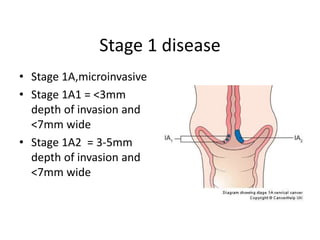
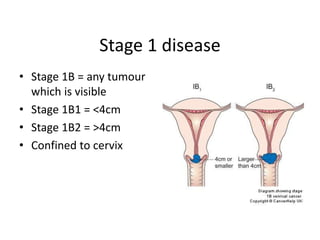
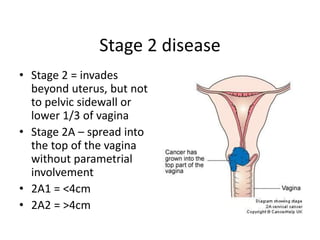
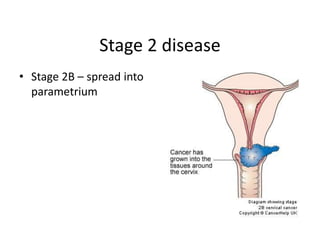
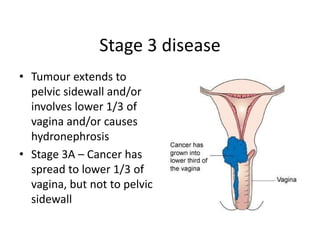
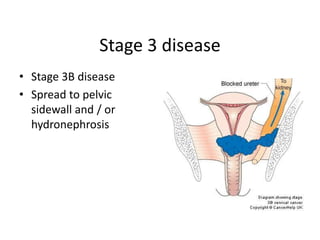
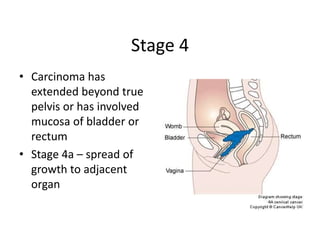
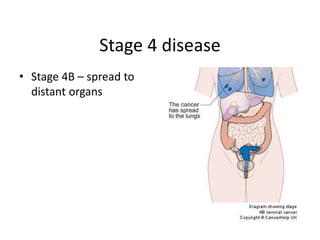
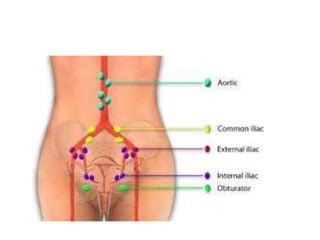
Cervical cancer is caused by HPV infection and is the leading cause of cancer deaths in many developing countries. HPV is present in over 99% of cervical cancers. Risk factors include young age of first sexual activity, multiple partners, early pregnancy, and smoking. Precancerous lesions usually develop over 10-15 years. Cervical cancer spreads locally through the cervix and vagina, and can metastasize to nearby lymph nodes and distant sites like the lungs and liver. Diagnosis involves identifying dysplastic cervical cells, and treatment depends on the cancer stage.



























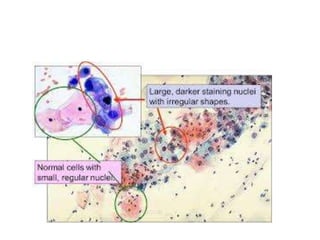
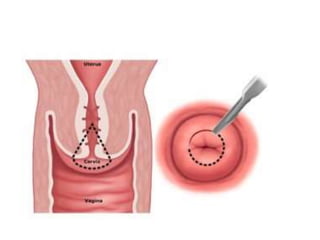
![Pap smear[Papanicolaou Testing]
• For many years, the Pap test has been the standard method
for cervical cancer screening.
• Screening programme has proved successful in reducing the
incidence of invasive cancer by 80% and mortality by 60% in
developed countries.
• Accurate calculation of false-negative rates for the Pap test is
difficult; estimates range from less than 5% to 20% or more
• False-negative tests mostly result from sampling error, which
can be reduced by ensuring that adequate material is taken
from both the endocervical canal and the ectocervix. Smears
without endocervical or metaplastic cells should be repeated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cervix-cancer-171212163444/85/Cervix-cancer-32-320.jpg)