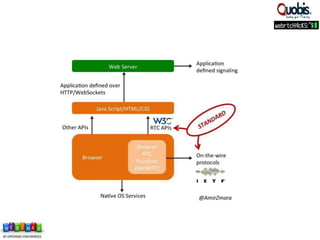
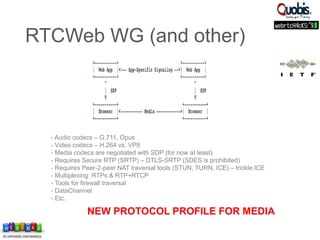
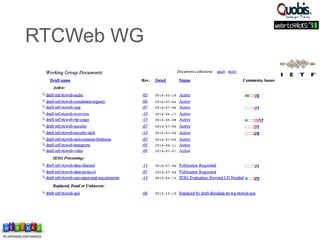
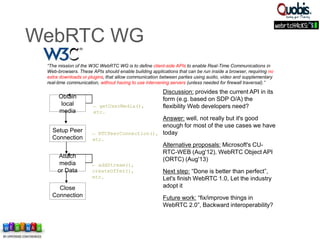
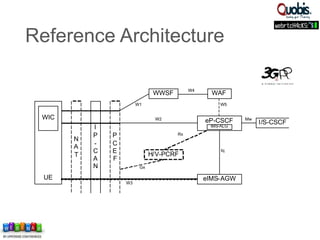
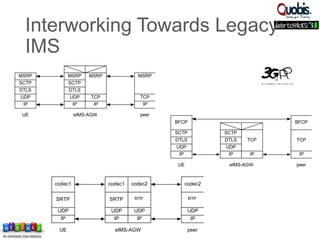
The document discusses updates on WebRTC standards as of July 2014, highlighting the technology's capabilities such as real-time voice, video, and data communication without requiring plugins. It outlines the challenges of signaling, codec selection, and interoperability with legacy VoIP systems, emphasizing that various proprietary signaling mechanisms are being implemented across different vendors. Future work is focused on finalizing WebRTC 1.0, improving aspects in WebRTC 2.0, and ensuring backward interoperability.