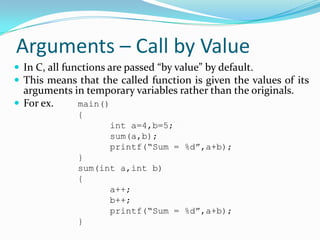
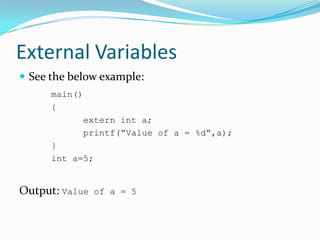
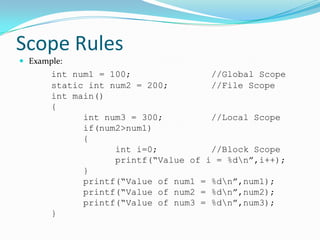
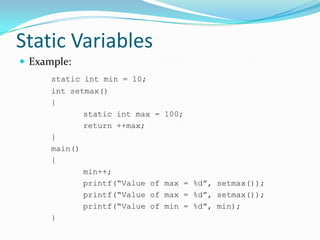
Functions are blocks of code that perform tasks in C programs. A function takes input, processes it, and returns a value. Functions must be declared with prototypes before use. Function definitions specify the return type, name, arguments, and body. Arguments are passed by value by default, but can be passed by reference using pointers. Recursion is when a function calls itself. External and static variables define scopes beyond the local function block.