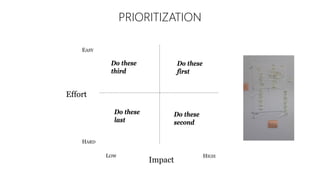
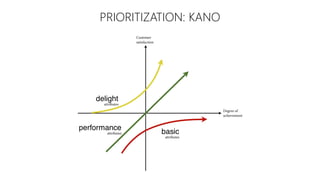
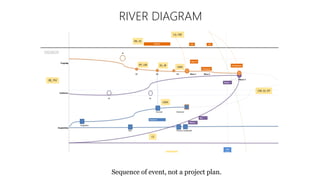
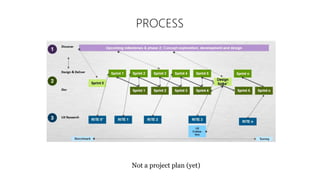
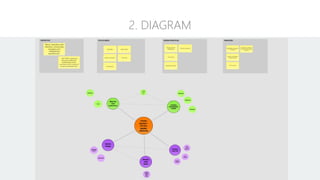
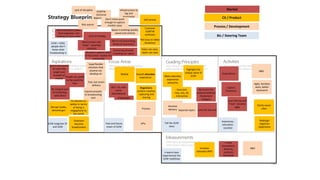
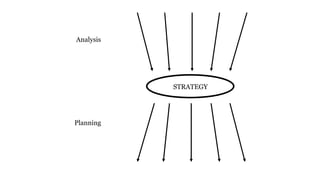
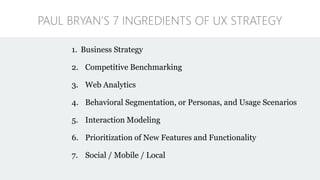
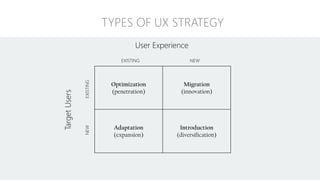
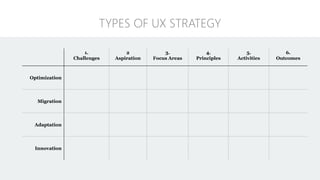
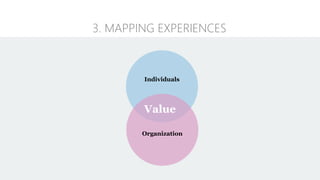
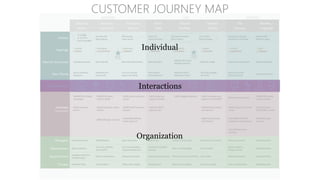
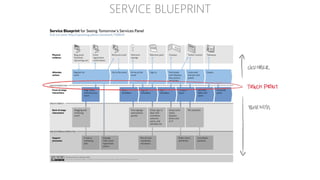
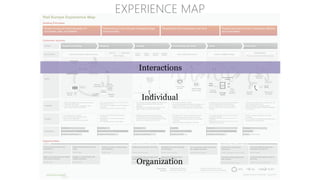
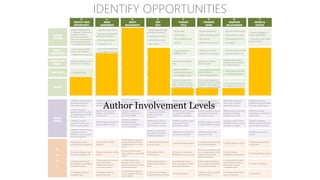
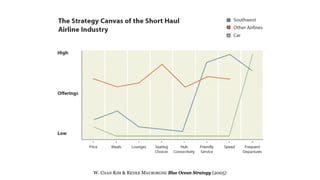
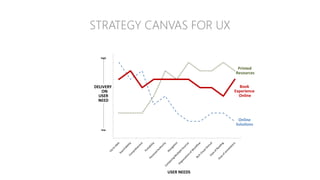
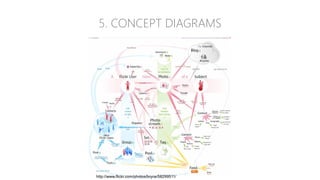
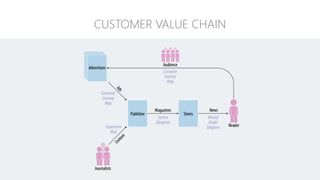
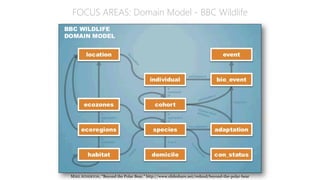
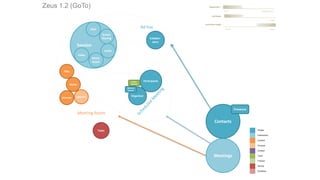
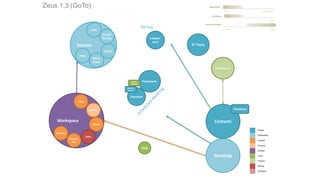
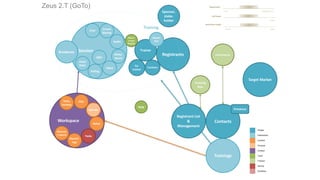
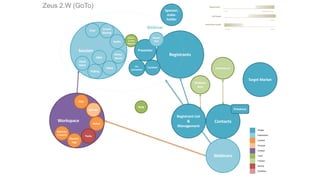
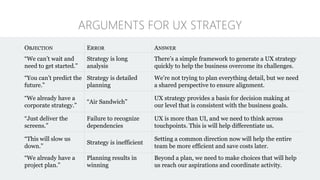
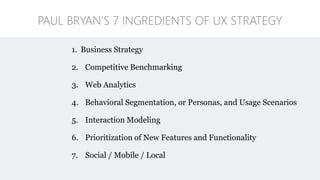
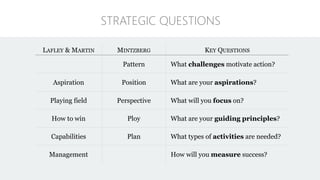
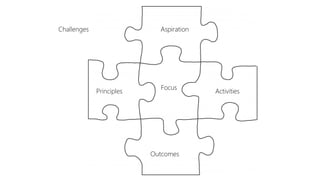
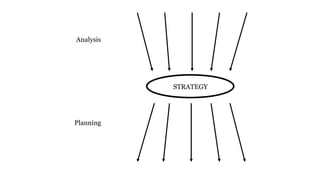
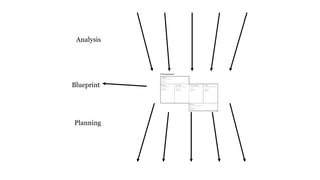
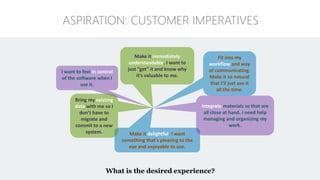
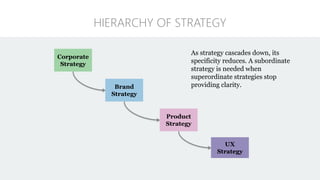
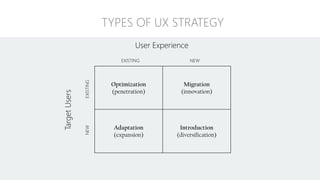
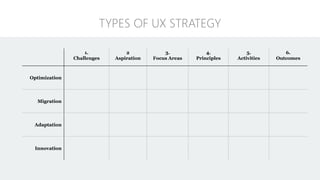
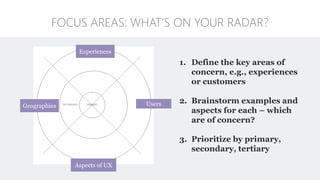
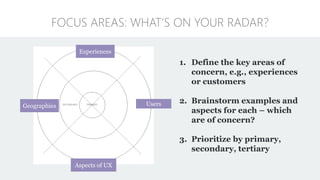
The document discusses UX strategy and provides examples of strategic analysis activities, elements of an effective strategy, and ways to communicate strategy. It emphasizes that UX strategy helps solve business problems through coordinated UX choices to achieve a desired experience. Key elements include analyzing challenges and aspirations, defining focus areas and guiding principles, planning activities and desired outcomes. Facilitating strategic conversations, diagramming insights, documenting the strategy, and illustrating the story are important for communication.










































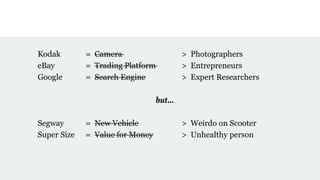
![[EASTMAN] recognized that his roll film could lead to a
revolution if he focused on the experience he wanted to
deliver, an experience captured in his advertising slogan,
“You press the button, we do the rest.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxstrategyuxlx-jkalbach-170527154439/85/UX-Strategy-Blueprint-59-320.jpg)