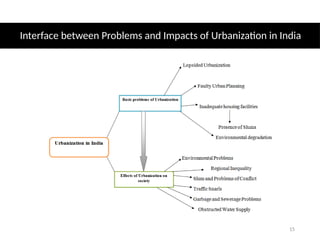
The document discusses urbanization, defining it as the movement of populations from rural to urban areas driven by factors such as economic opportunities, industrialization, education, and social services. It addresses both positive impacts, including economic growth and improved living standards, and negative impacts like pollution and increased crime rates. The necessity for proper planning to mitigate adverse effects while maximizing urbanization benefits is emphasized.