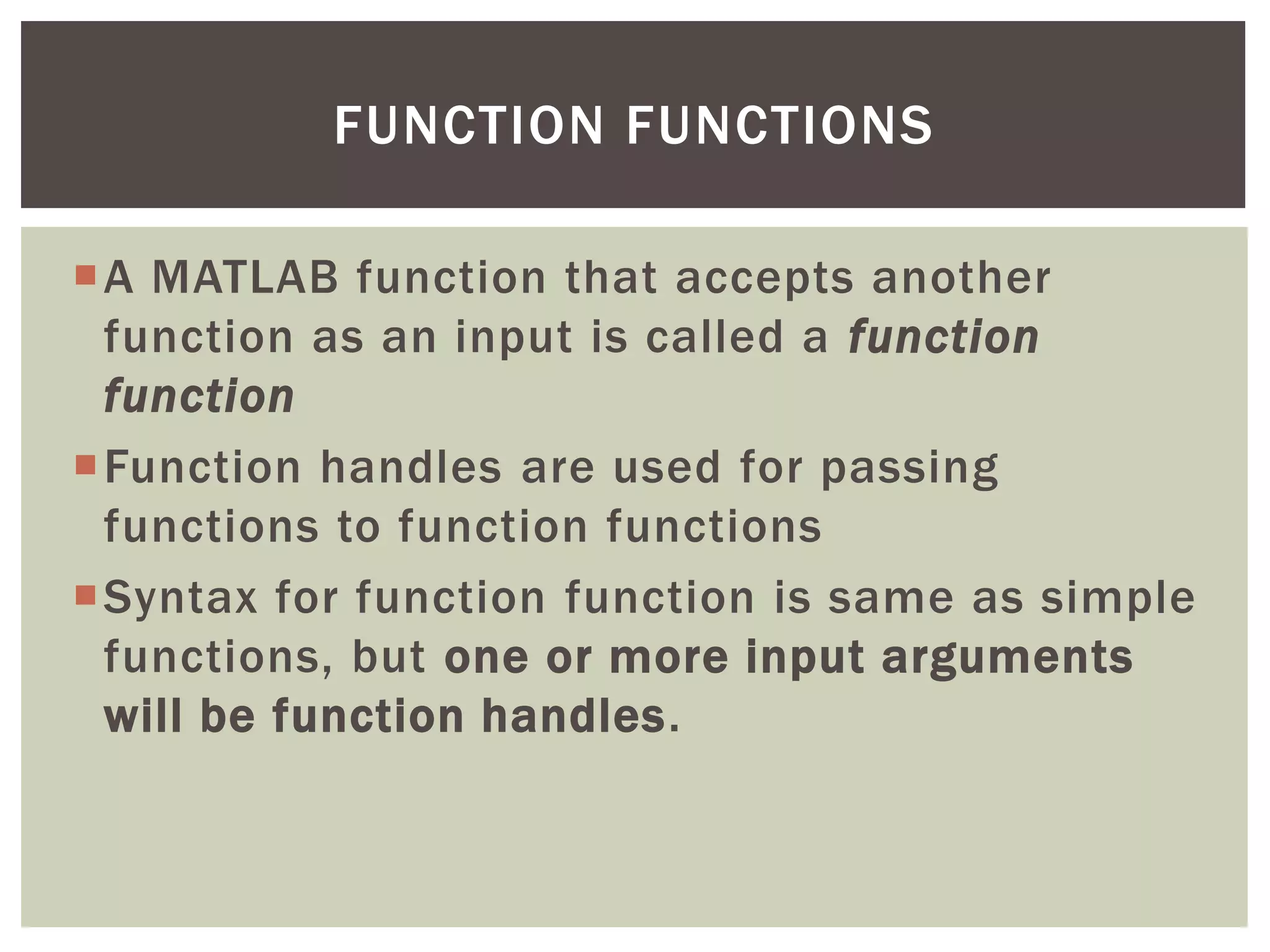
The document explains the concept of function handles in MATLAB, which are data types that store associations with functions, allowing indirect calls to both built-in and user-defined functions. It discusses various uses, such as passing functions to other functions, callback functions in GUI programming, and creating anonymous functions. Additionally, it covers local and private functions, emphasizing their visibility and scope within the code structure.





![function [a, b, c] = basicmath(x, y)
% basicmath is the main function.
a = add(x,y);
b = sub(x,y);
c = mult(x,y);
end
function l = add(u,v)
% add is a local function.
l = u+v;
end
function m = sub(u,v)
% sub is another local function.
m = u-v;
end
function n = mult(u,v)
% sub is another local function.
n = u*v;
end
EXAMPLE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/userdefinedfunctionsinmatlabpart4-170115122908/75/User-Defined-Functions-in-MATLAB-Part-4-8-2048.jpg)
