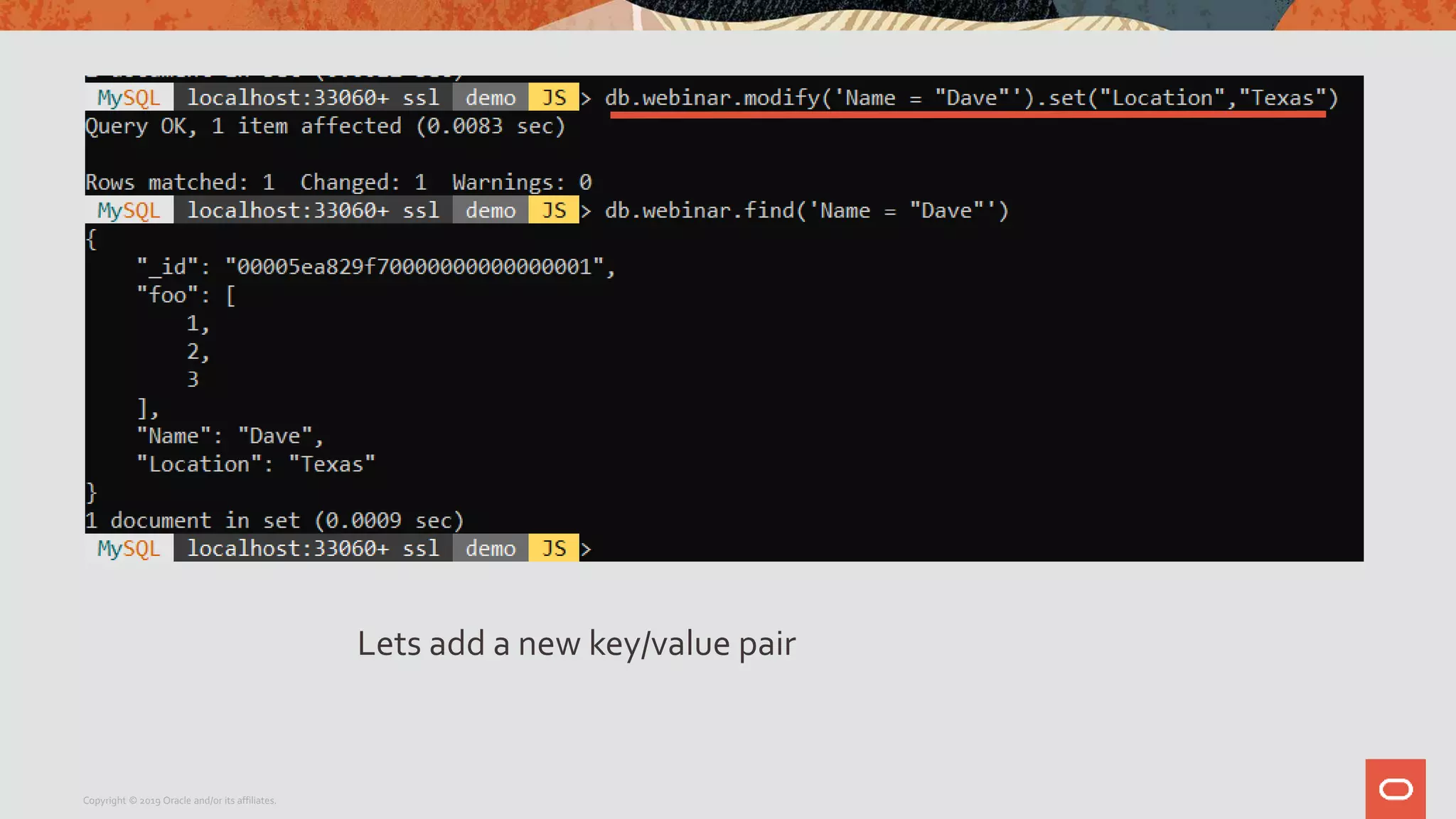
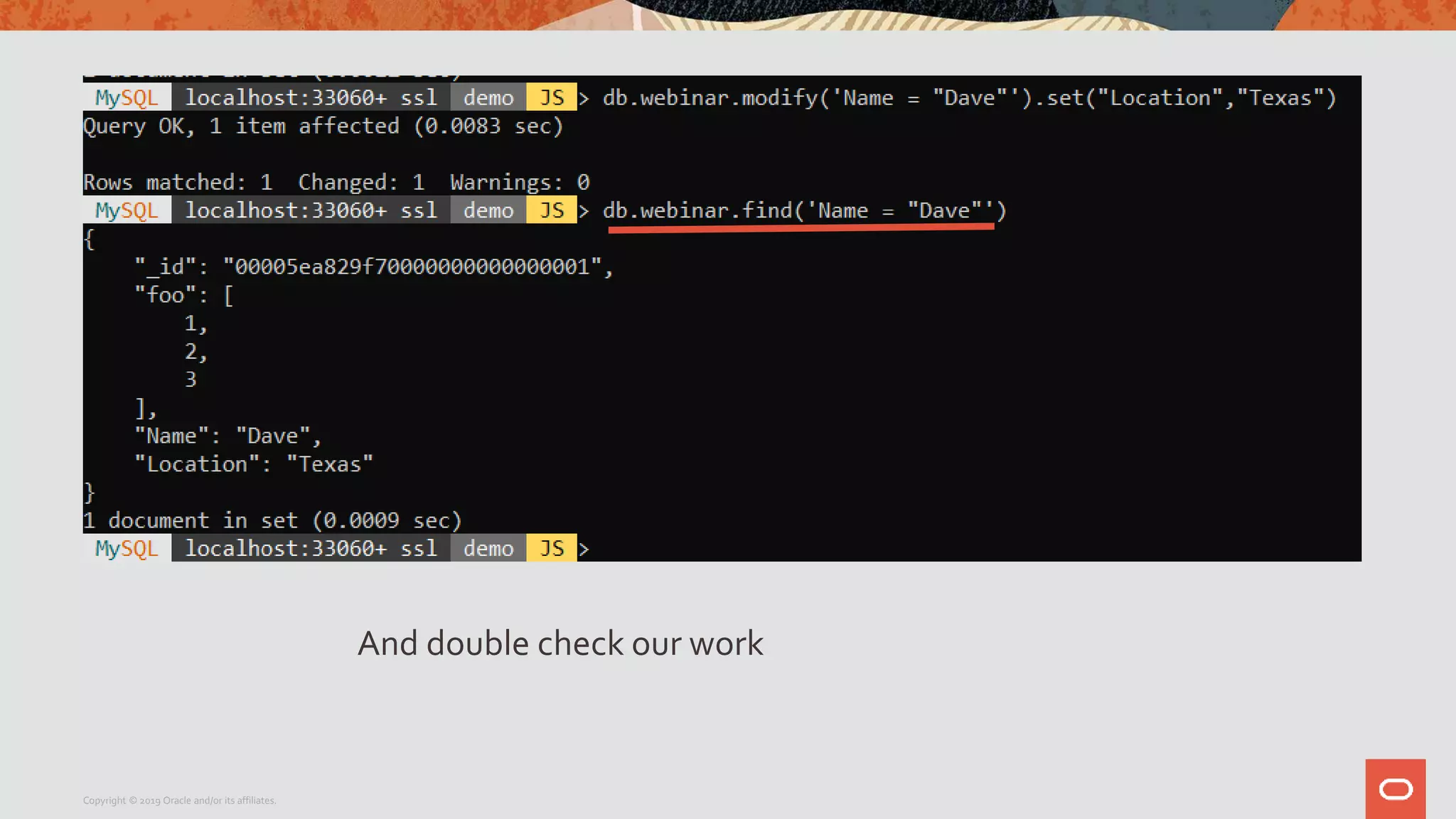
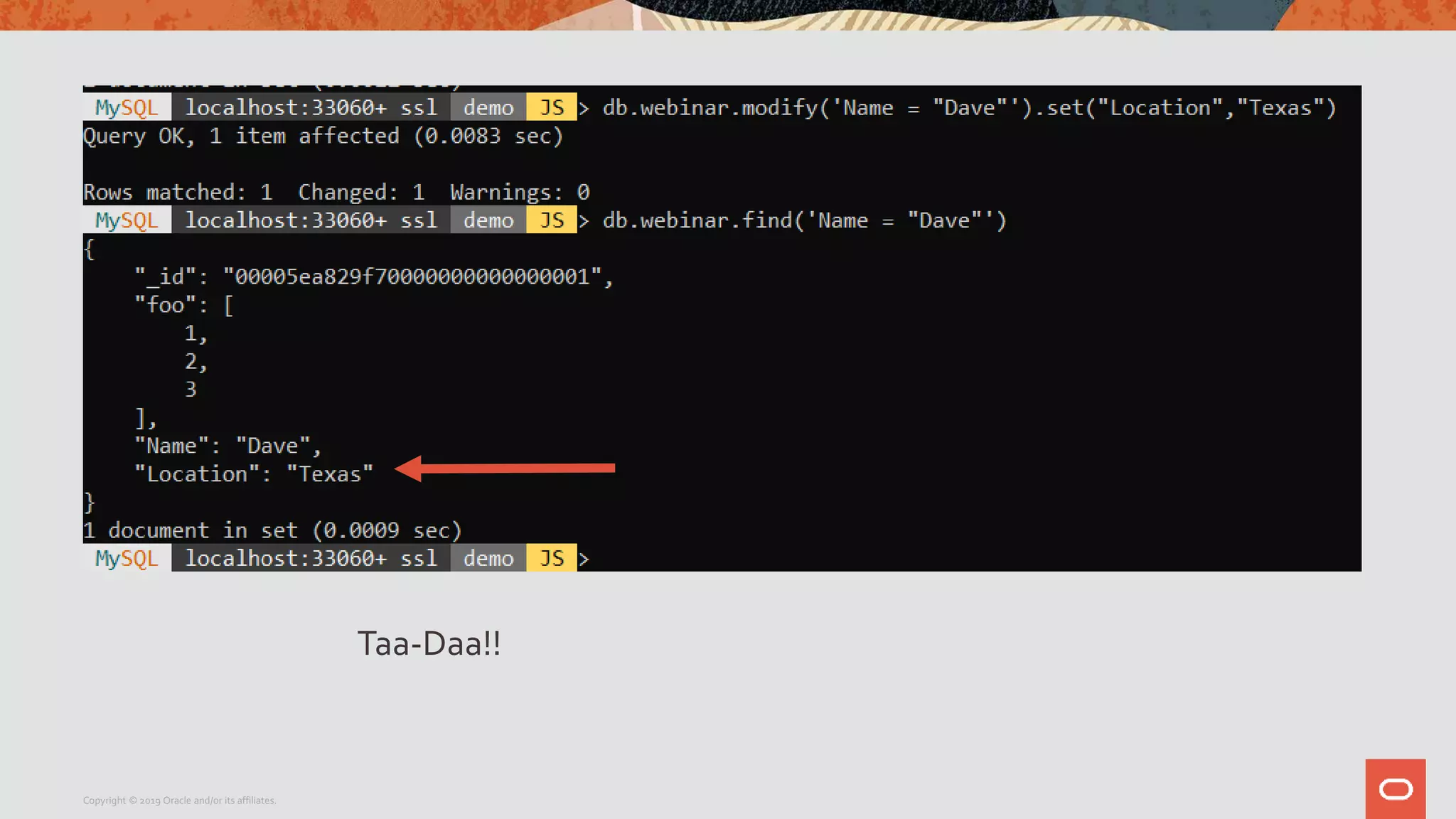
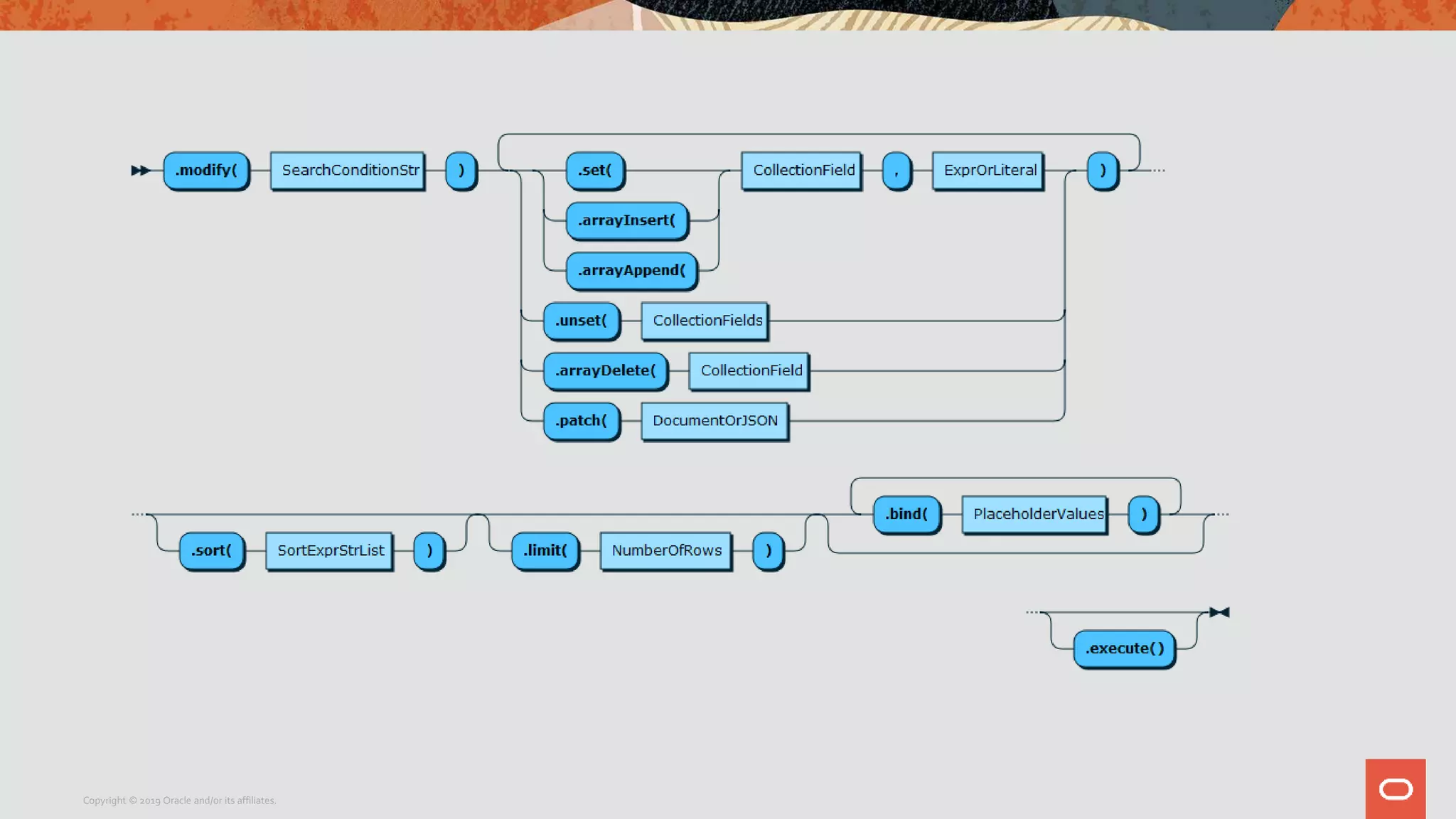
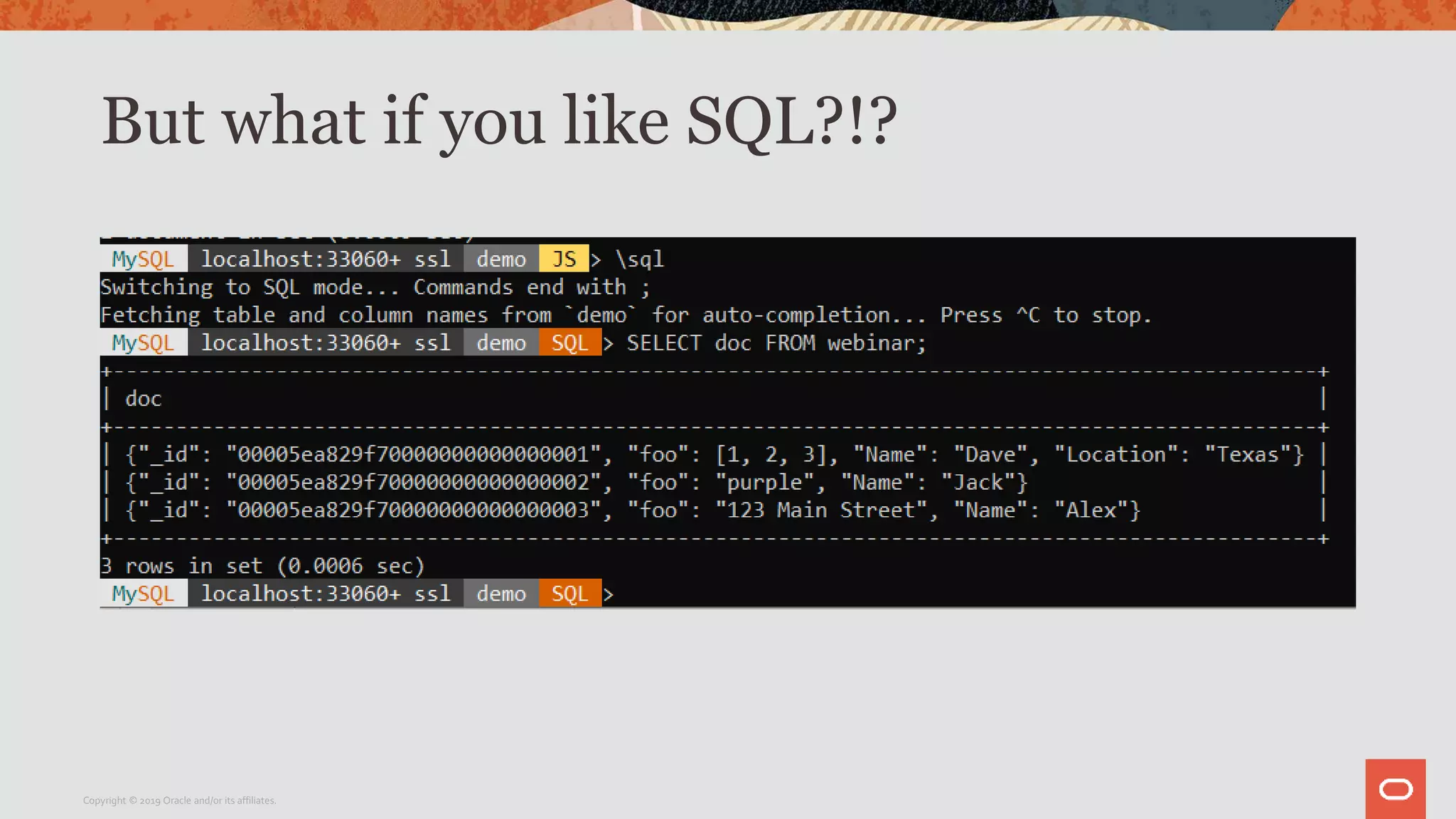
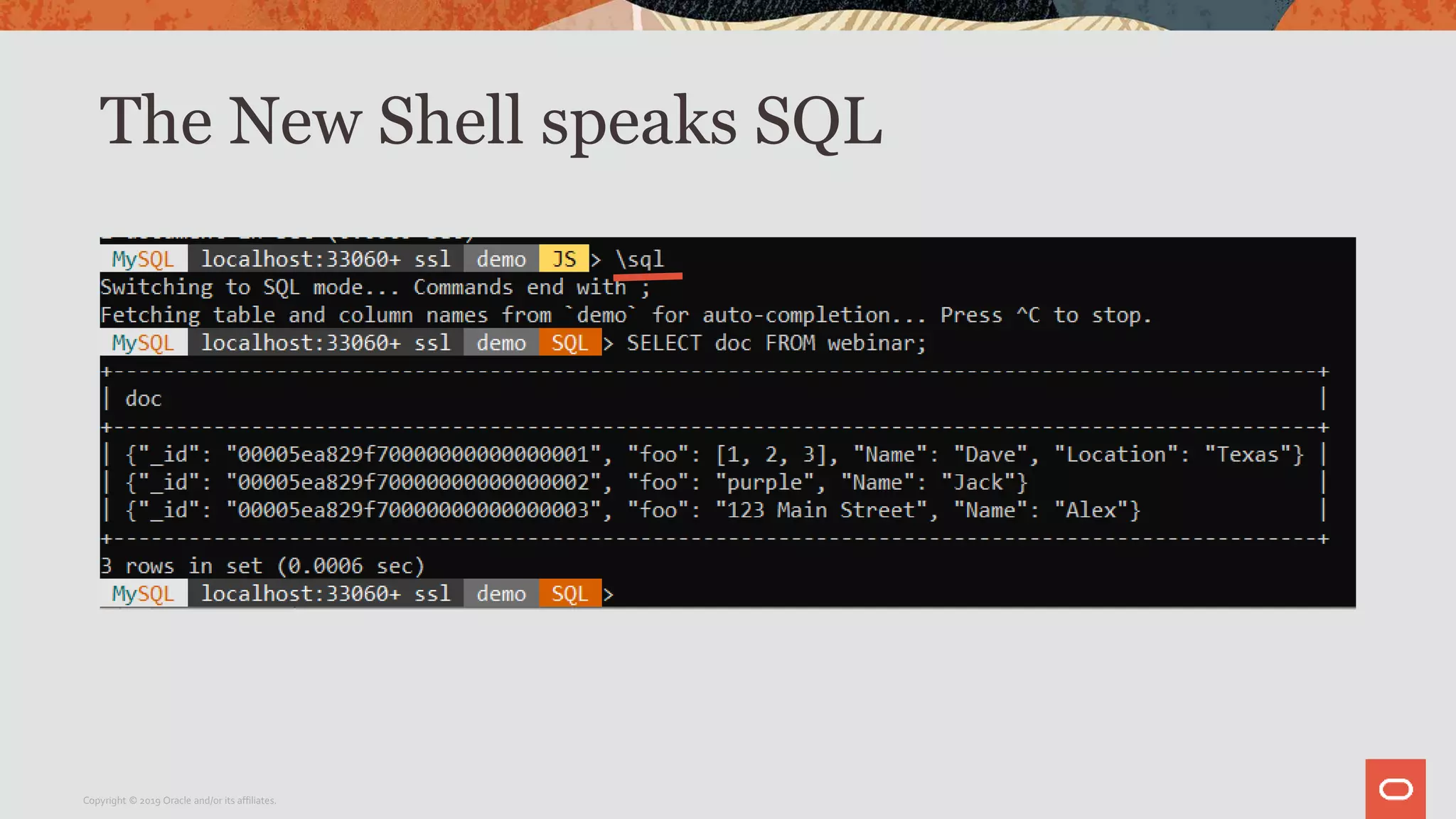
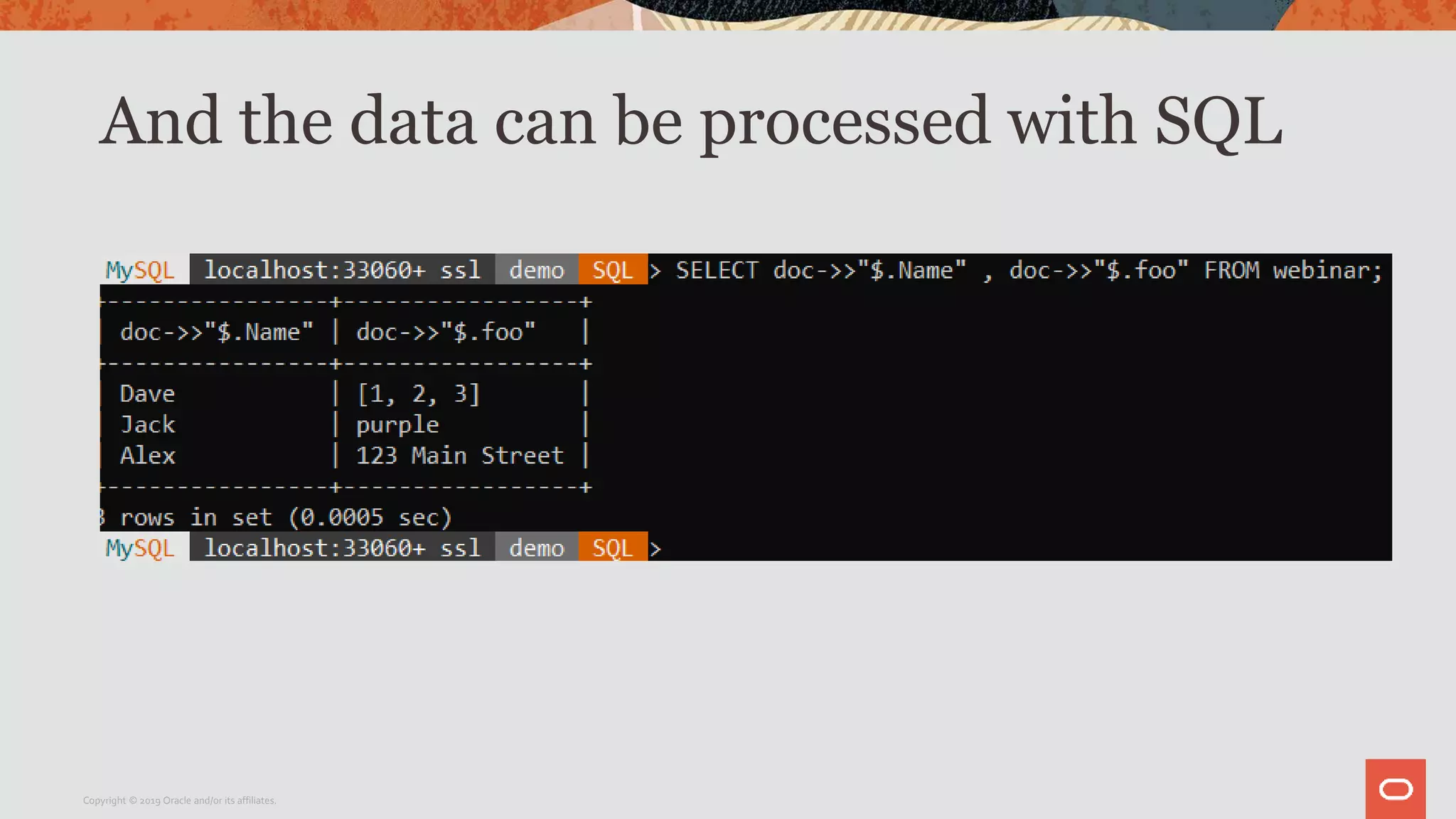
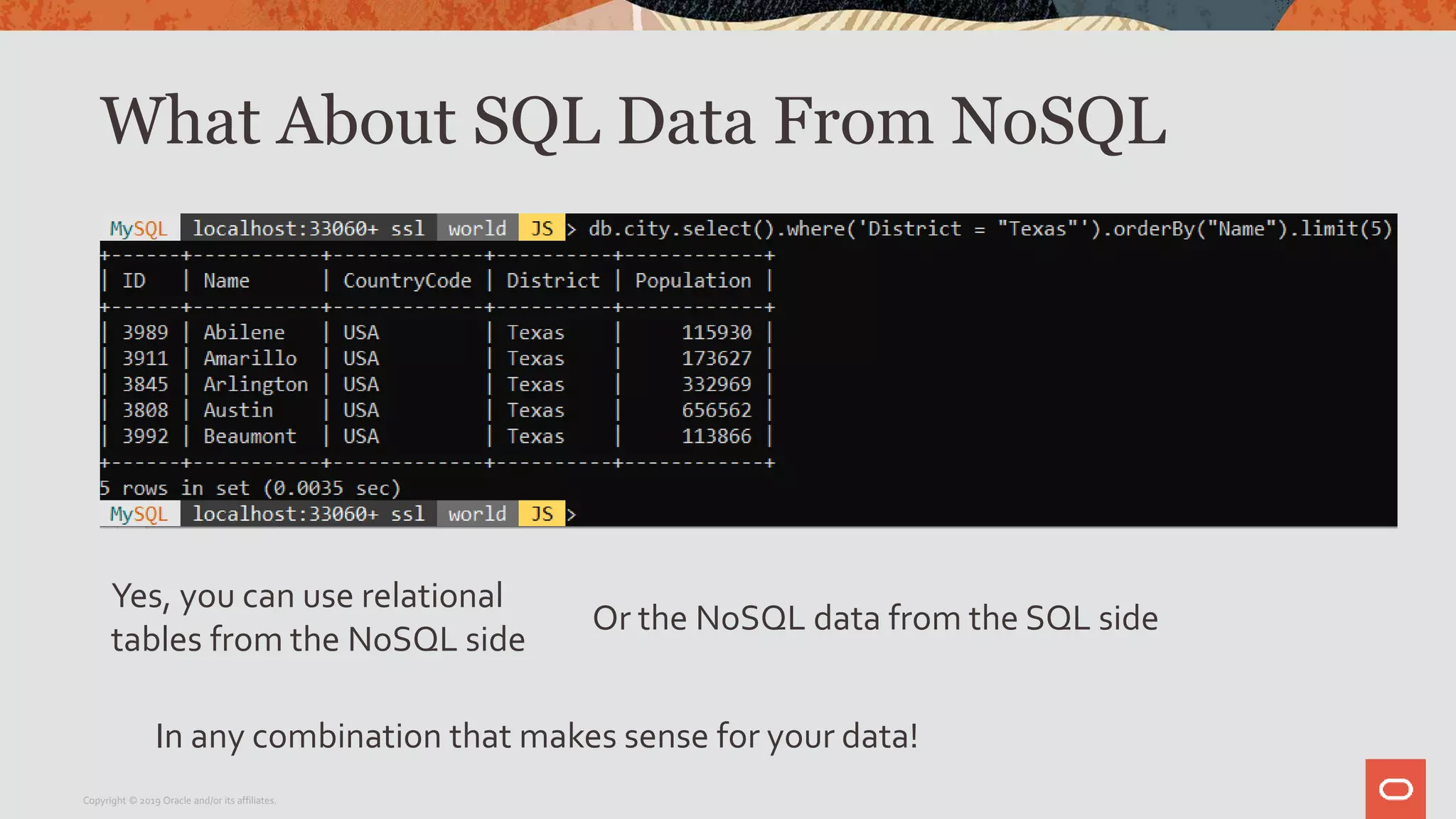
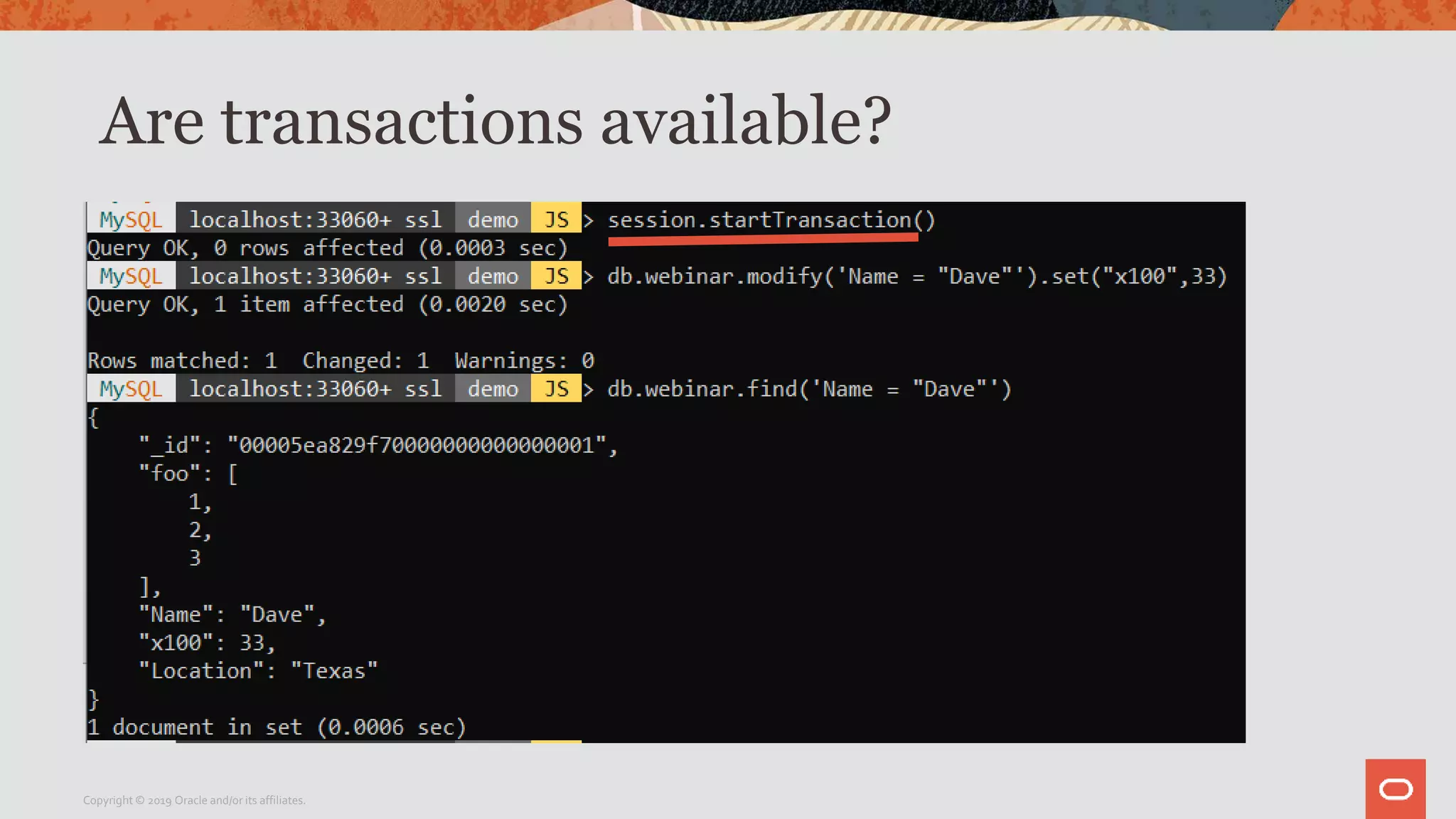
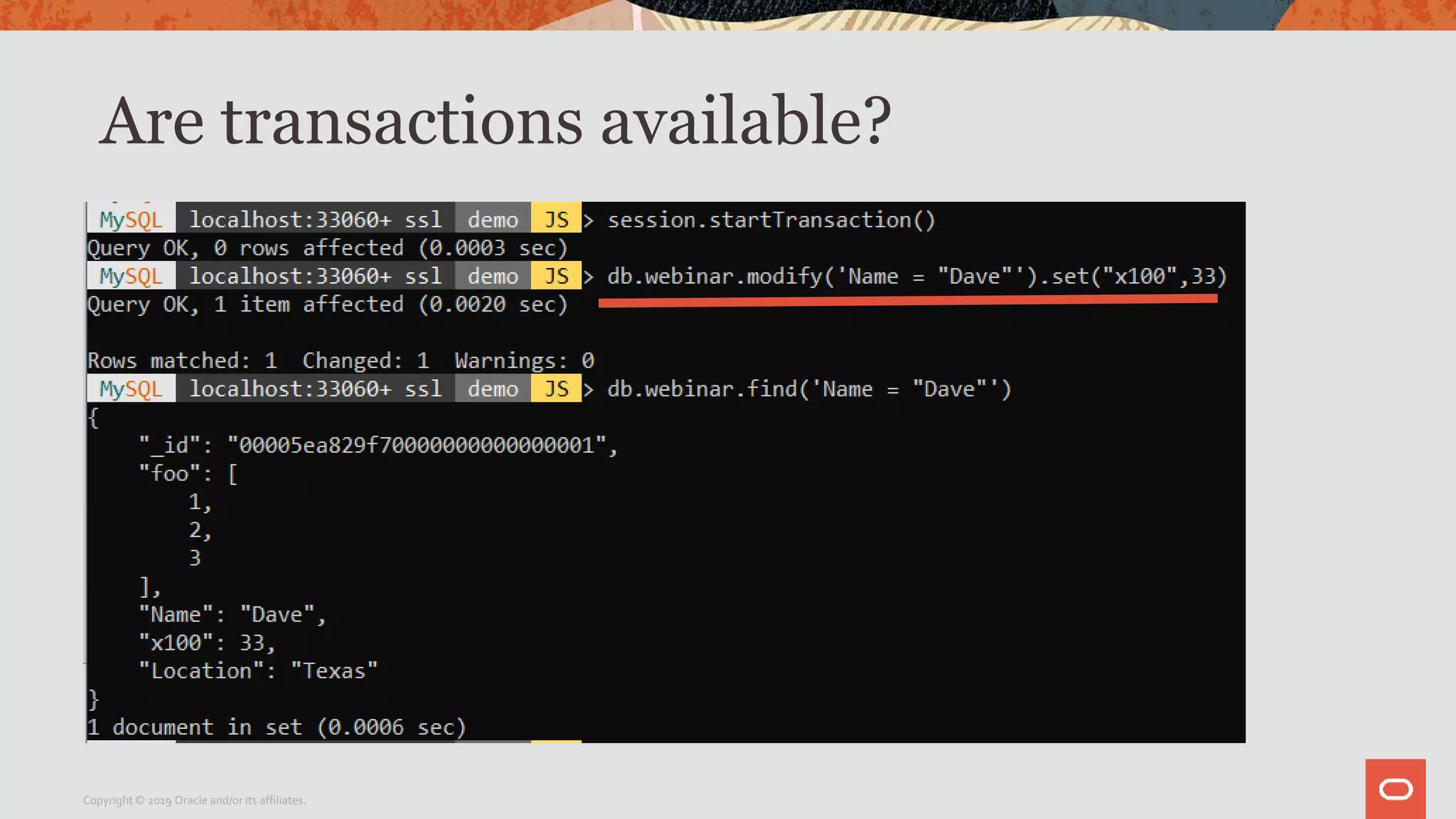
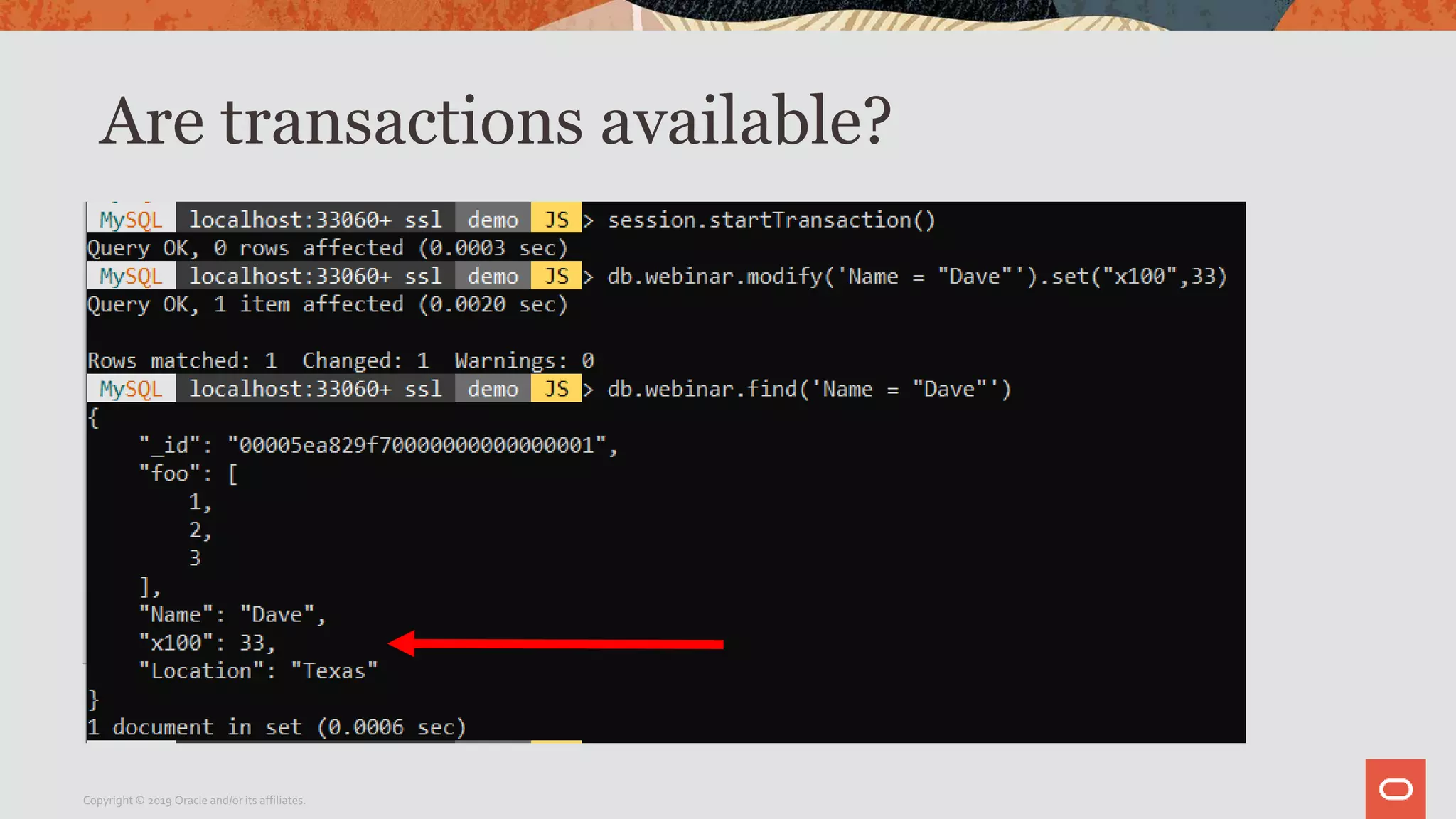
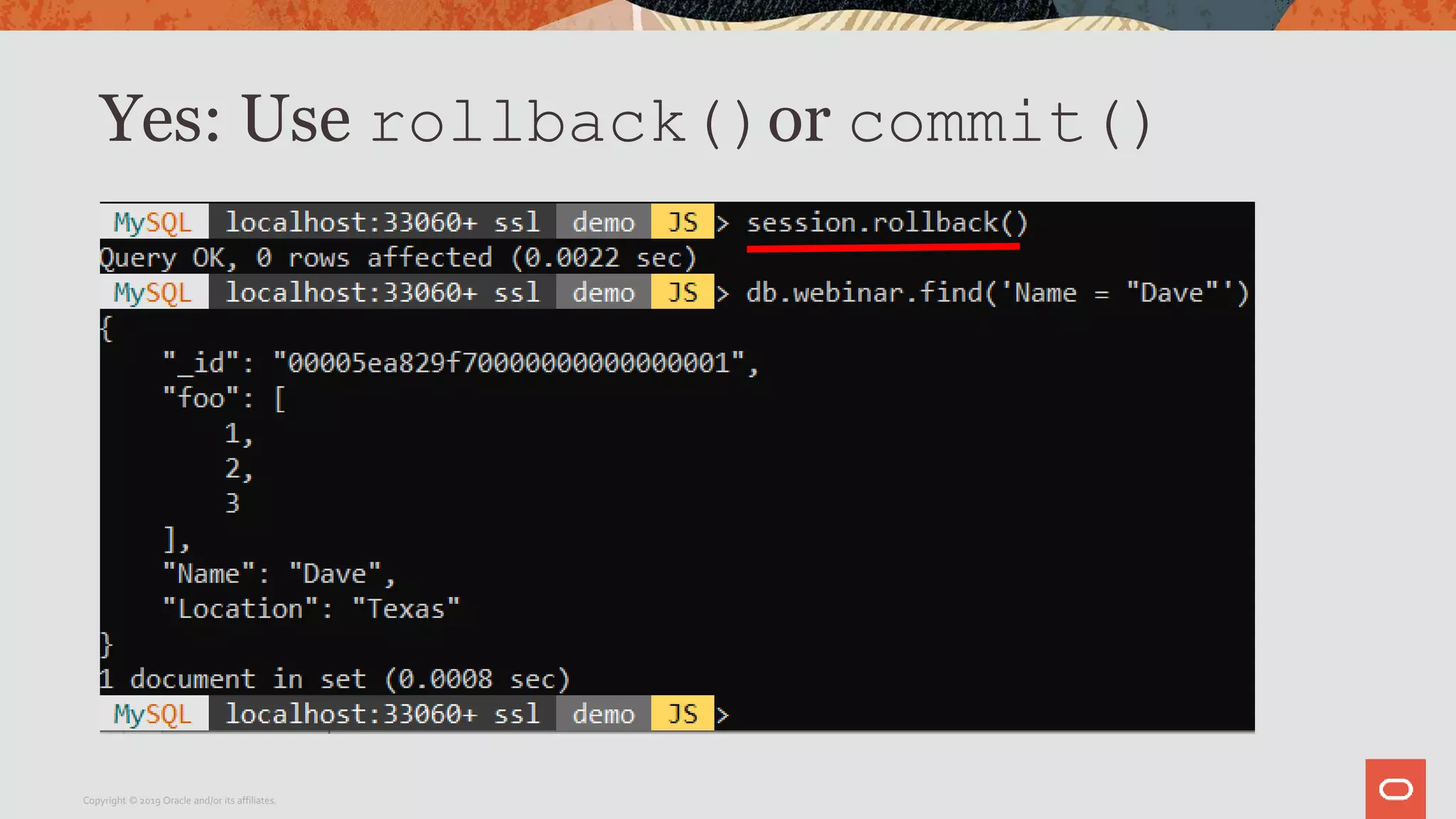
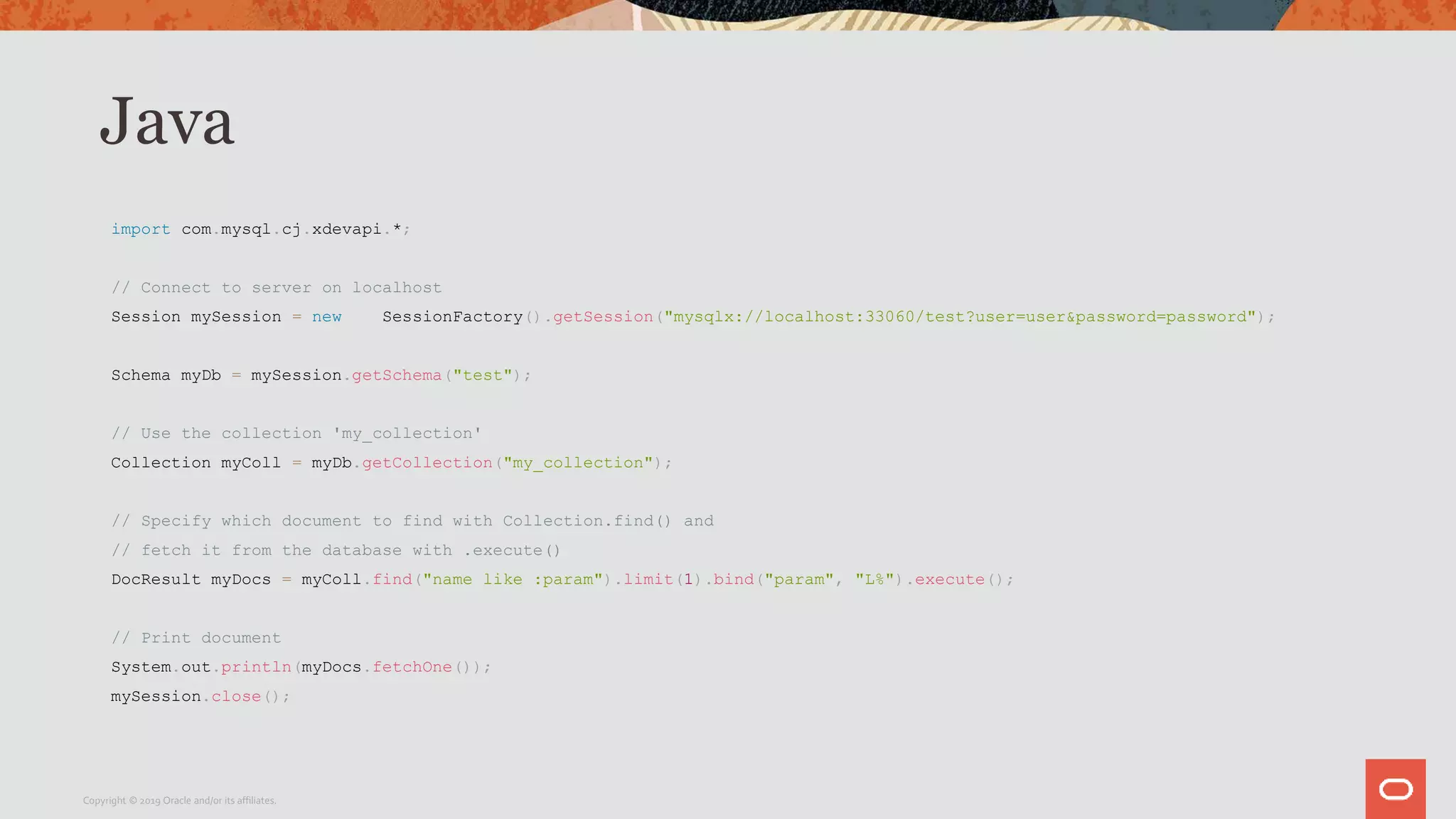
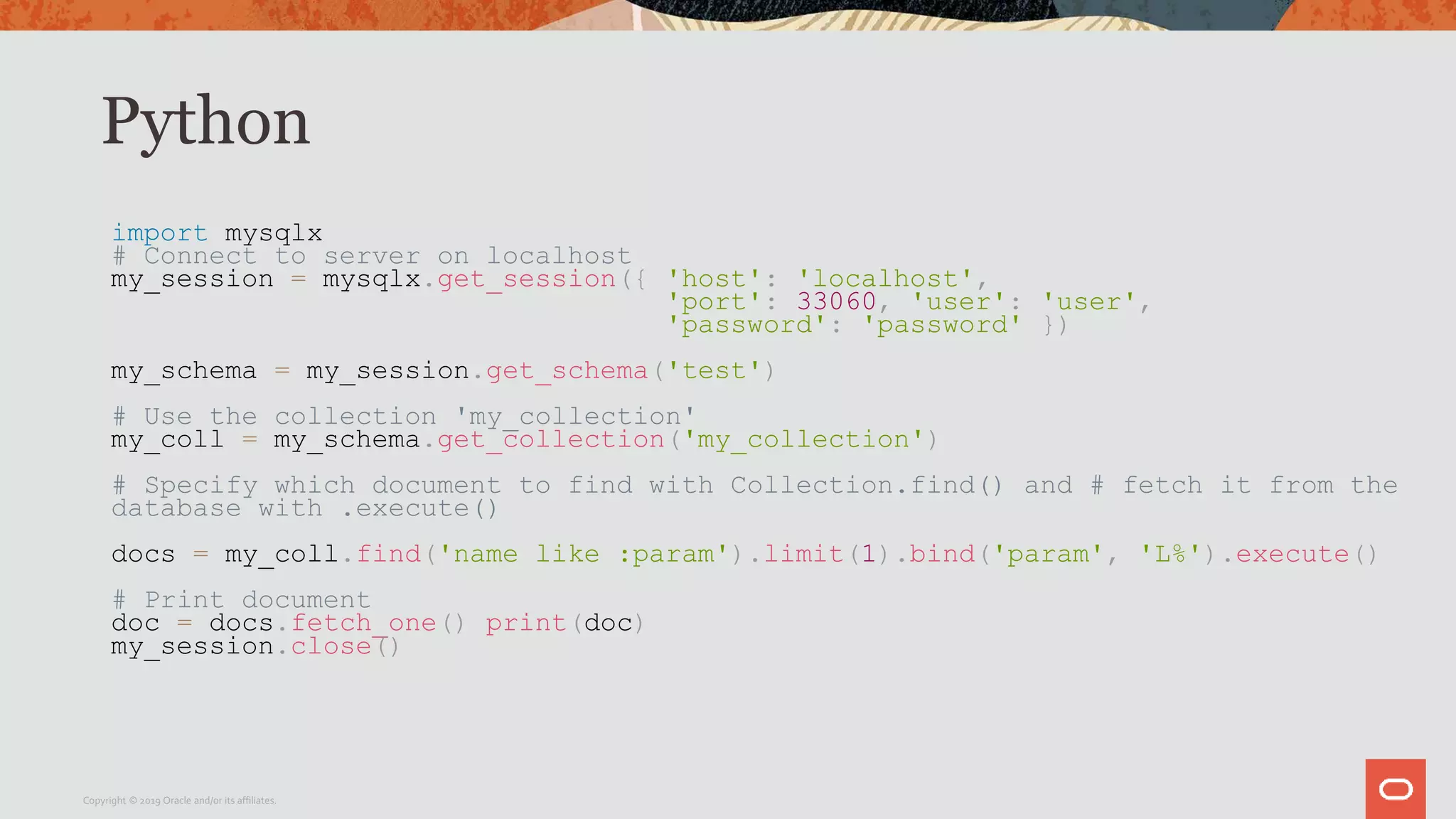
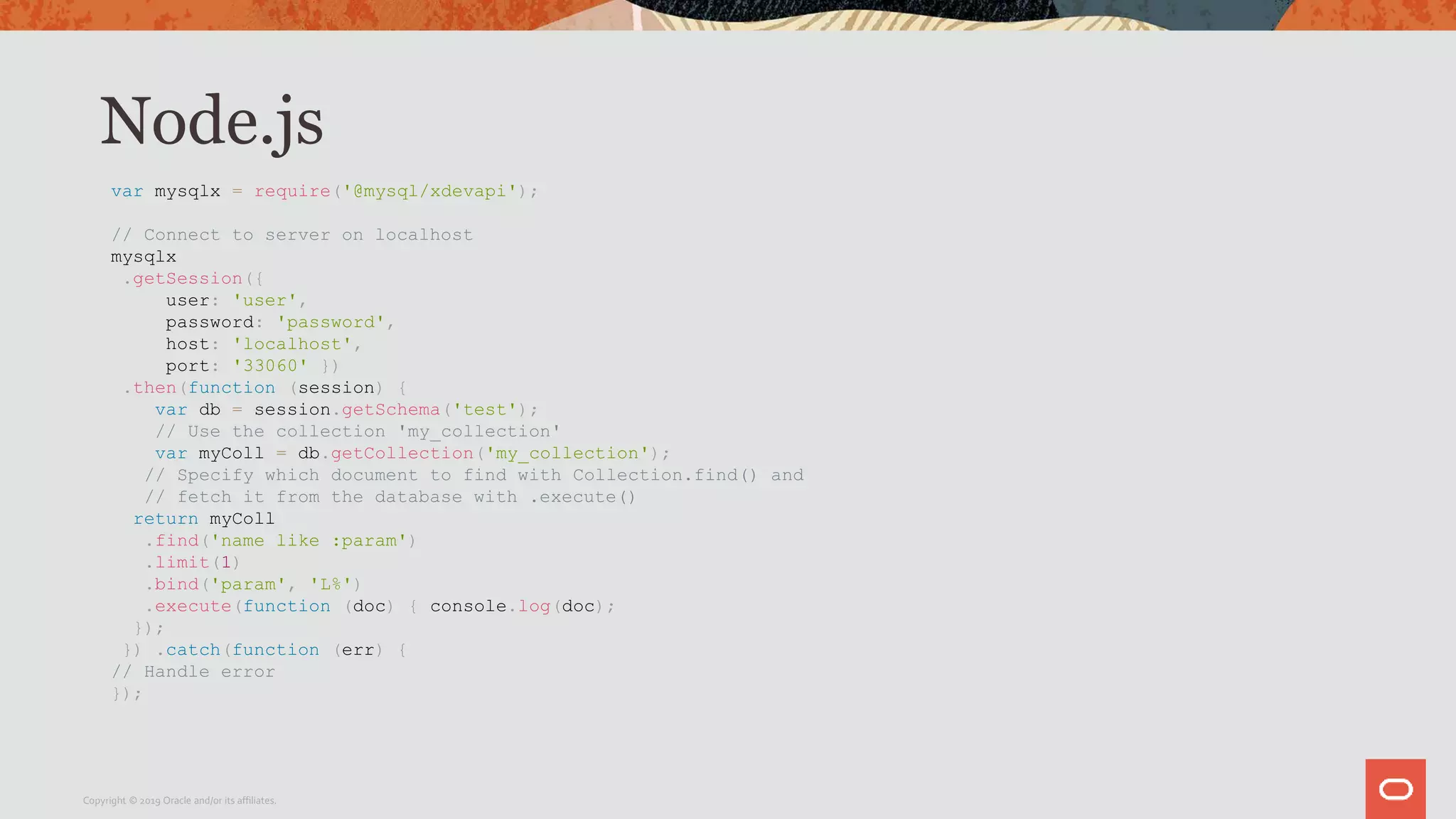
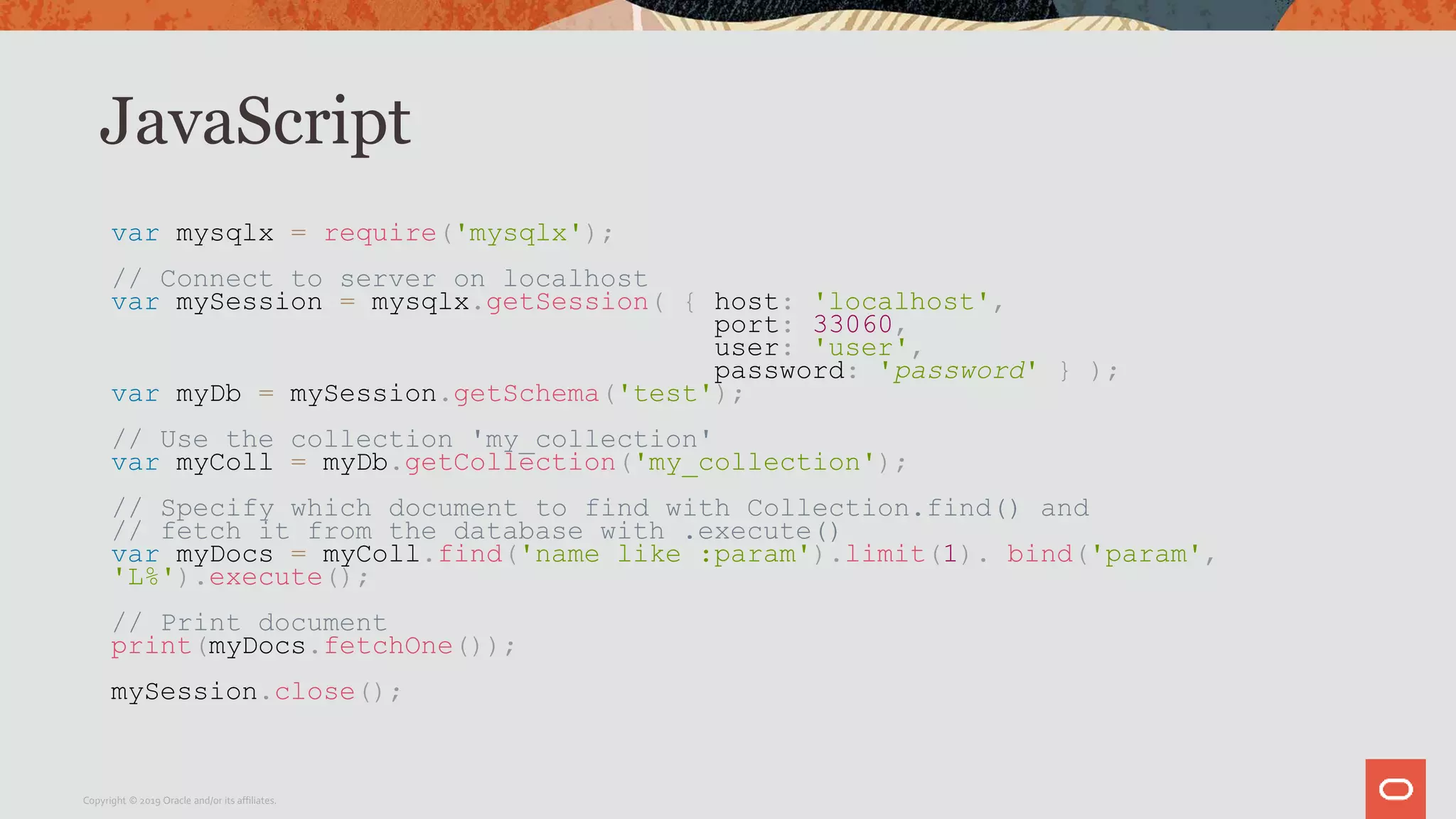
The document provides a step-by-step introduction to the MySQL Document Store, highlighting its ease of use and functionality as a NoSQL database that stores data in JSON format. It outlines initial setup commands, the benefits of a schema-less design, and how it supports CRUD operations through a simple API, while also allowing use of SQL for those who prefer it. Additionally, it includes resources for further information and reminders about MySQL version updates and features.















![PHP
<?php
$marco = [
"name" => "Marco",
"age" => 19,
"job" => "Programmer"
];
$mike = [
"name" => "Mike",
"age" => 39,
"job" => "Manager"
];
$schema = $session->getSchema("test");
$collection = $schema->getCollection("example");
$collection->add($marco, $mike)->execute();
var_dump($collection->find("name = 'Mike'")->execute()->fetchOne());
?>
Copyright © 2019 Oracle and/or its affiliates.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docstorestepbystep-200507184432/75/A-Step-by-Step-Introduction-to-the-MySQL-Document-Store-40-2048.jpg)


![Indexes
db.b.createIndex("nbr_idx",
{fields:[{"field": "$.nbr", "type":"INT", required:true}]}
);
Copyright © 2019 Oracle and/or its affiliates.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docstorestepbystep-200507184432/75/A-Step-by-Step-Introduction-to-the-MySQL-Document-Store-47-2048.jpg)

![Required Fields
CREATE TABLE `testx` (
`col` JSON,
CONSTRAINT `myage_inRange`
CHECK (JSON_SCHEMA_VALID(
'{"type": "object",
"properties": {
"myage": {
"type" : "number",
"minimum": 28,
"maximum": 99
}
},"required": ["myage"]
}', `col`) = 1)
);
Copyright © 2019 Oracle and/or its affiliates.
mysql> insert into testx values('{"myage":27}');
ERROR 3819 (HY000): Check constraint 'myage_inRange' is violated.
mysql> insert into testx values('{"myage":97}');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docstorestepbystep-200507184432/75/A-Step-by-Step-Introduction-to-the-MySQL-Document-Store-49-2048.jpg)



