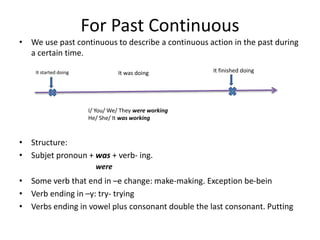
- The document provides rules for forming simple past tense, past continuous tense, and comparative adjectives in English.
- For simple past tense, regular verbs add "-ed" and irregular verbs have unique forms; past continuous uses "was/were + verb+ing" to describe ongoing actions.
- Comparative adjectives are formed by adding "-er" for one-syllable adjectives or "more" for multi-syllable adjectives, with some irregular forms like "good-better" and "bad-worse."