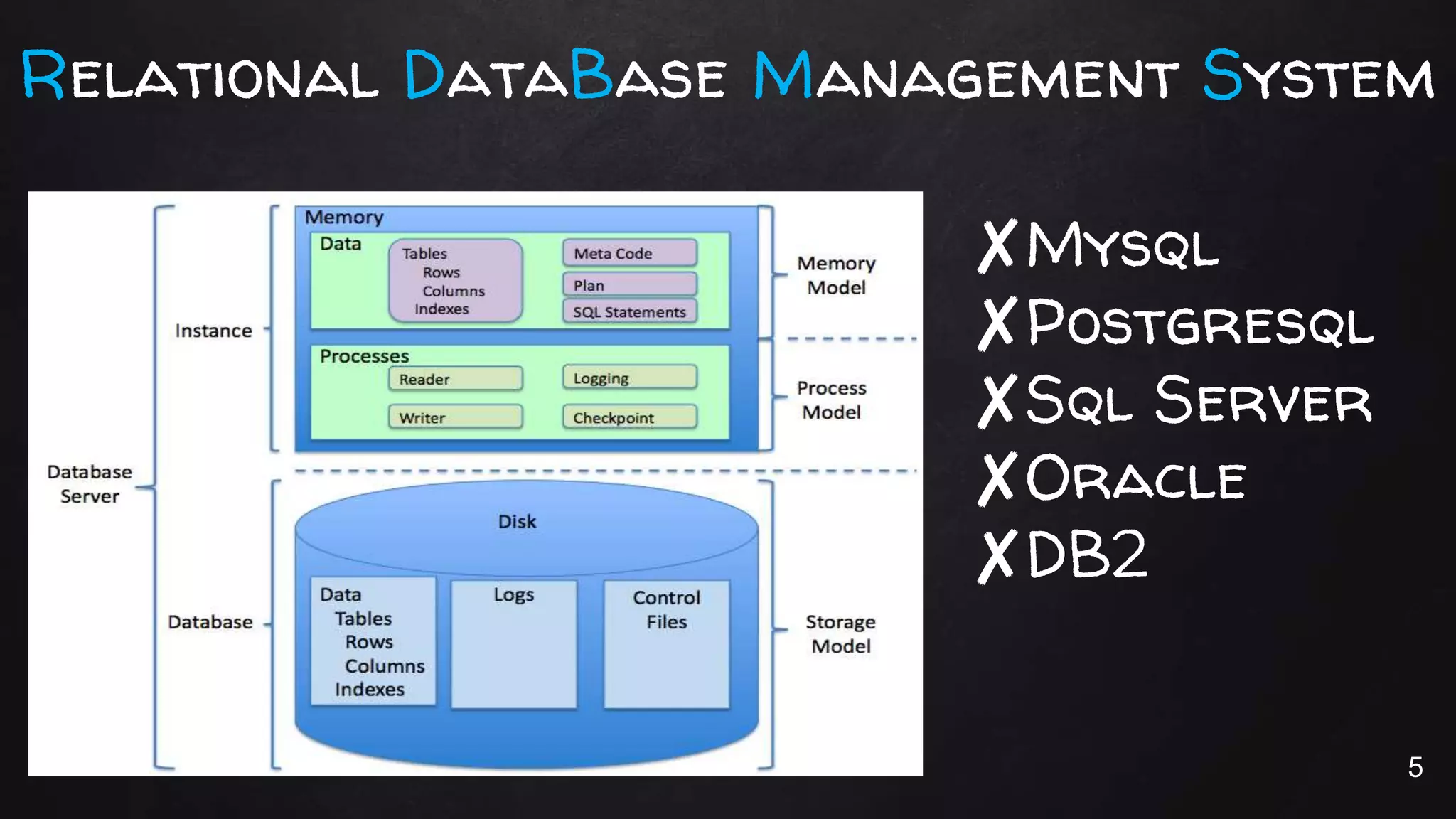
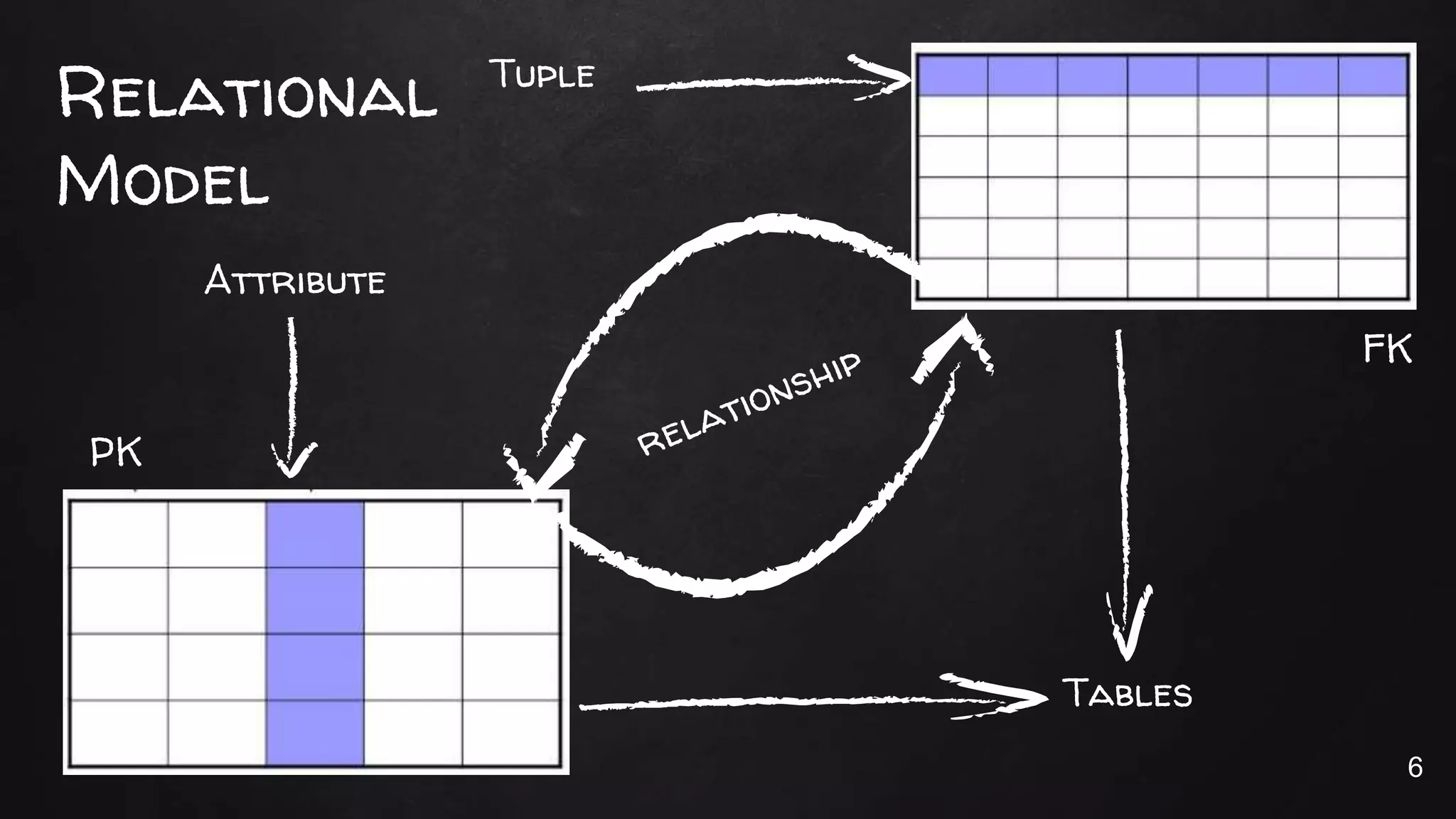
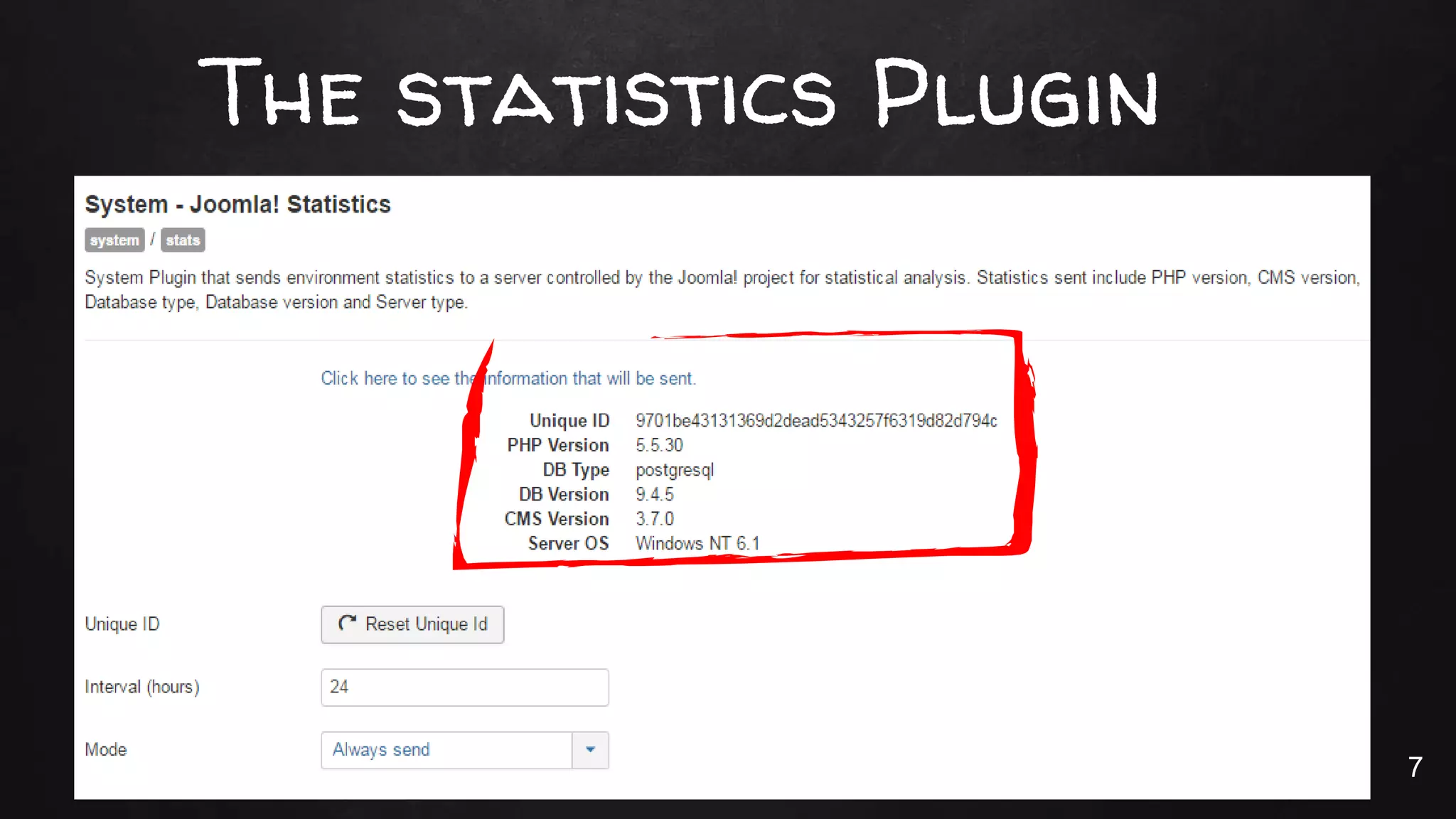
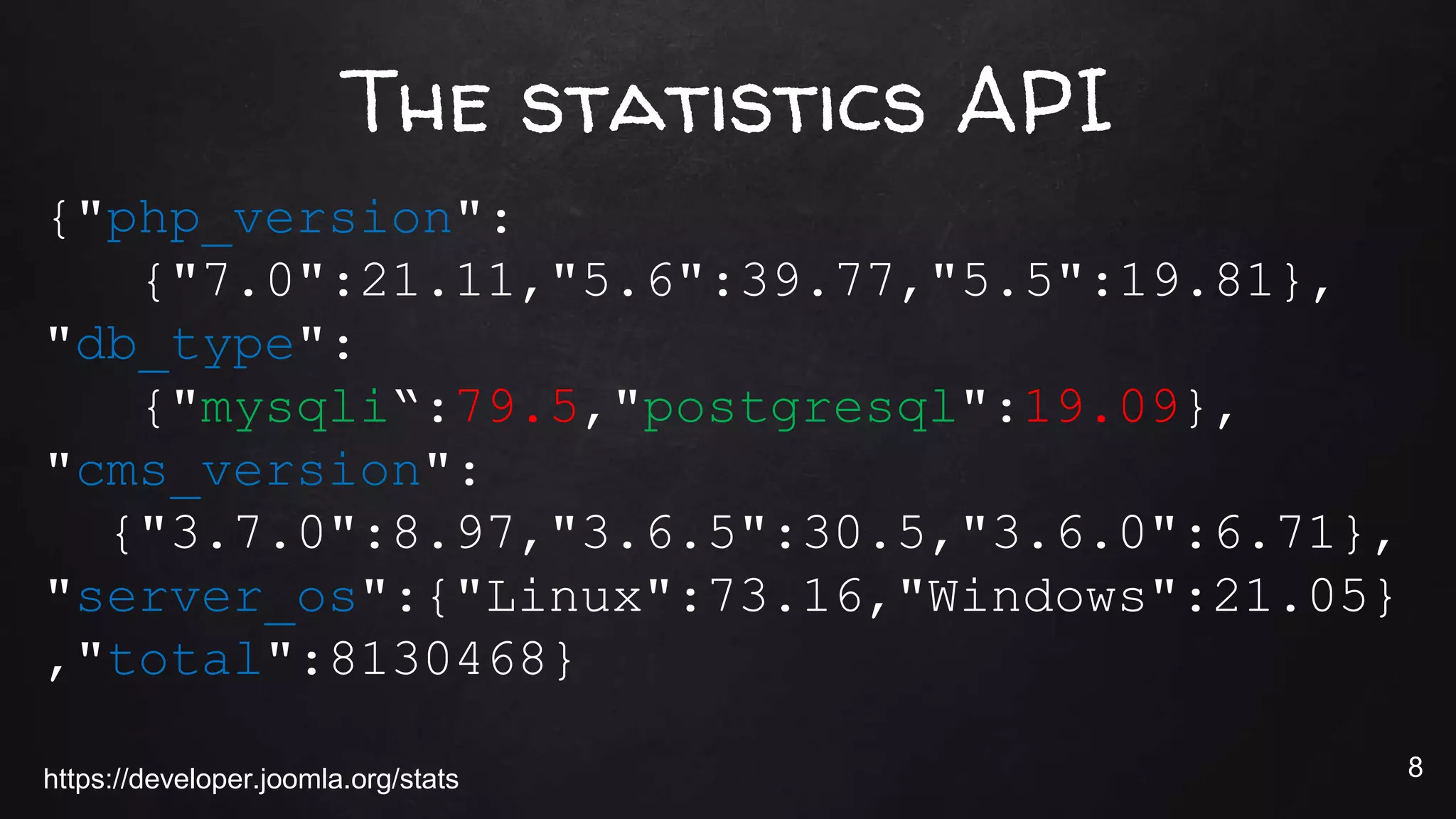
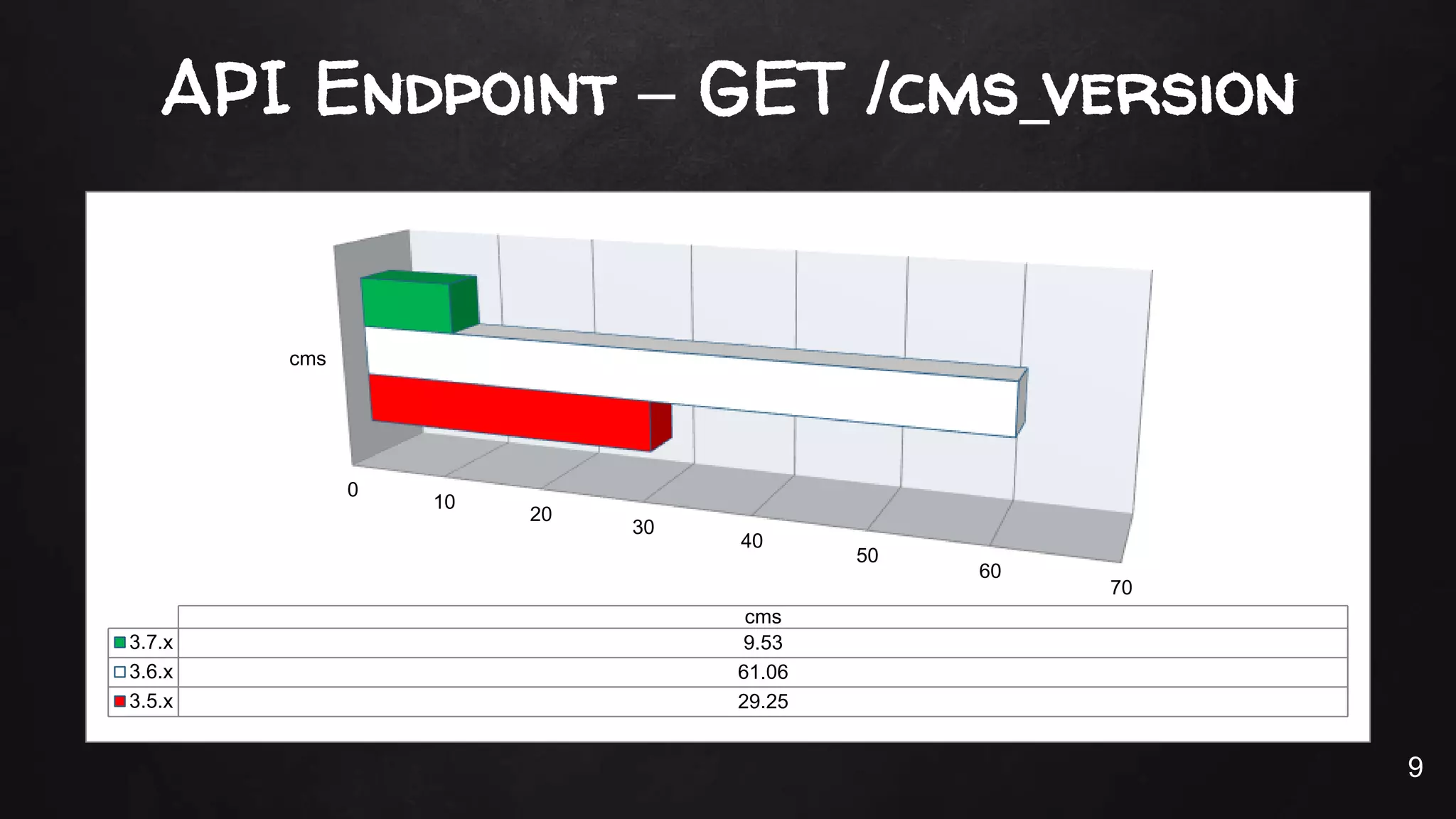
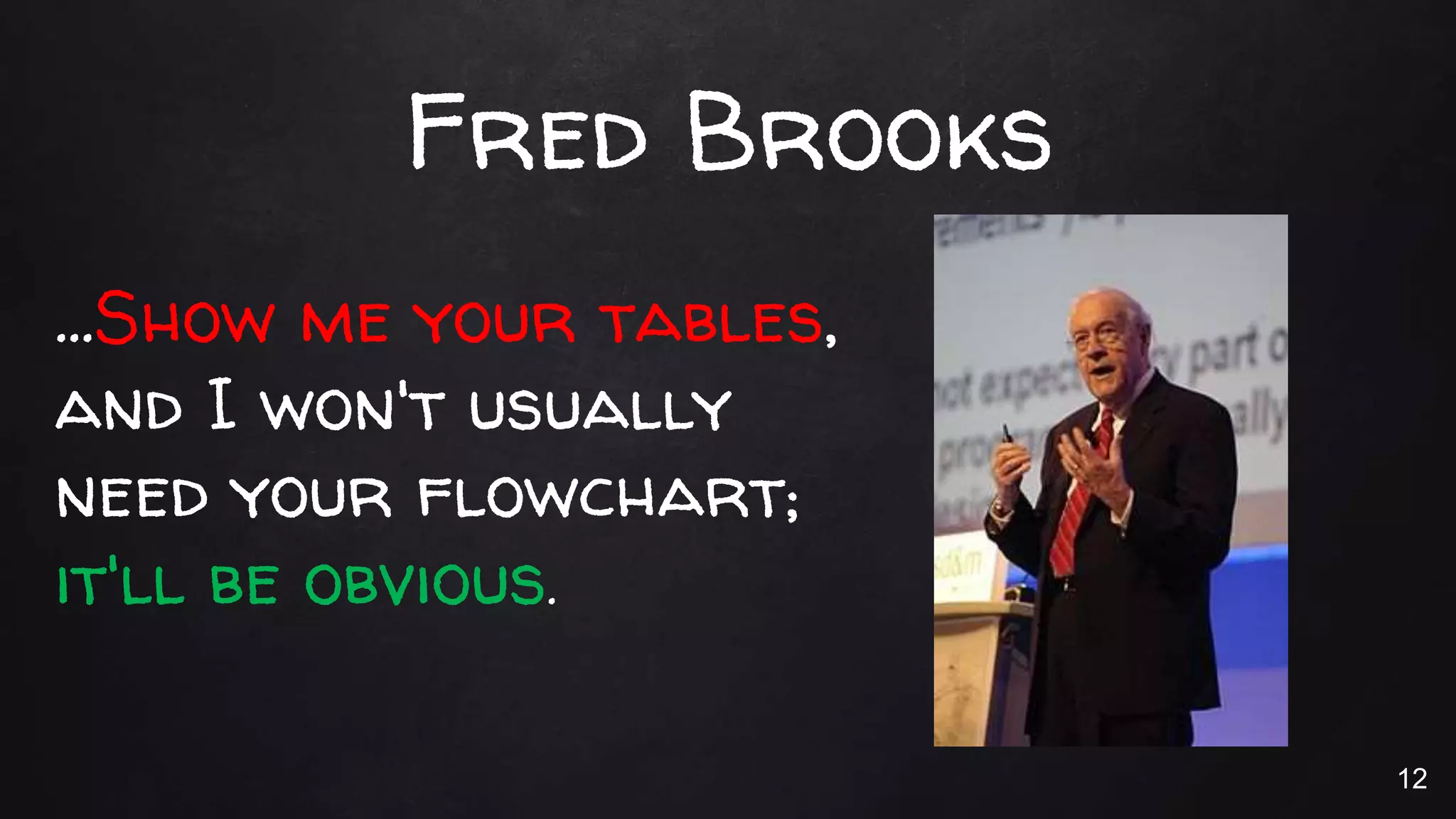
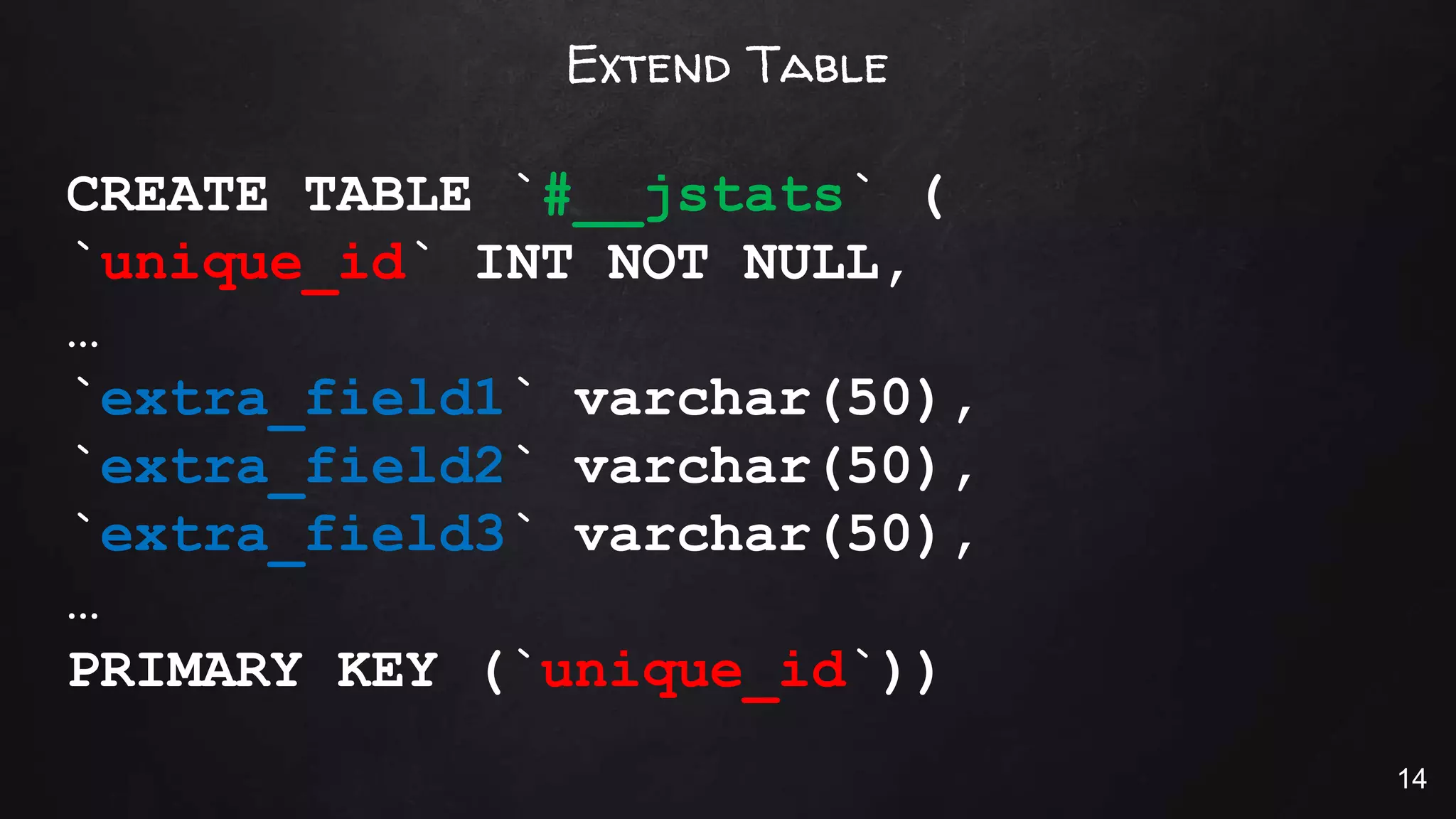
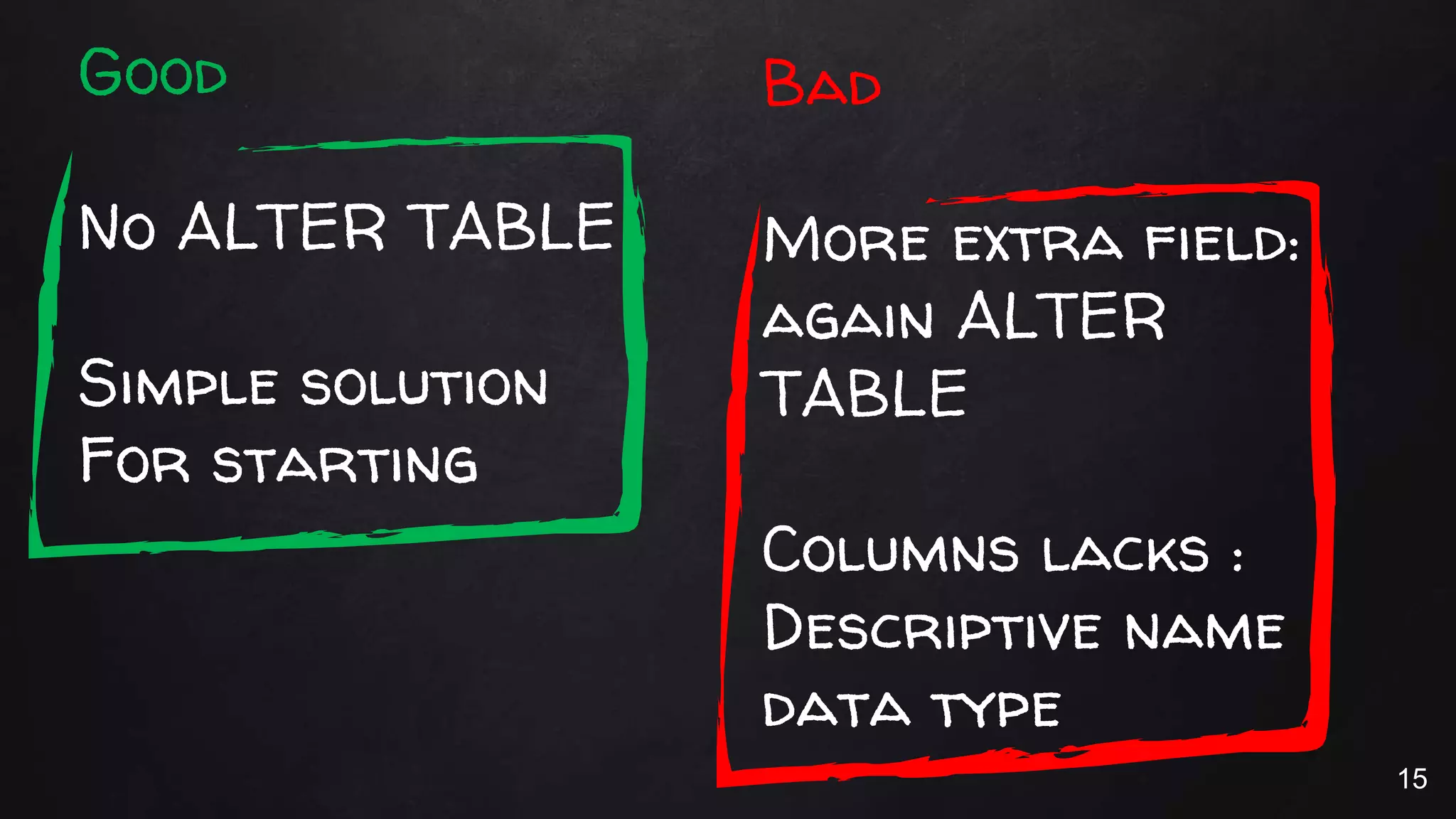
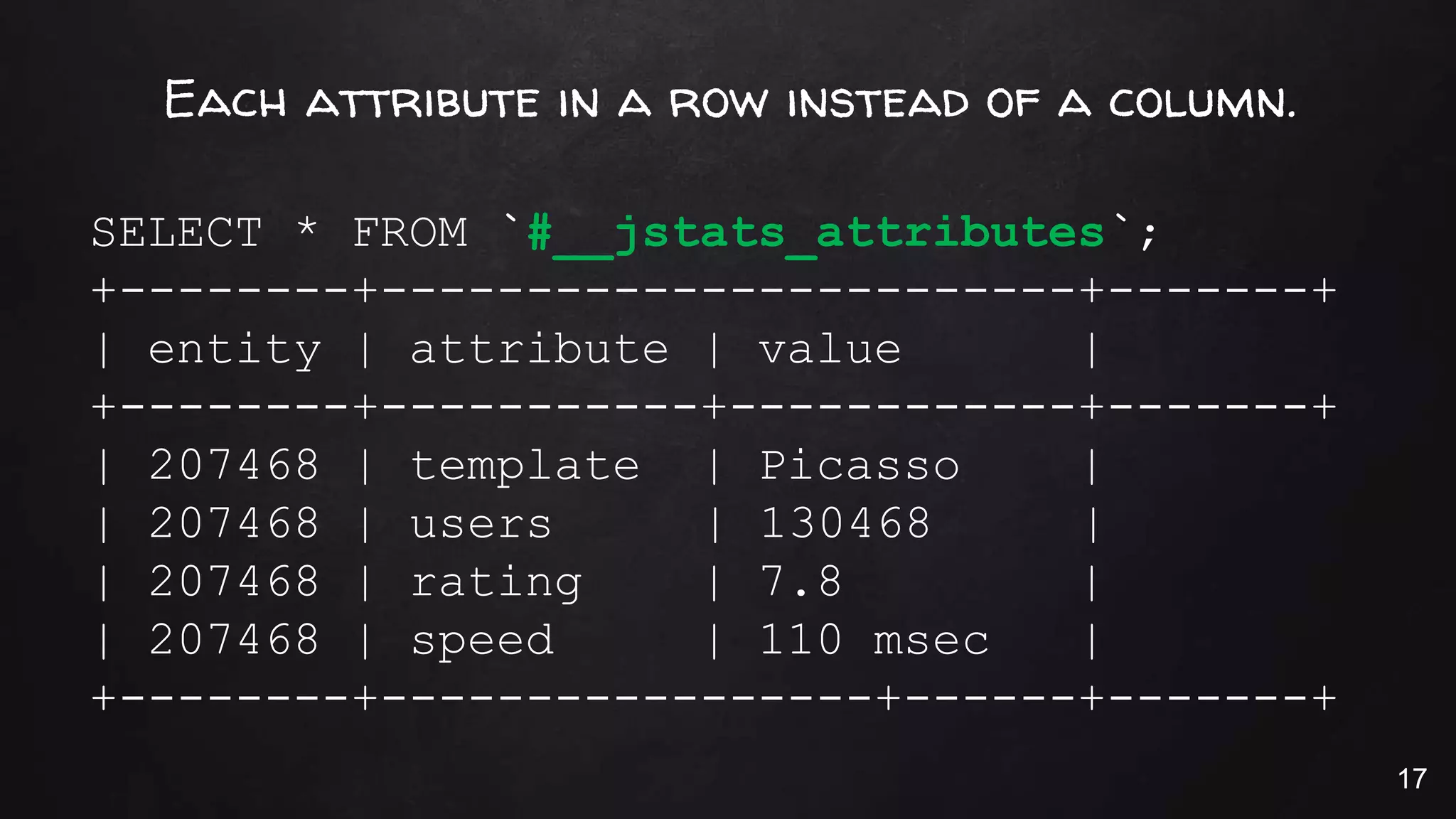
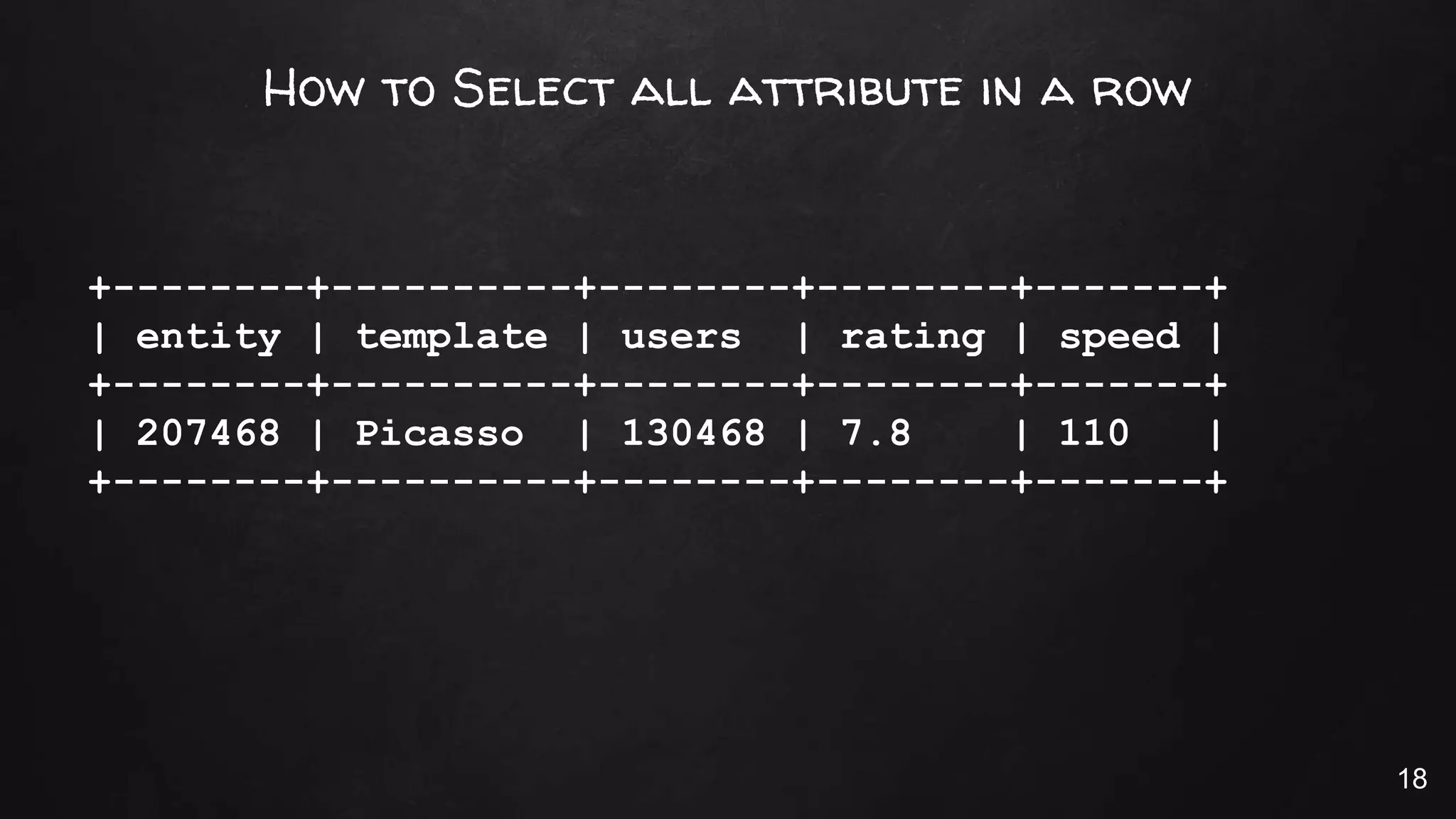
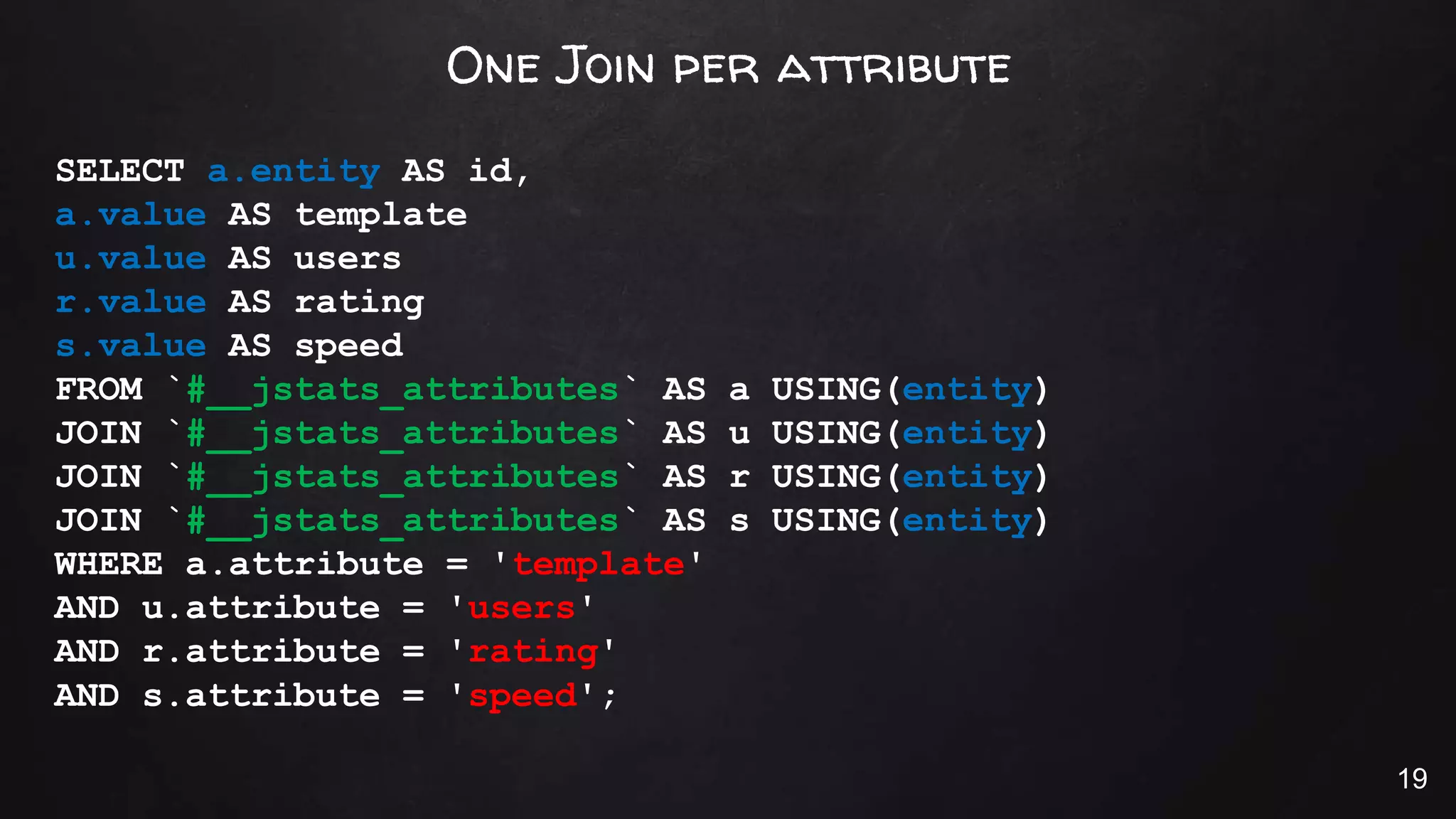
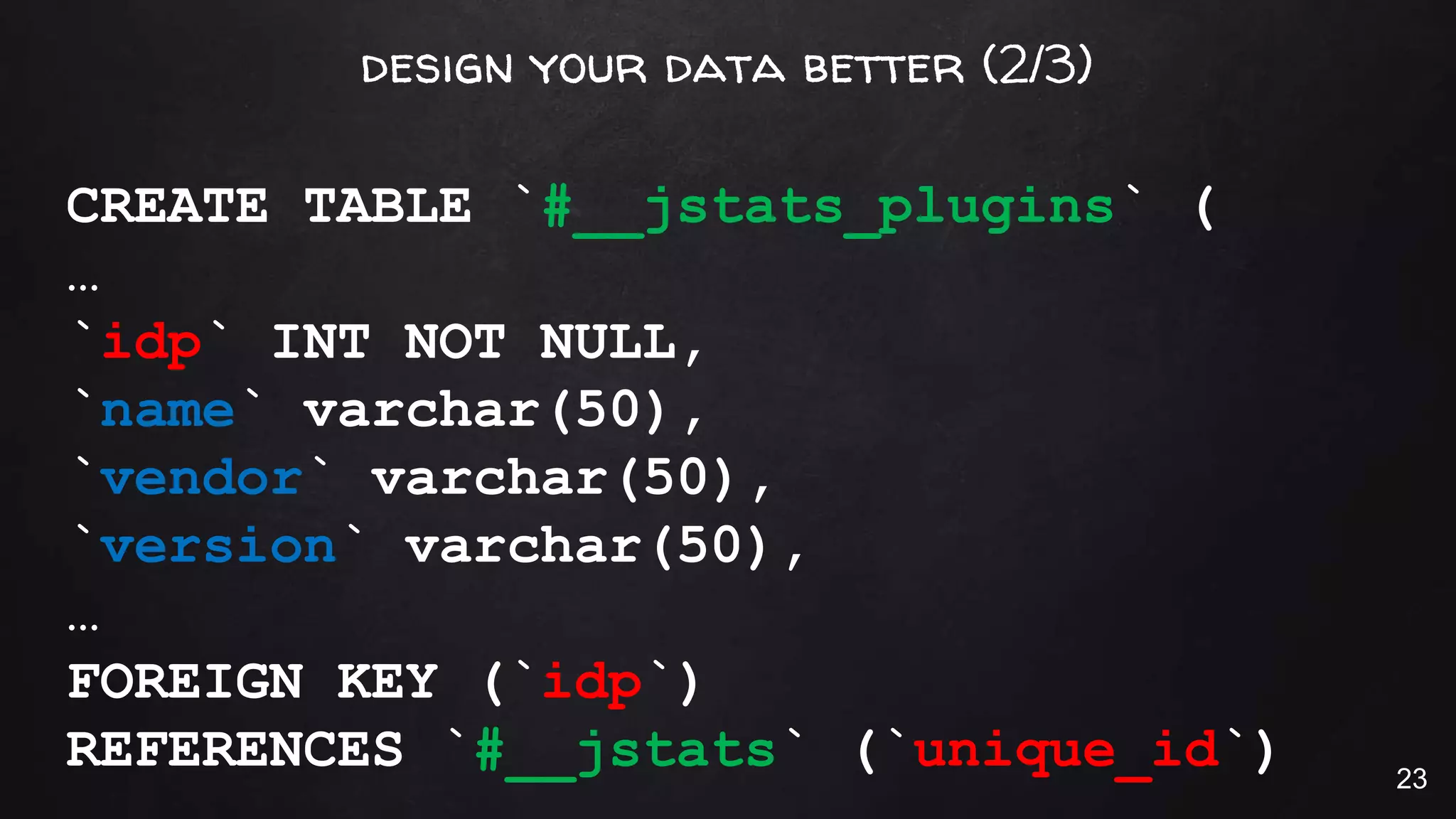
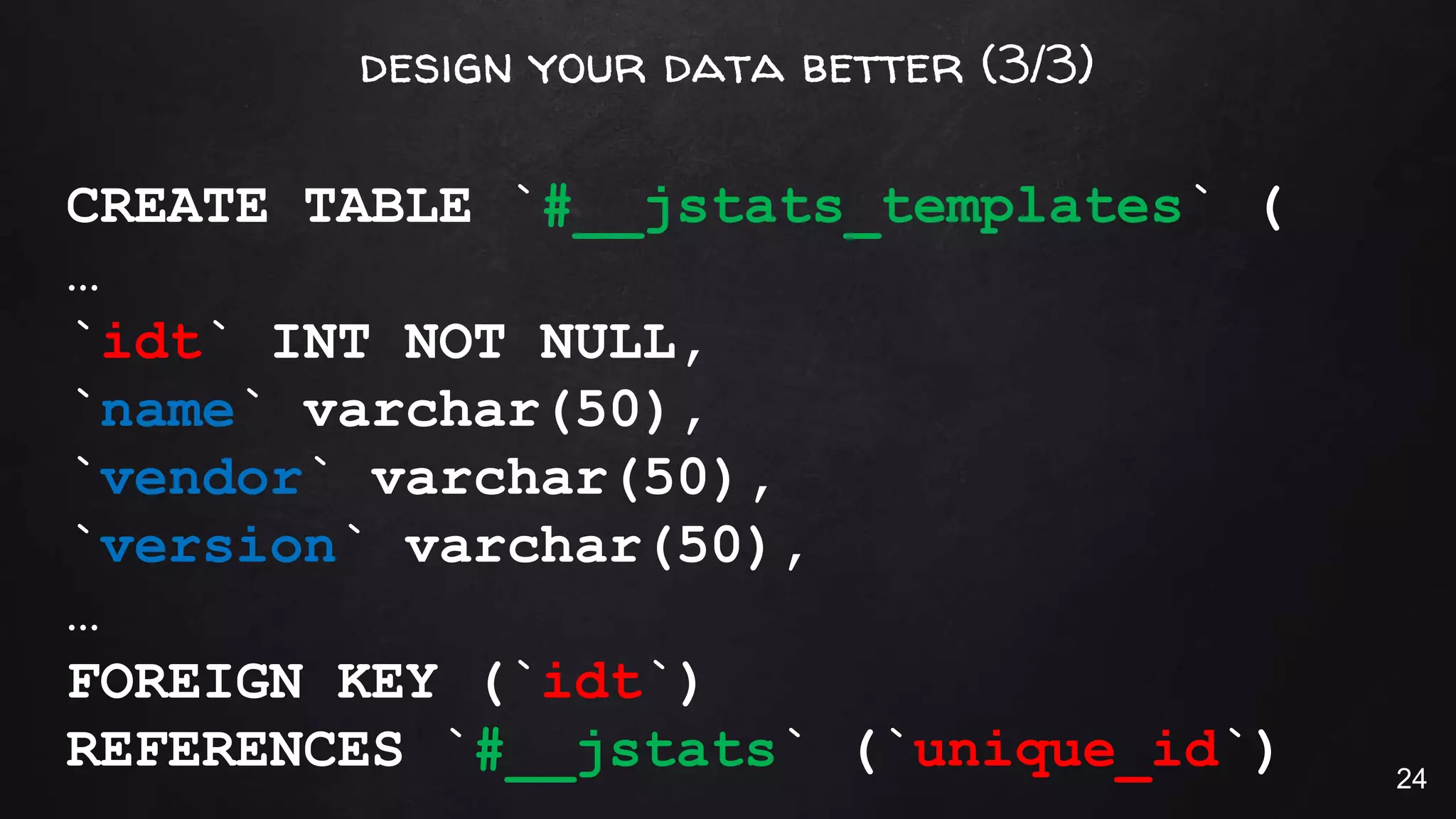
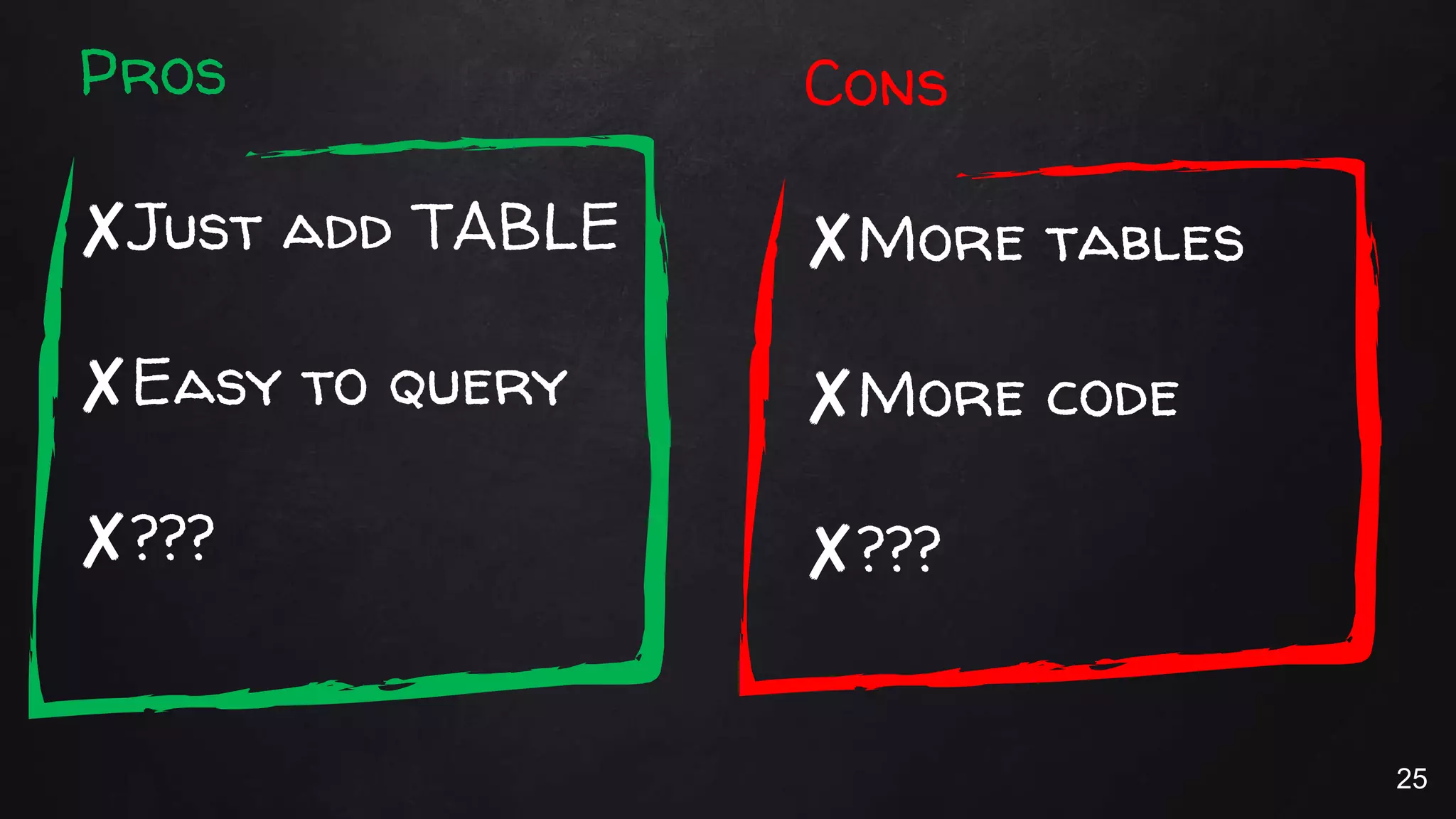
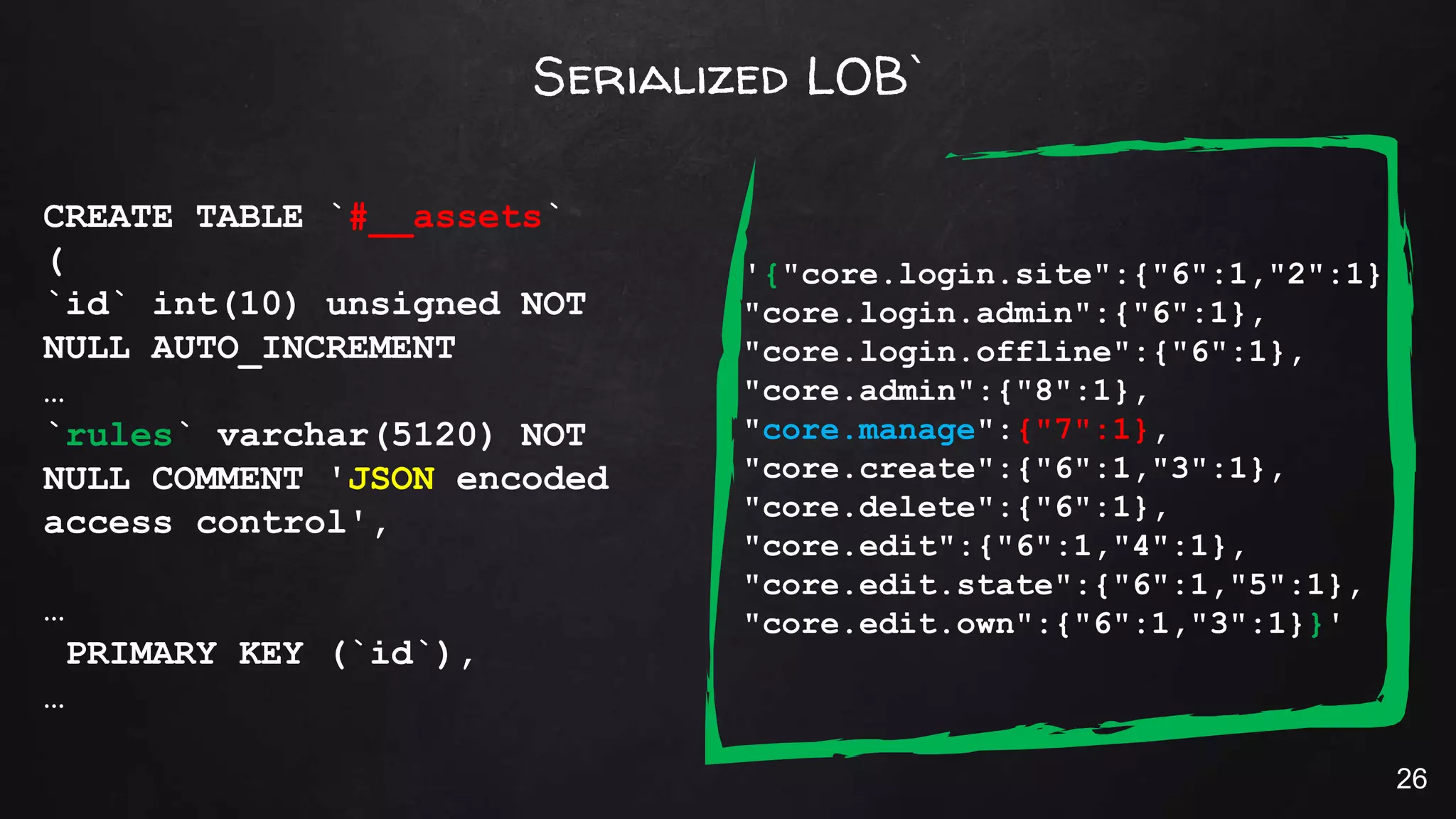
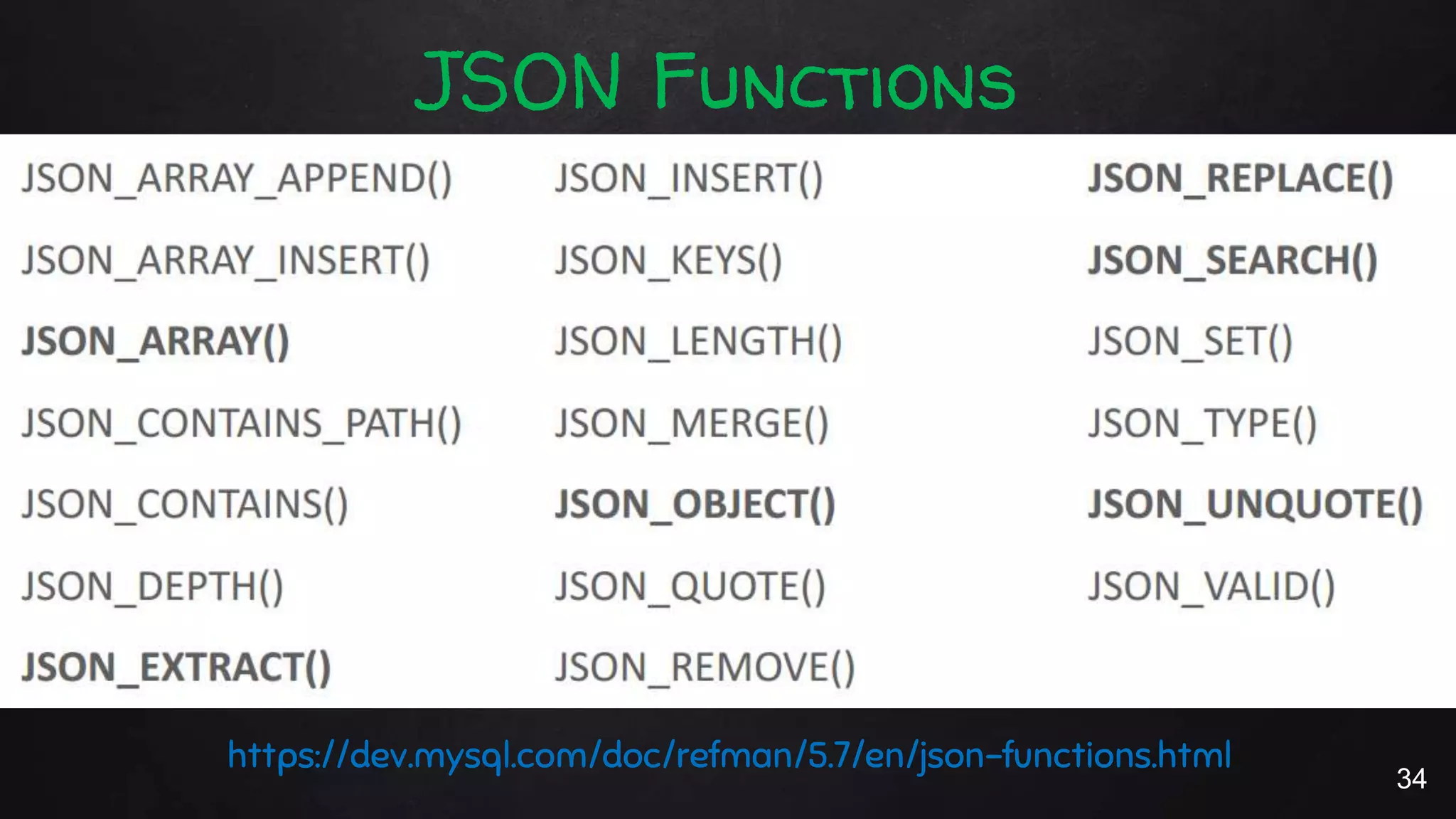
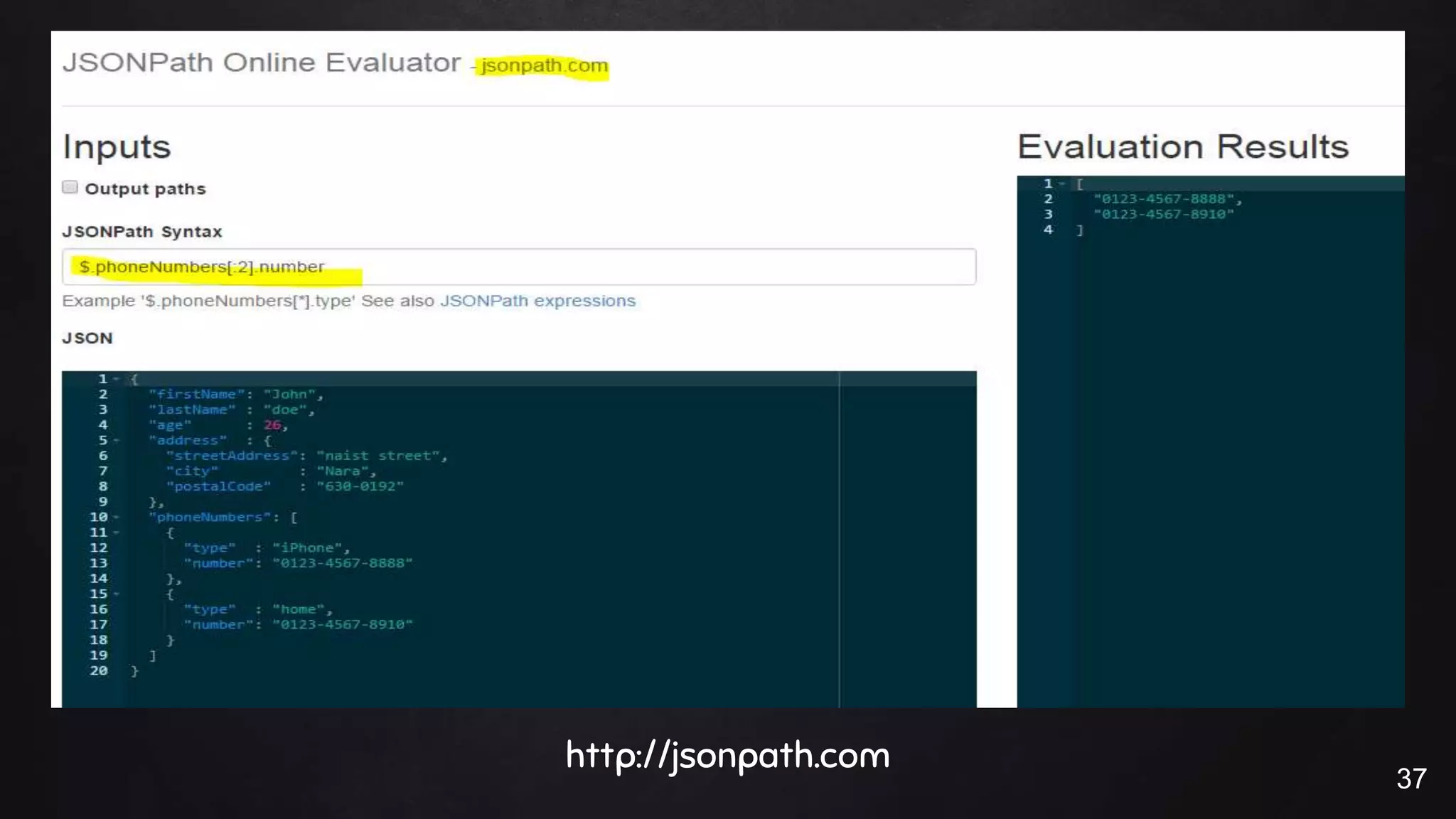
This document discusses the rise of JSON usage in relational database management systems (RDBMS). It provides an overview of JSON and its benefits as a lightweight data format. It then examines different approaches to storing and querying JSON data in an RDBMS, including using JSON columns, entity-attribute-value modeling, and document-oriented modeling that treats documents as records. The document discusses pros and cons of each approach and emphasizes the importance of good data modeling and structure. It also shows examples of using JSON functions and indexing in MySQL.


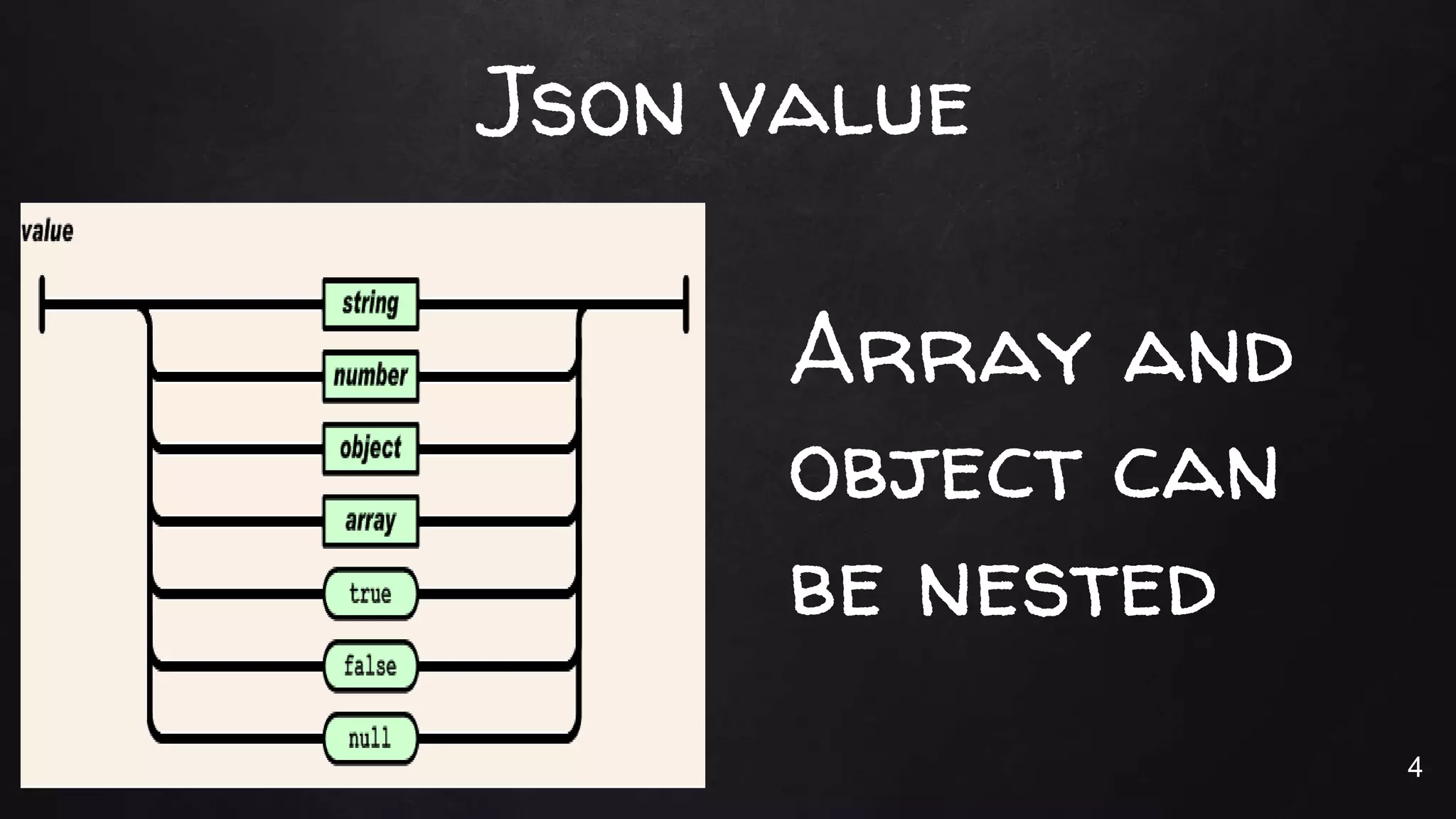












![The Json Values
mysql> SELECT CAST('{}' AS JSON) object
-> , CAST('[]' AS JSON) array
-> , CAST('null' AS JSON) "null"
-> , CAST('true' AS JSON) "true"
-> , CAST('false' AS JSON) "false"
-> , CAST('"string"' AS JSON) string
-> ;
+--------+-------+------+------+-------+----------+
| object | array | null | true | false | string |
+--------+-------+------+------+-------+----------+
| {} | [] | null | true | false | "string" |
+--------+-------+------+------+-------+----------+
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theriseofjsoninrdbmslandjab17-170530074611/75/The-rise-of-json-in-rdbms-land-jab17-32-2048.jpg)
![The Json Data Type
SELECT JSON_TYPE(CAST('{}' AS JSON))
-> ,JSON_TYPE(CAST('""' AS JSON))
-> ,JSON_TYPE(CAST('true' AS JSON))
-> ,JSON_TYPE(CAST('null' AS JSON))
-> ,JSON_TYPE(CAST(1 AS JSON))
-> ,JSON_TYPE(CAST(1.1 AS JSON))
-> ,JSON_TYPE(CAST(PI() AS JSON))
-> ,JSON_TYPE(CAST(CURRENT_DATE AS JSON))
-> ,JSON_TYPE(CAST(CURRENT_TIME AS JSON))
-> ,JSON_TYPE(CAST('[]' AS JSON))
OBJECT
STRING
BOOLEAN
NULL
INTEGER
DECIMAL
DOUBLE
DATE
TIME
ARRAY
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theriseofjsoninrdbmslandjab17-170530074611/75/The-rise-of-json-in-rdbms-land-jab17-33-2048.jpg)
![JSON Array and Object
SELECT
JSON_ARRAY(1, 2, 3) array,
JSON_OBJECT(‘key1','value1',‘key2','value2') object;
+-----------+----------------------------------------+
| array | object |
+-----------+----------------------------------------+
| [1, 2, 3] | {“key1": "value1", “key2": "value2"} |
+-----------+----------------------------------------+
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theriseofjsoninrdbmslandjab17-170530074611/75/The-rise-of-json-in-rdbms-land-jab17-35-2048.jpg)



![JSON FUNCTIONS
SELECT JSON_ARRAY(id, data->"$.name",
data->"$.version") AS json_array
FROM #__jstats_templates WHERE
JSON_EXTRACT(data,"$.vendor")=JSON_QUOTE("templater");
+-------------------------------+
| json_array |
+-------------------------------+
| [11298, "Picasso", "1.0.3"] |
| [12293, "Dalì", "2.3.1"] |
| [17284, "Leonardo", "1.1.8"] |
+-------------------------------+
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theriseofjsoninrdbmslandjab17-170530074611/75/The-rise-of-json-in-rdbms-land-jab17-40-2048.jpg)
![JSON Replace
set @json = CAST('{"foo":"bar"}' AS JSON);
set @json =
JSON_REPLACE(@json,'$.foo',JSON_ARRAY('bar','car','far'))
mysql> SELECT @json;
+-------------------------------+
| @json |
+-------------------------------+
| '{"foo":["bar","car","far"]}' |
+-------------------------------+
41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theriseofjsoninrdbmslandjab17-170530074611/75/The-rise-of-json-in-rdbms-land-jab17-41-2048.jpg)
![Generated columns
Virtual (default)
✘will be calculated on the fly when a
record is read from a table
✘secondary indexes
✘No space
Stored
✘ will be calculated when a new
record is written in the table
✘indexing unique keys
✘Space required
column_name data_type [GENERATED ALWAYS] AS (expression)
[VIRTUAL | STORED] [UNIQUE [KEY]]
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theriseofjsoninrdbmslandjab17-170530074611/75/The-rise-of-json-in-rdbms-land-jab17-42-2048.jpg)