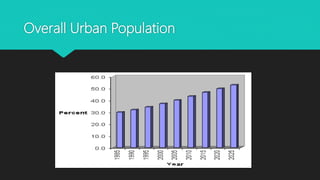
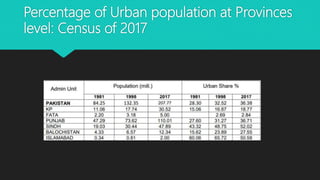
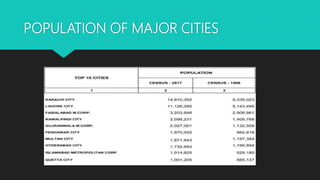
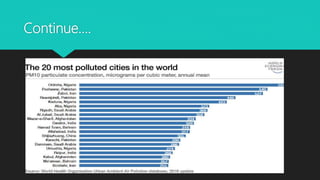
Urbanization refers to the increasing proportion of people living in cities and urban areas. It is closely connected to industrialization. The document discusses the causes and effects of urbanization in Pakistan. The major causes include population growth, migration for jobs and services, and economic opportunities in cities. Effects include issues like unemployment, housing shortages, pollution, and disease. To address problems, the document recommends strengthening rural economies to reduce migration, improving public transport, providing jobs, and sustainable urban development.