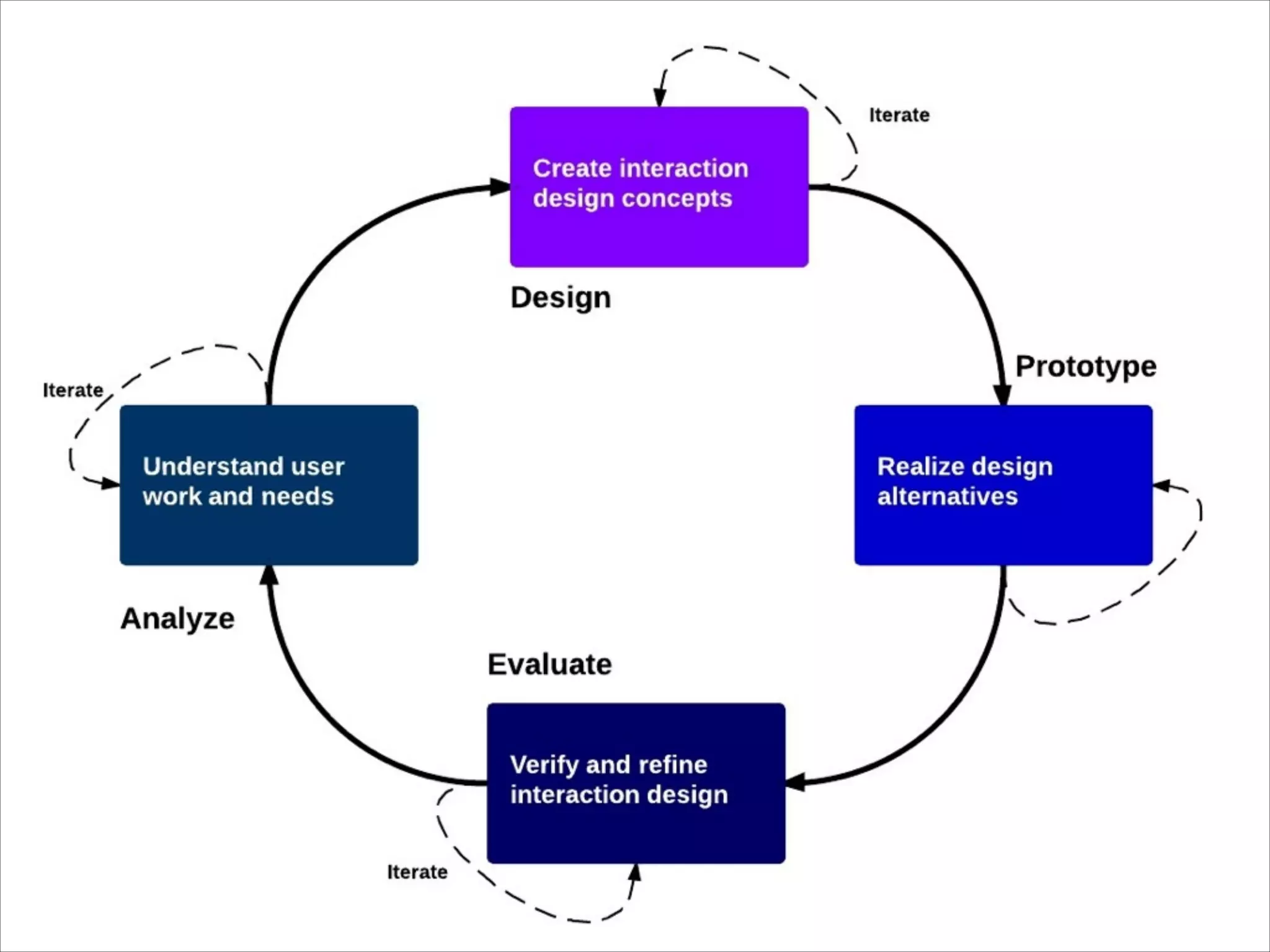
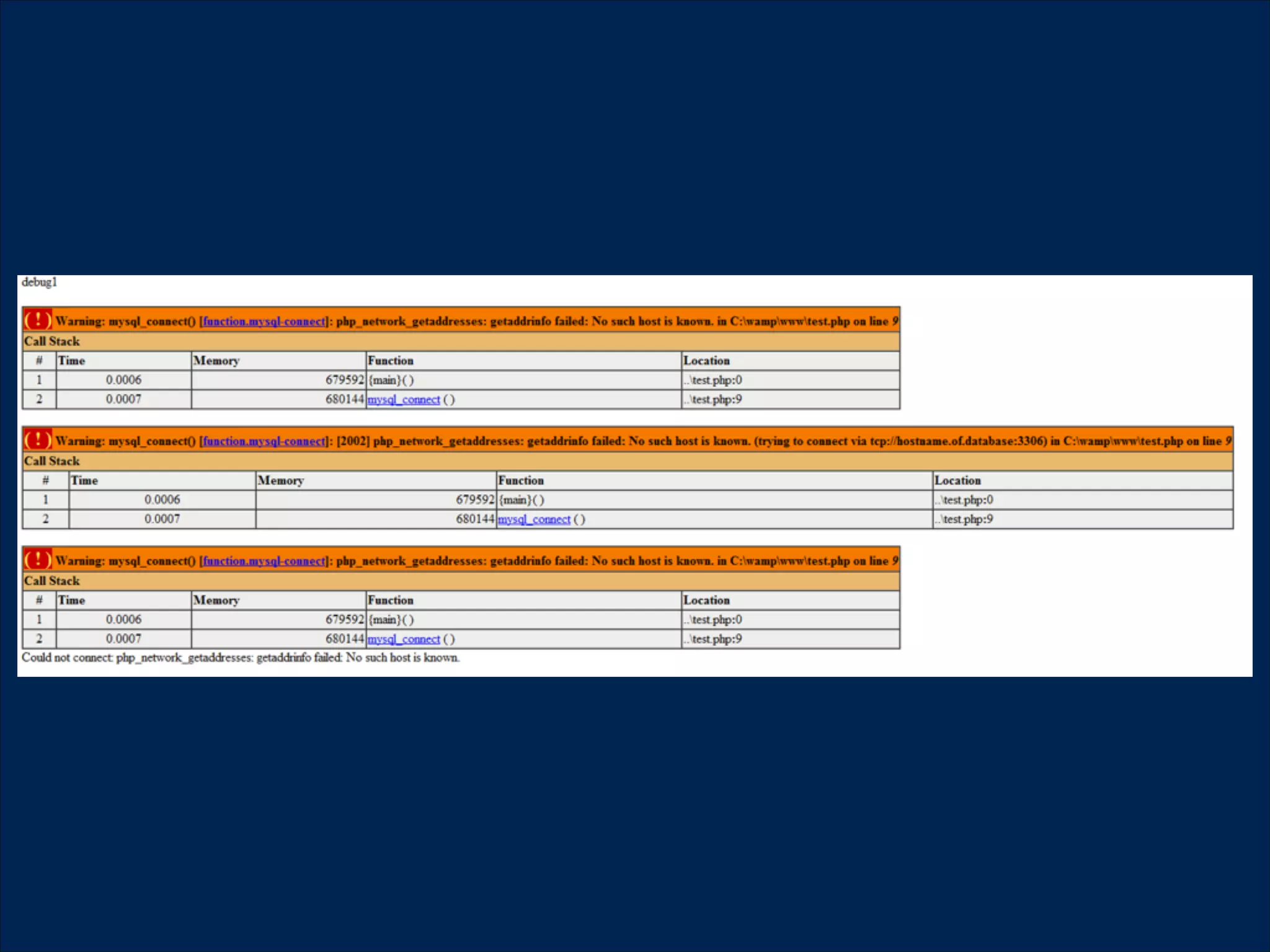
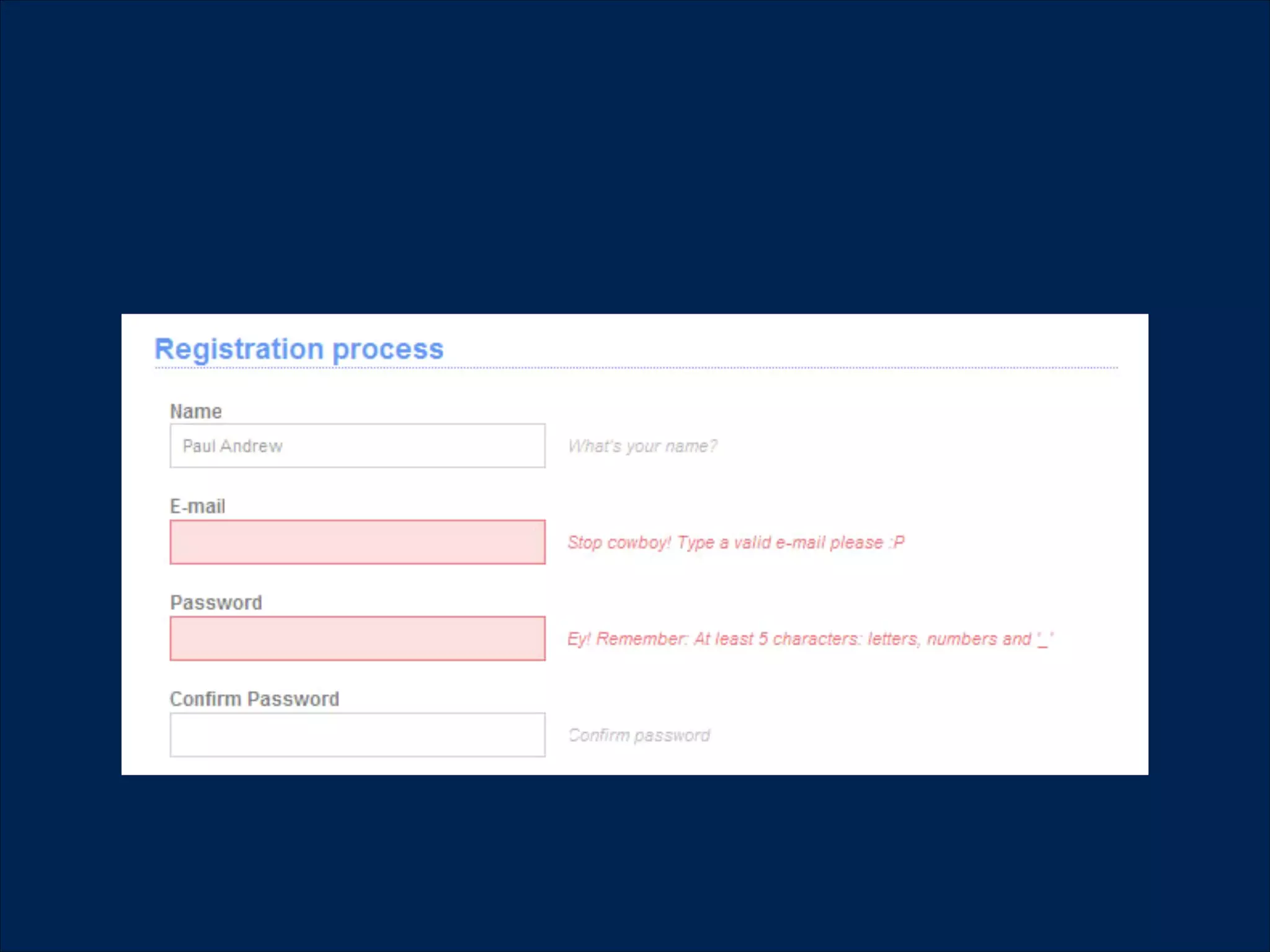
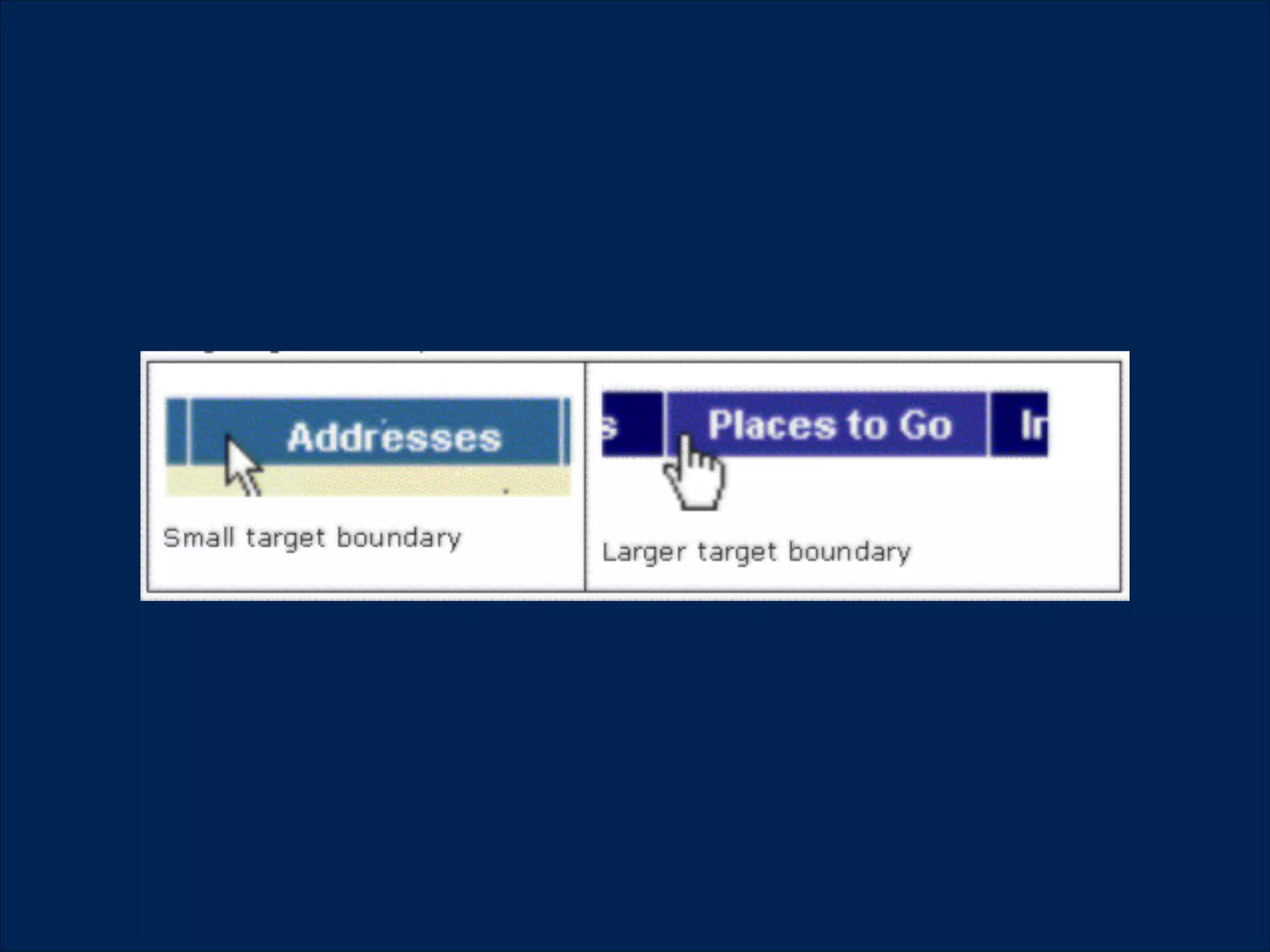
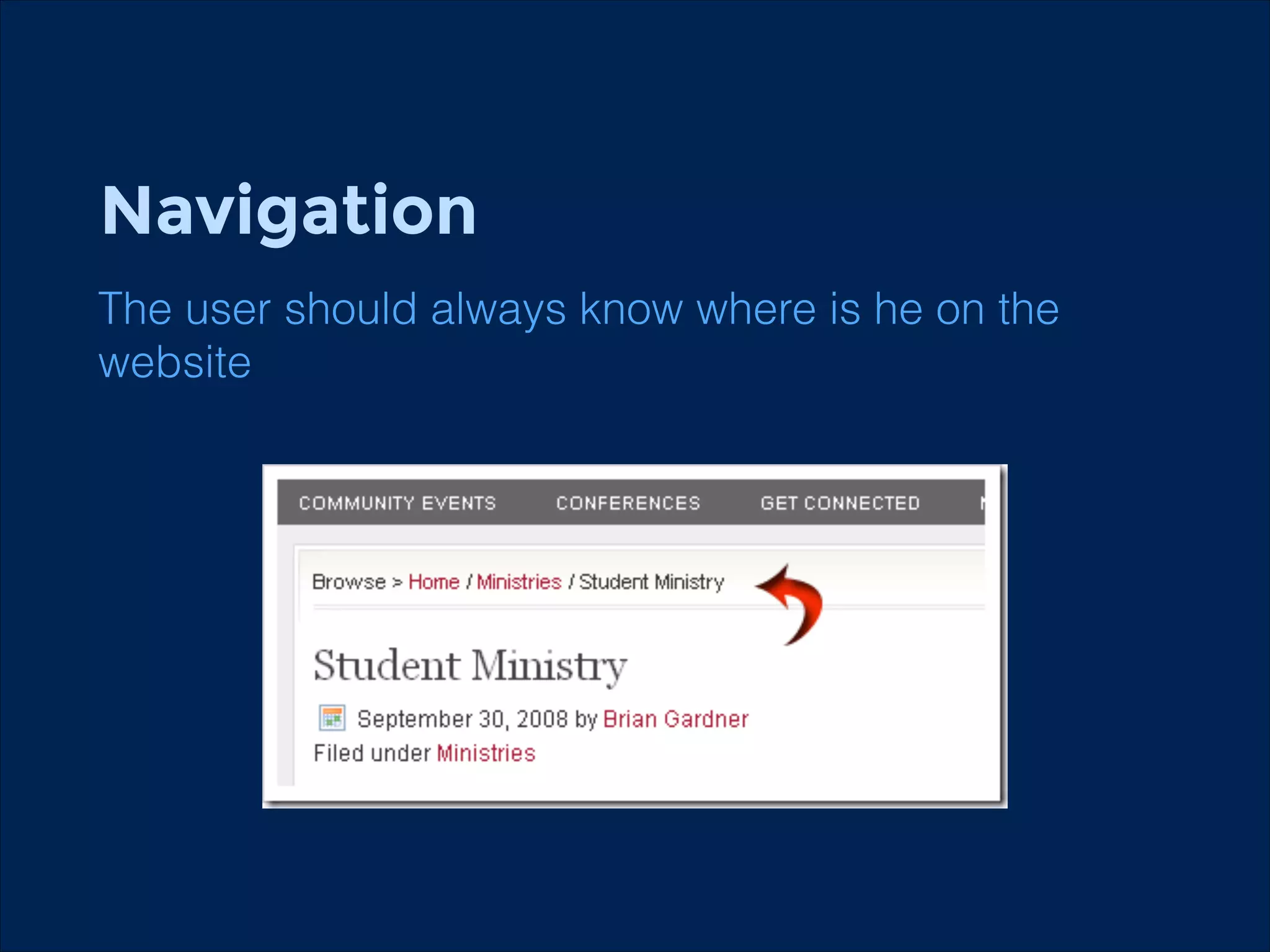
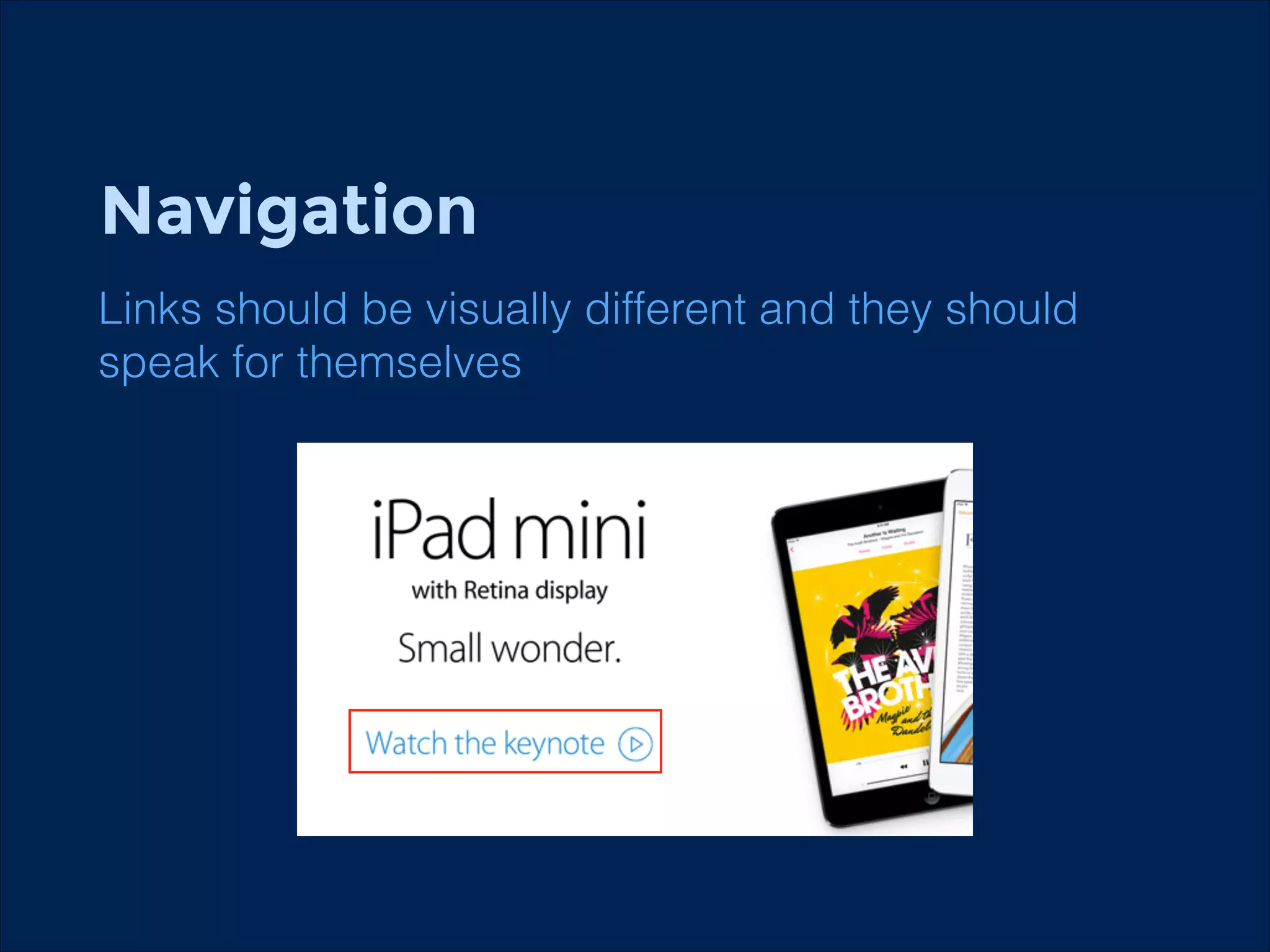
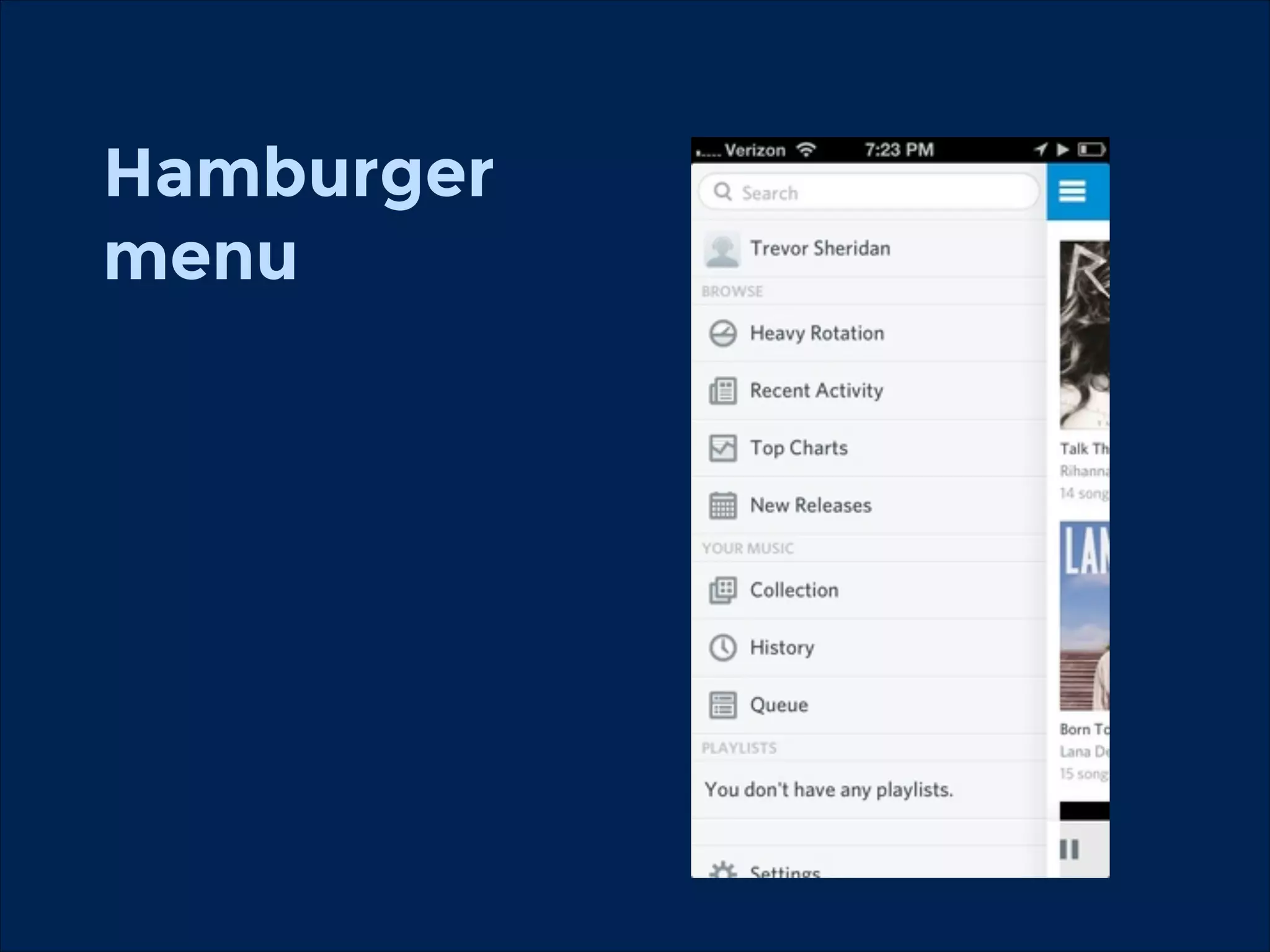
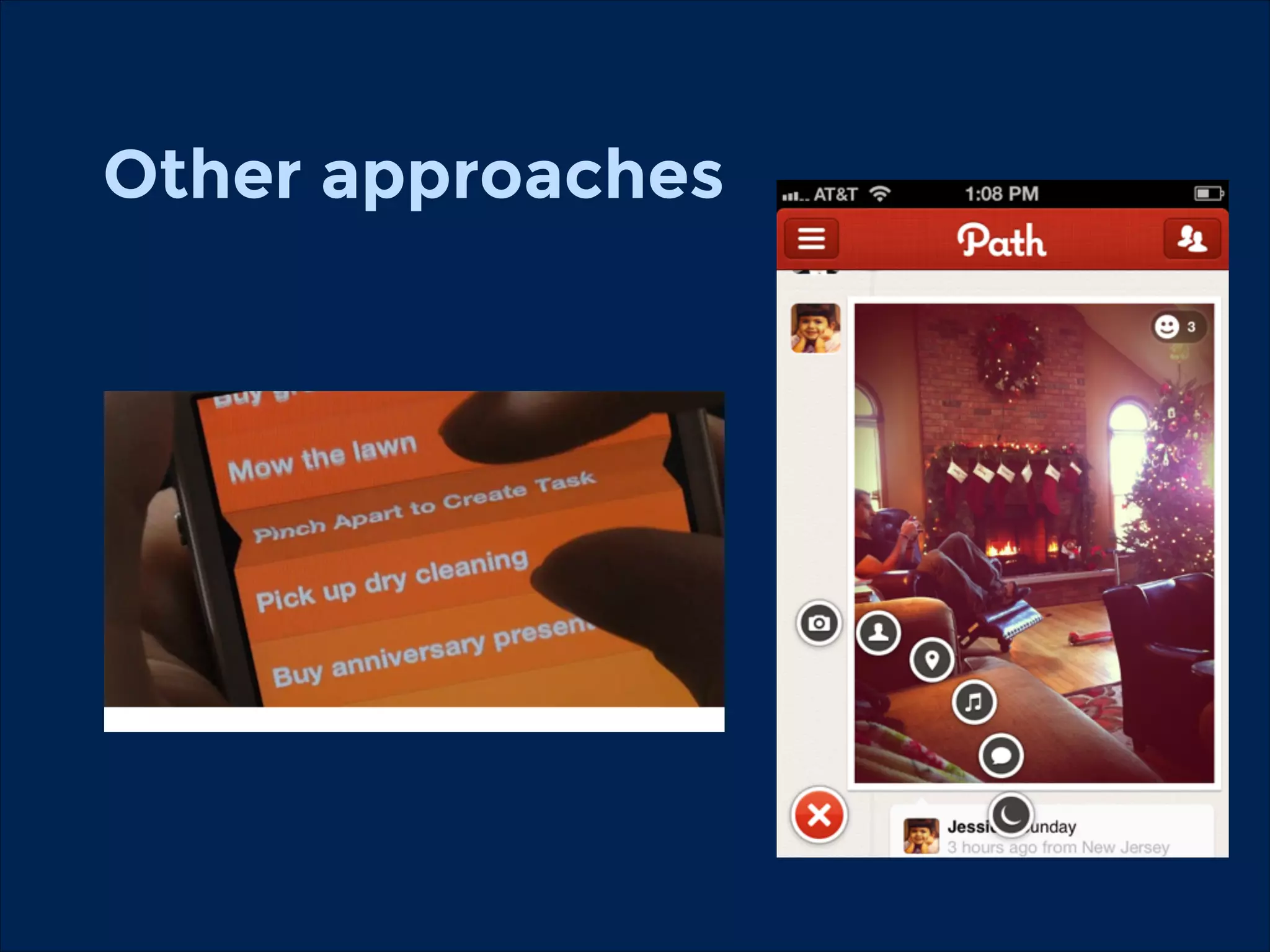
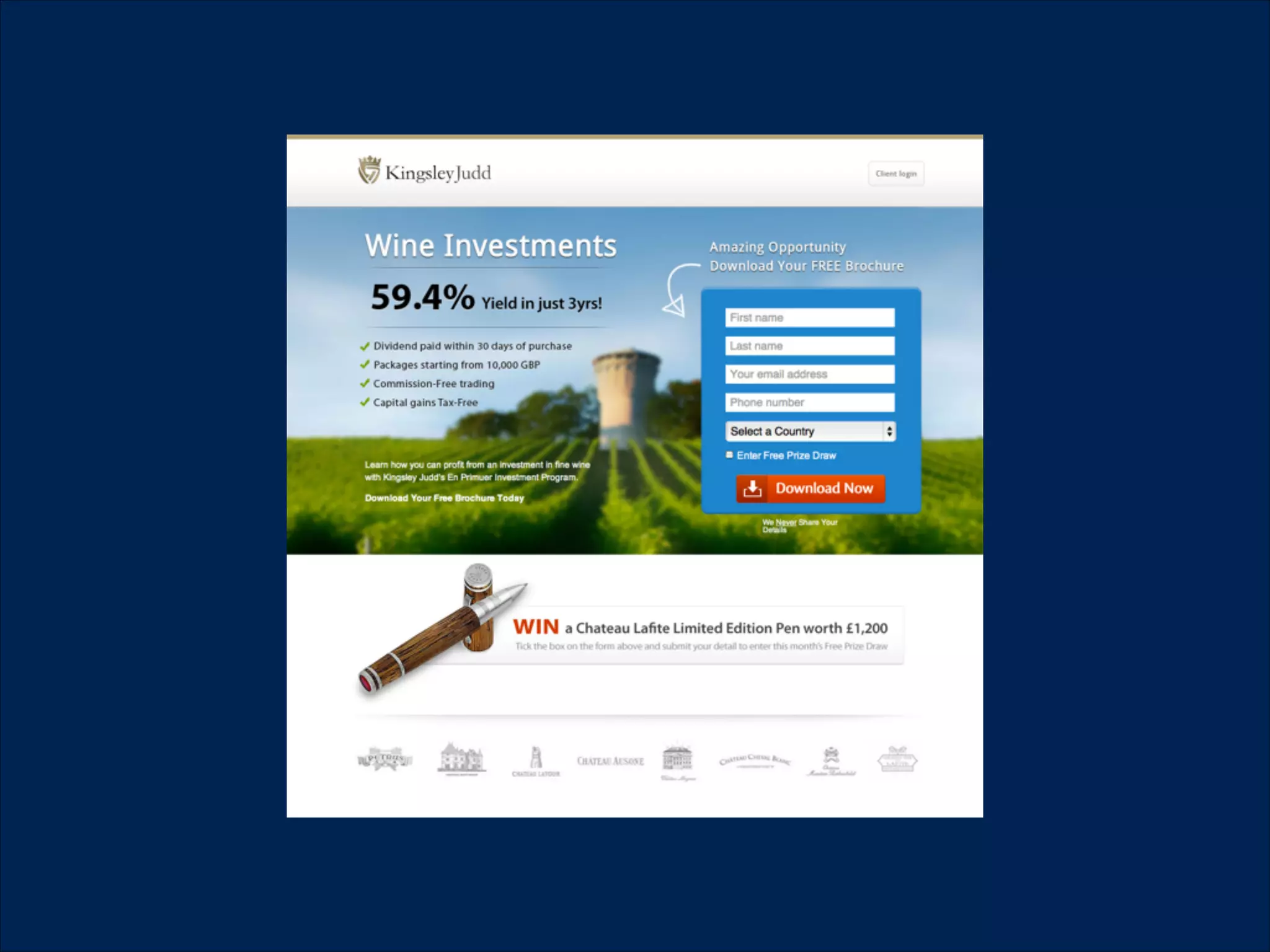
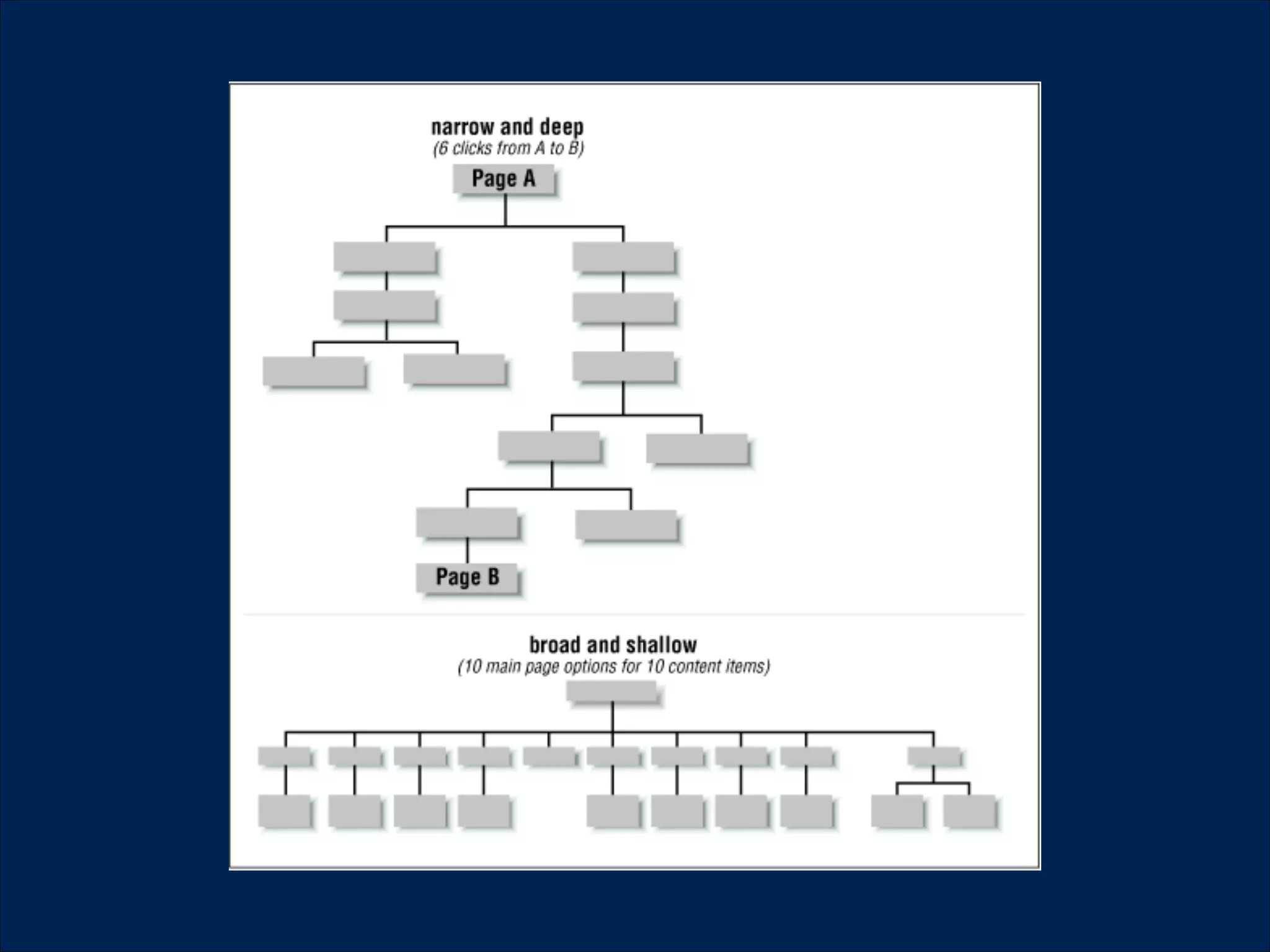
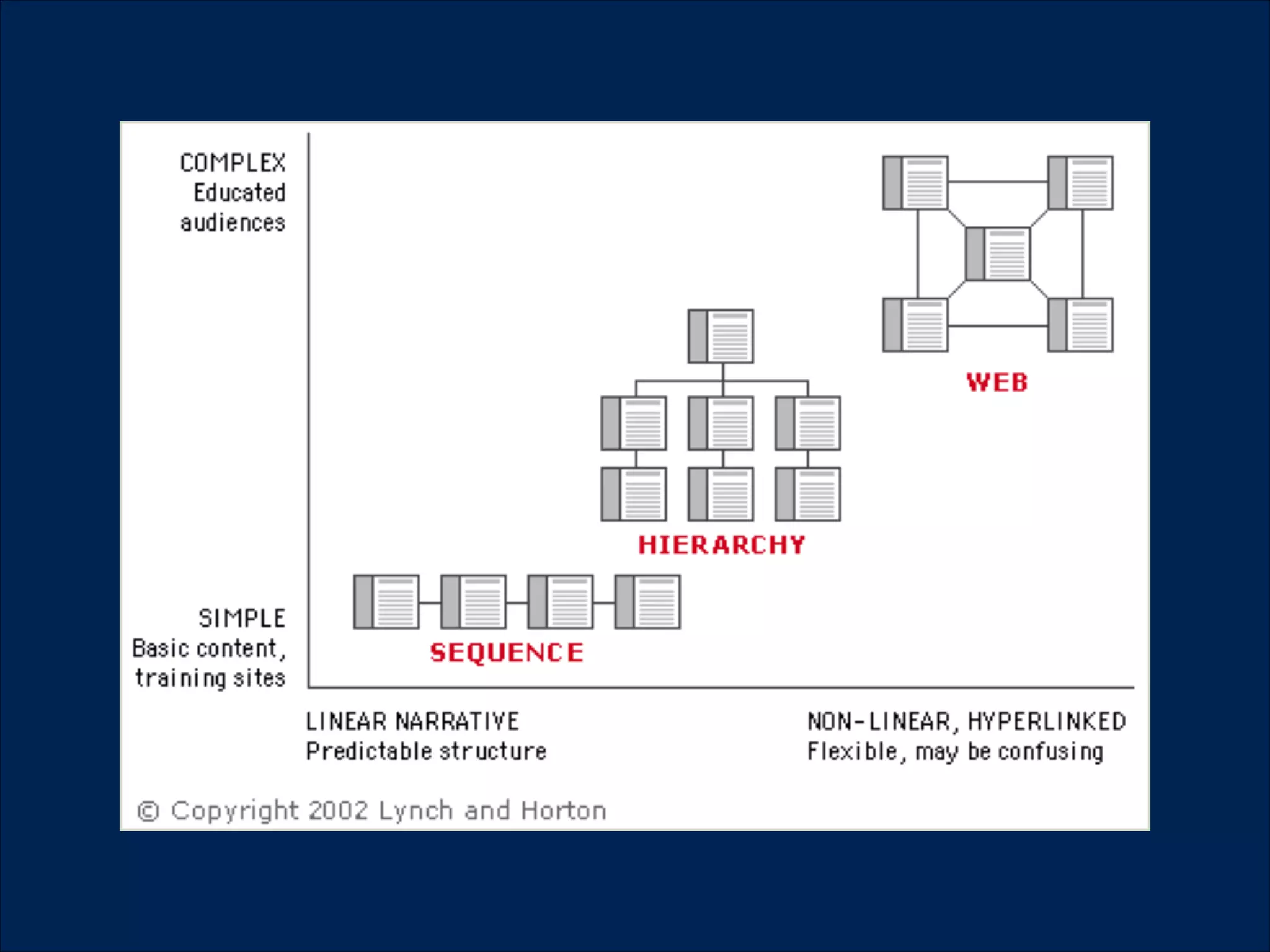
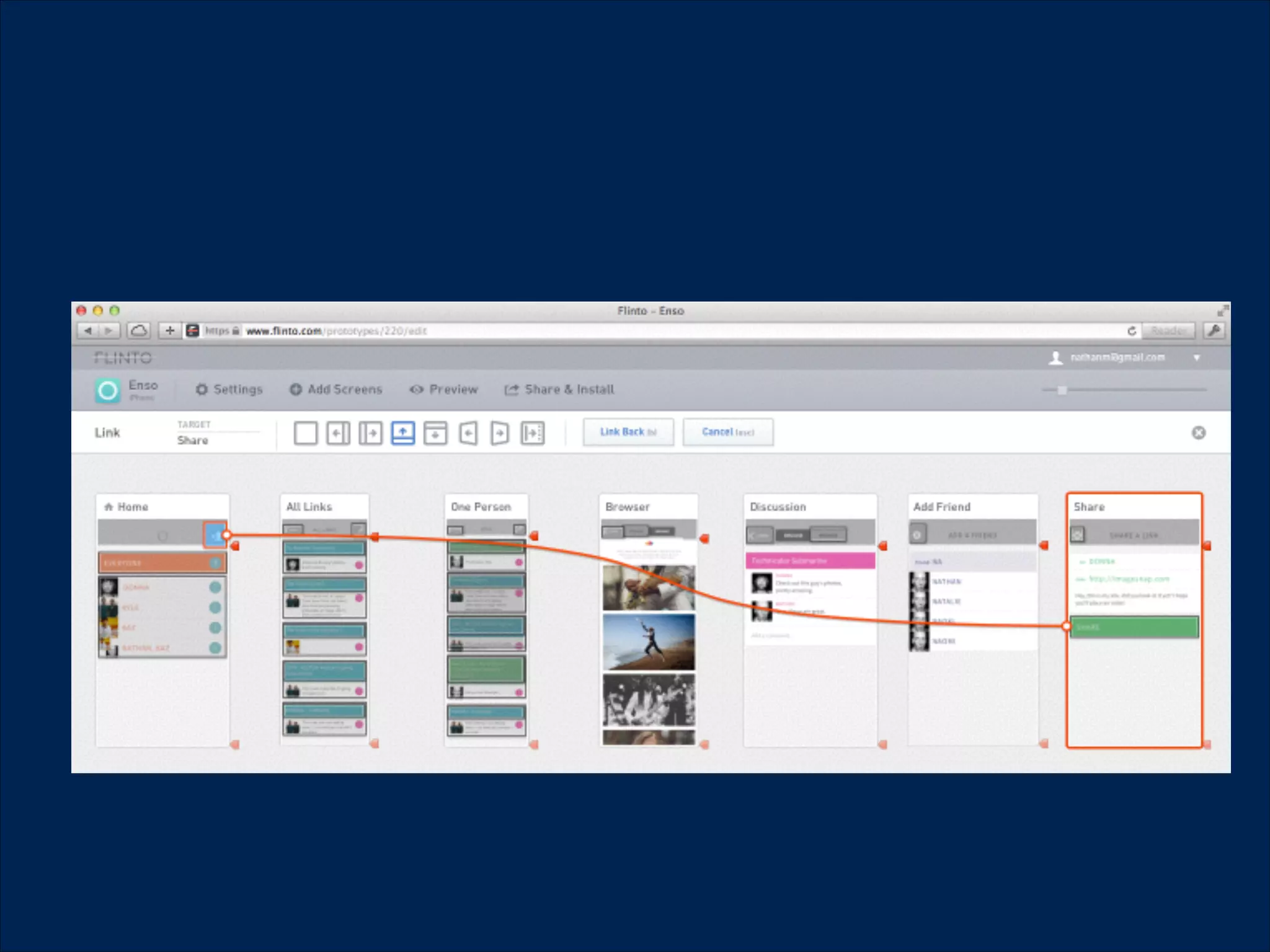
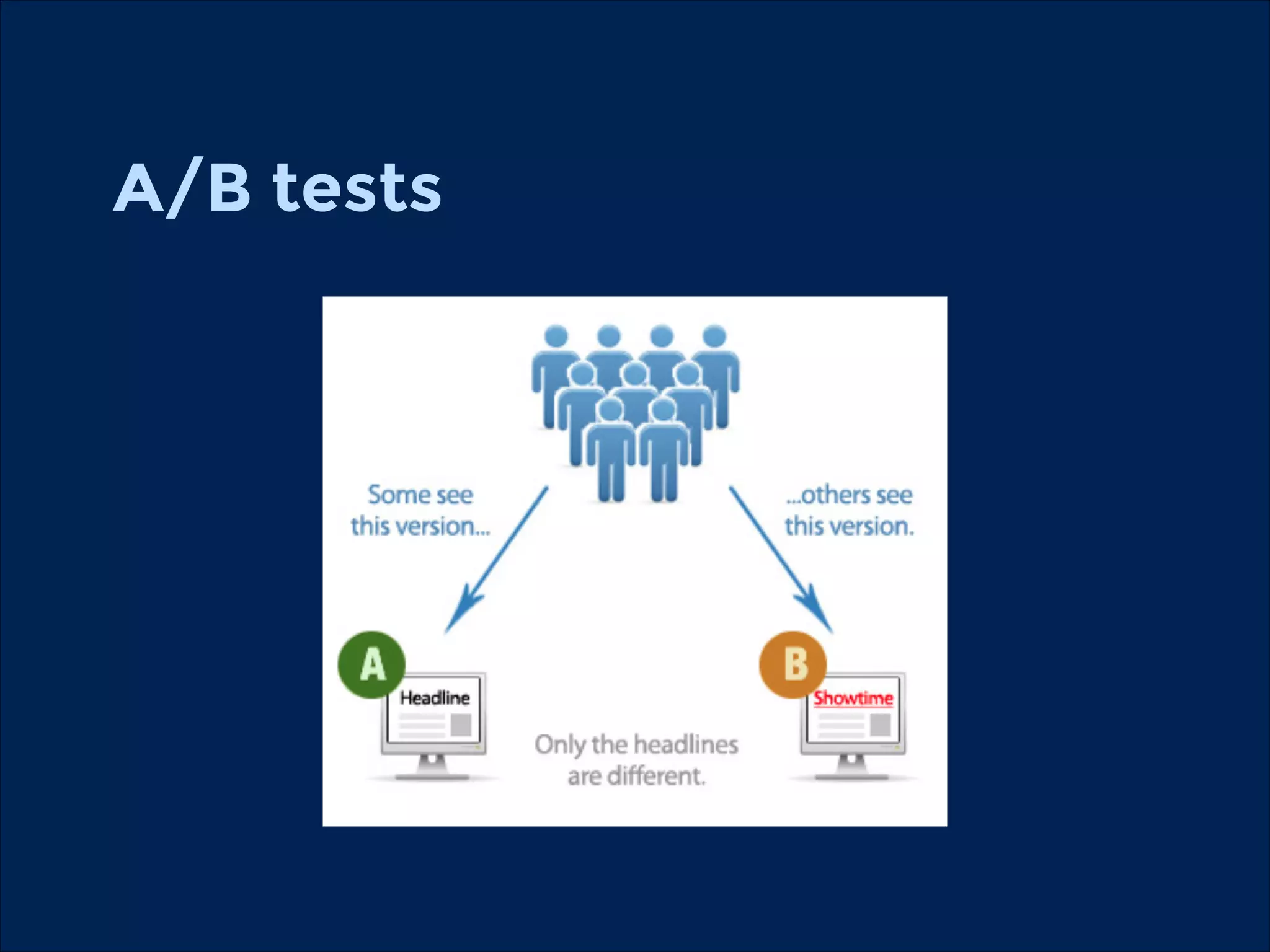
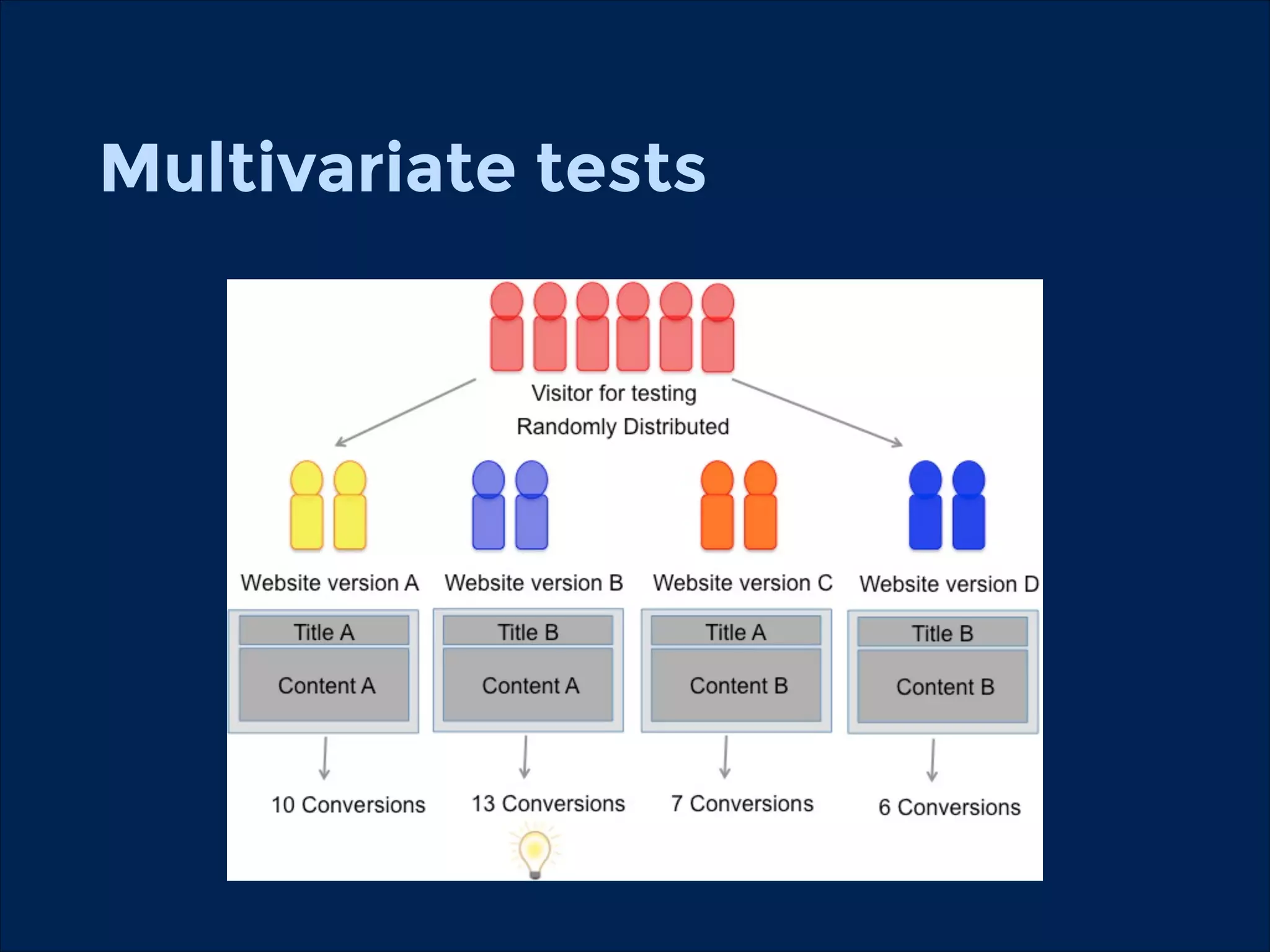
The document summarizes key points about usability workshops and testing. It defines usability and discusses its importance. Usability is defined as how easy user interfaces are to use based on factors like learnability, efficiency and satisfaction. The document outlines usability testing methods like card sorting, prototyping and A/B testing. It emphasizes the need to test assumptions and iteratively improve products based on user research.