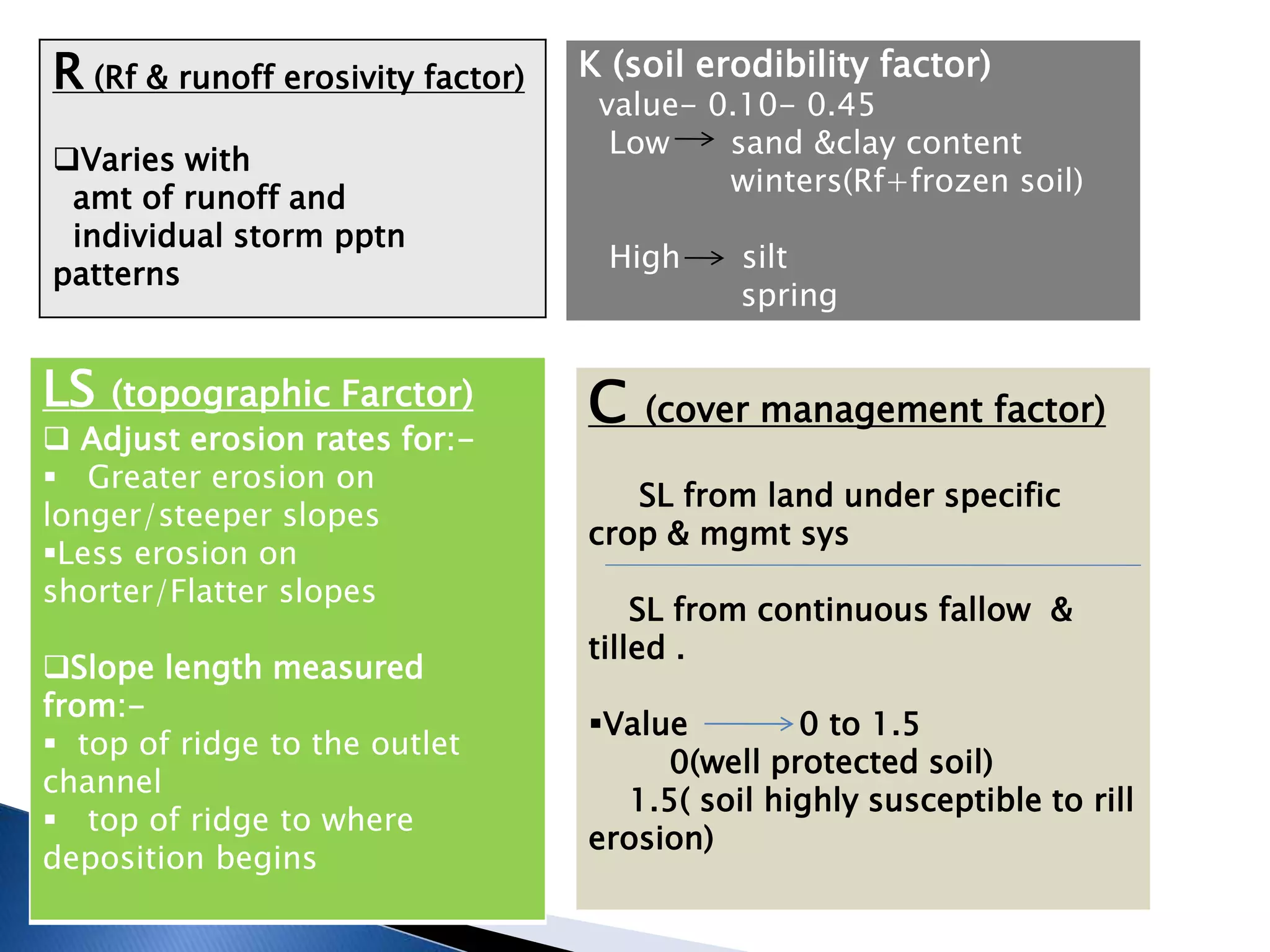
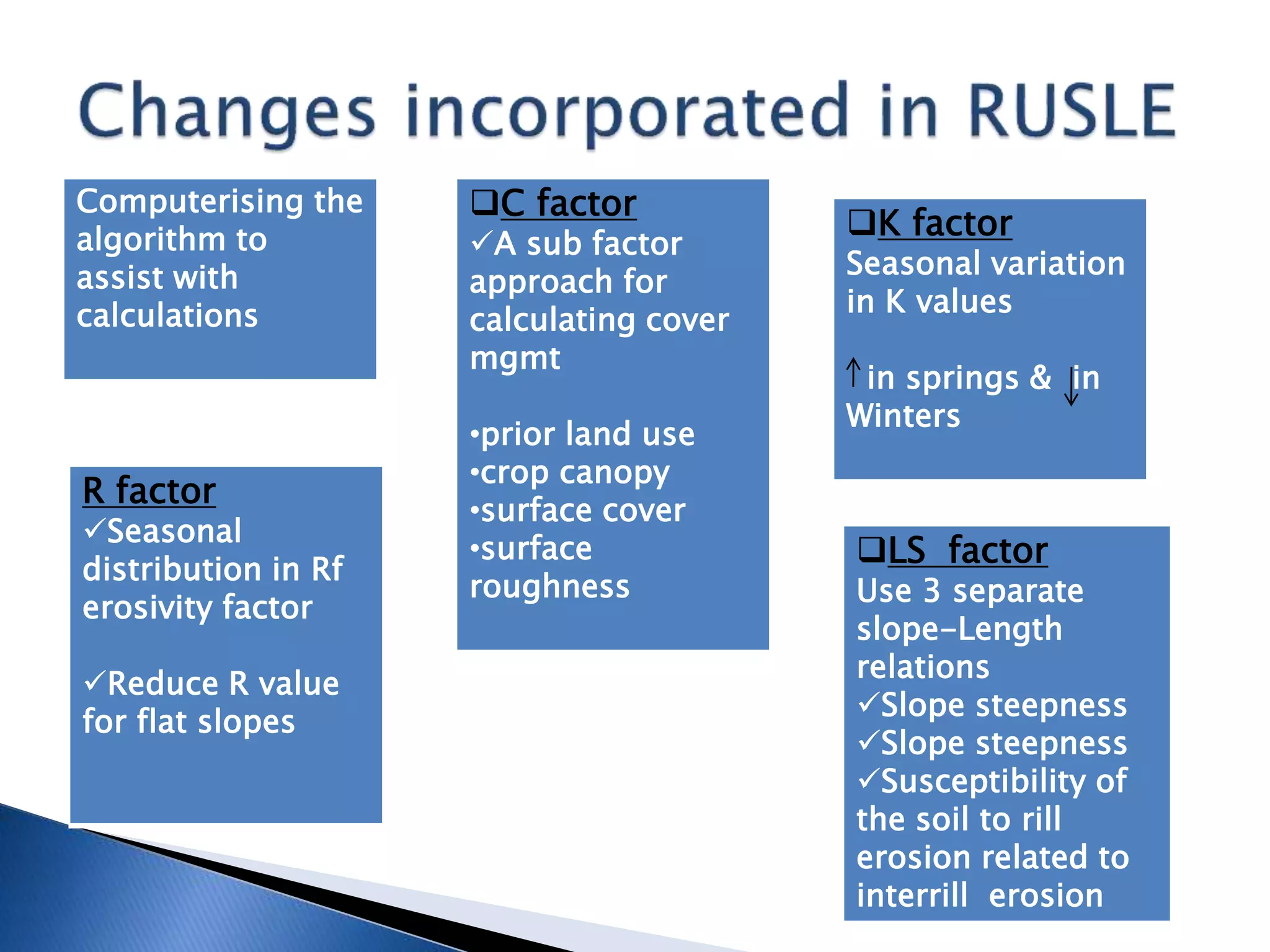
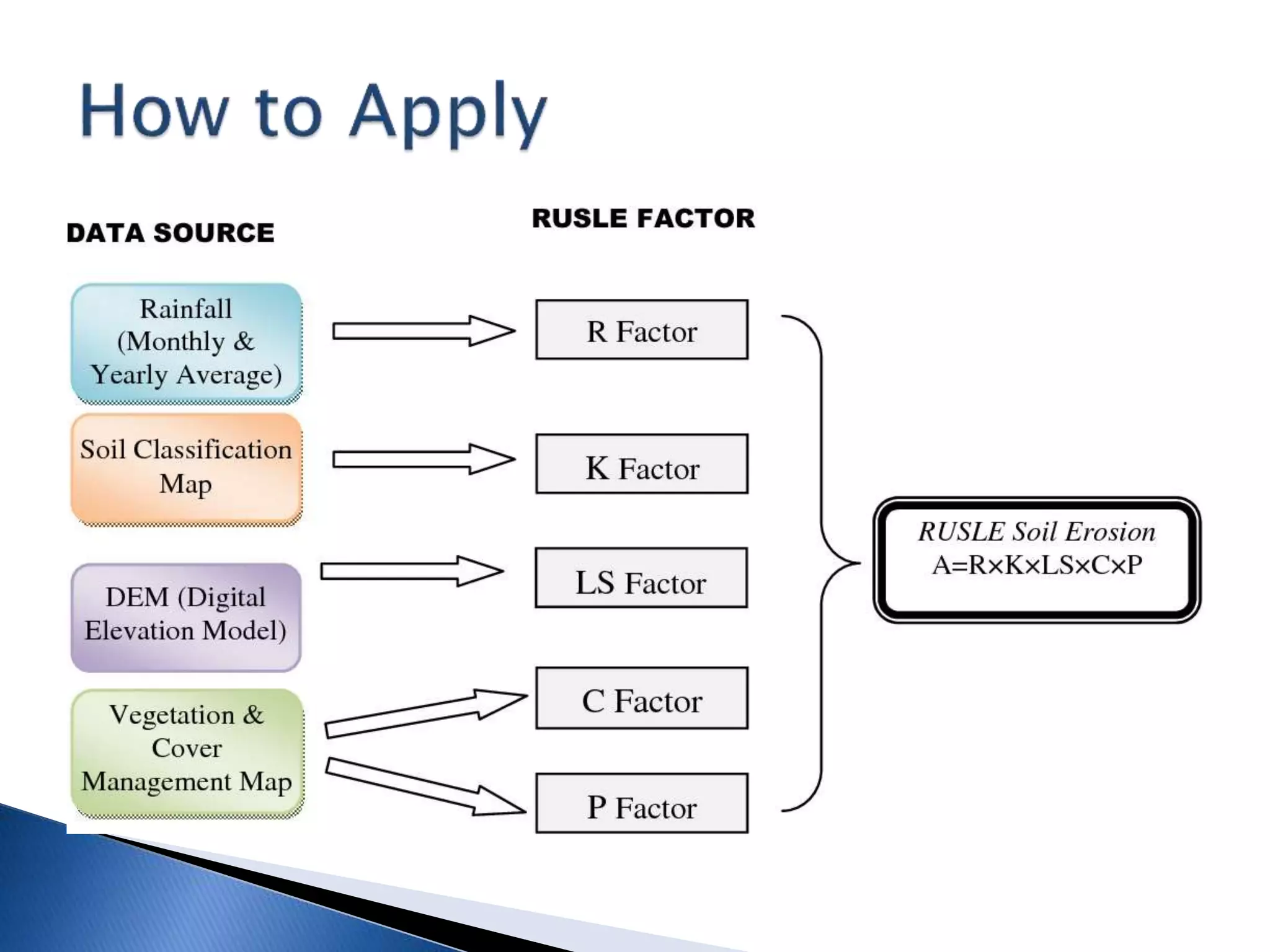
The document summarizes the empirical USLE and RUSLE models for predicting long-term soil loss on fields. The USLE model, developed in 1978, estimates soil erosion based on 5 factors: rainfall erosivity, soil erodibility, slope length and steepness, cover management, and conservation practices. The RUSLE revision in 1992 incorporated new research using computers and GIS to update factors and the calculation algorithm. Both models assist with soil conservation planning but have limitations as they only estimate rill and sheet erosion, not deposition or gully erosion.