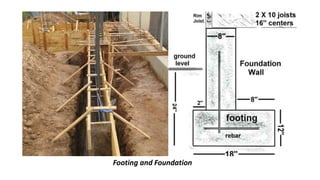
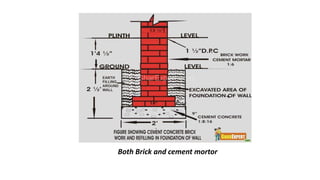
The document discusses various building materials essential for construction, emphasizing the significance of sand, bricks, stones, and concrete in structure integrity. It also covers specific materials like lime, cement, and different roofing options, highlighting their properties, advantages, and uses in building design. Additionally, it outlines floor design considerations, including solid and deep litter floors, to promote hygiene and durability in animal housing.