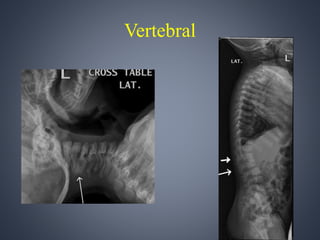
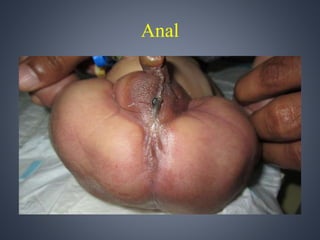
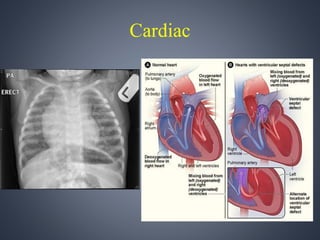
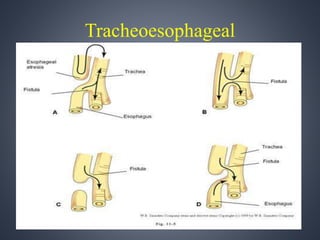
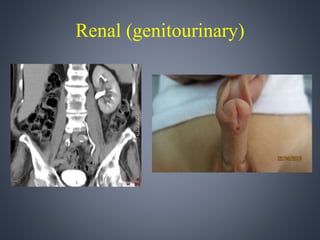
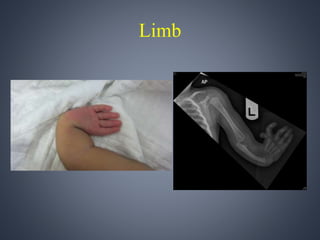
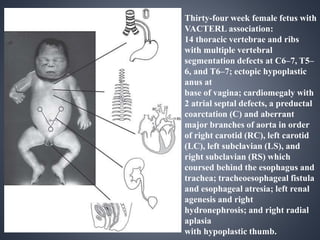
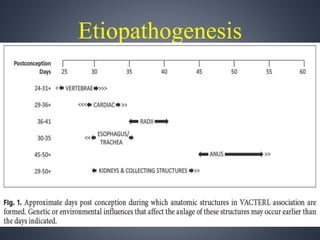
Vacterl association is a non-random grouping of birth defects that includes vertebral anomalies, anal atresia, cardiac defects, tracheo-esophageal fistula with or without esophageal atresia, and renal and limb abnormalities. It is considered an association because the defects do not have a predictable pattern and the underlying etiology is unknown. Proposed causes include abnormal segmentation of the vertebrae, effects of teratogenic agents, malformation sequences initiated by vertebral defects, and disturbances in fundamental embryological processes of mesoderm development and migration. Diagnosis requires at least three components of the association to be present.






![Theories
• Abnormal or asymmetric timing of a molecular
oscillator termed the segmentation clock has
been shown to result in malsegmentation of the
vertebrae [Pourquié and Kusumi, 2001; Oates
et al., 2012].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vacterlassociation-140904100843-phpapp02/85/Vacterl-association-embryology-and-recognition-15-320.jpg)
![• Environmental agents such as Thalidomide (in
humans) [Knapp et al., 1962; Quibell, 1981;
Lenz, 1988] and Adriamycin (inrats) [Beasley
et al., 2000] can produce malformations
similar to VACTERL.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vacterlassociation-140904100843-phpapp02/85/Vacterl-association-embryology-and-recognition-16-320.jpg)





