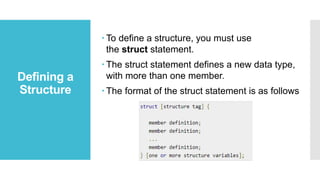
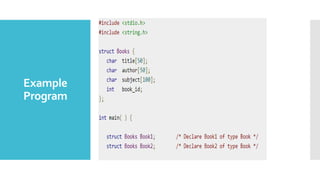
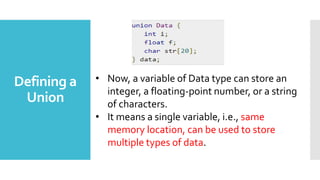
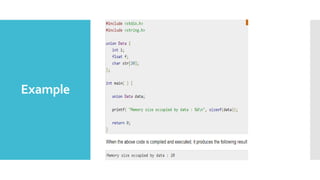
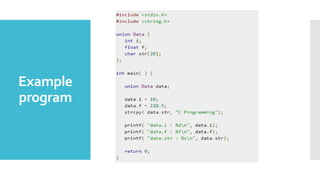
Structures and unions are user-defined data types in C that allow combining data of different types. Structures store different data types together under one name while unions share the same memory location for multiple data types. Structures are useful for storing related data together but take more memory, while unions are more memory efficient but can only access one member at a time. Both allow grouping data for easier handling and passing to functions.