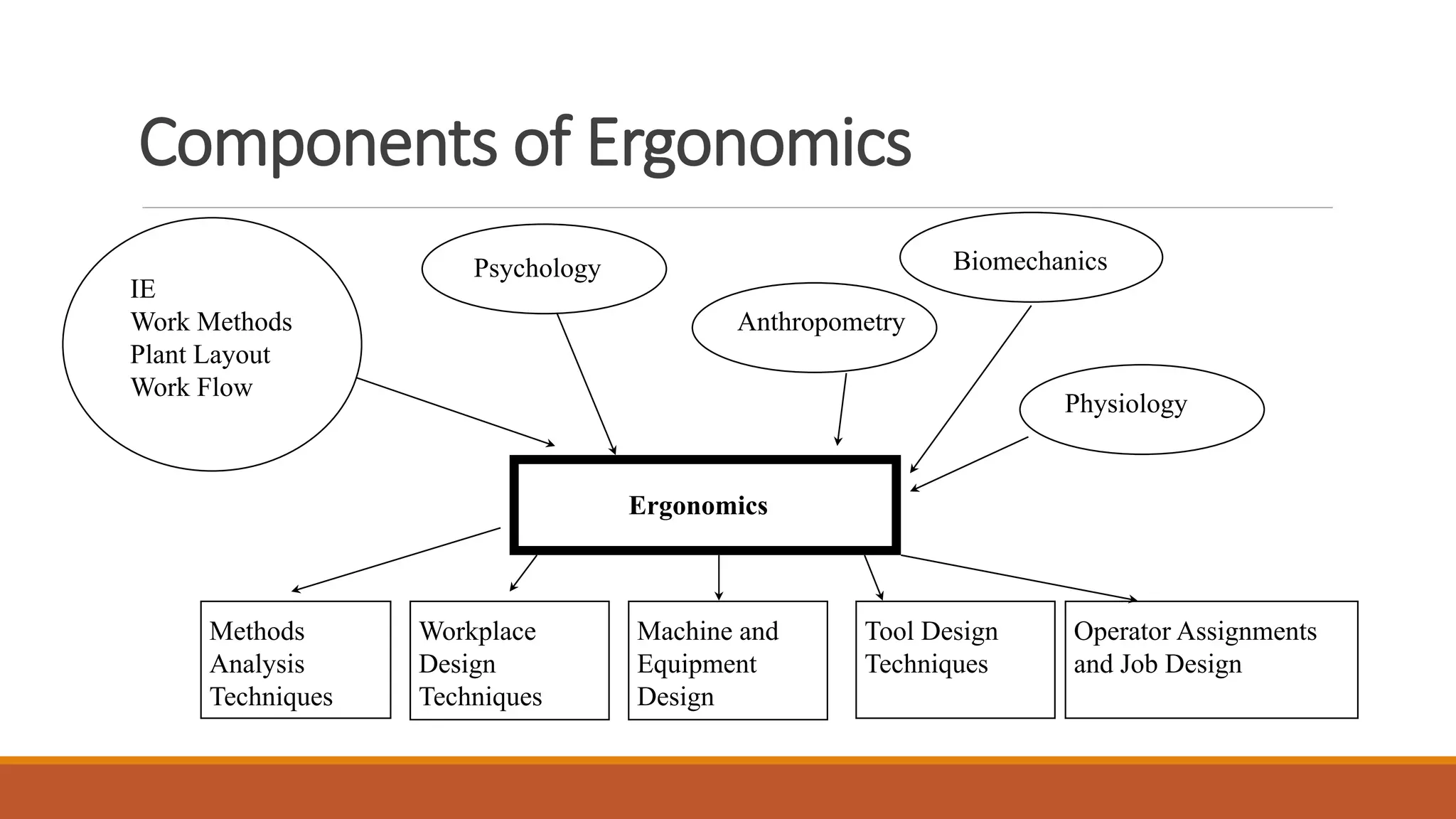
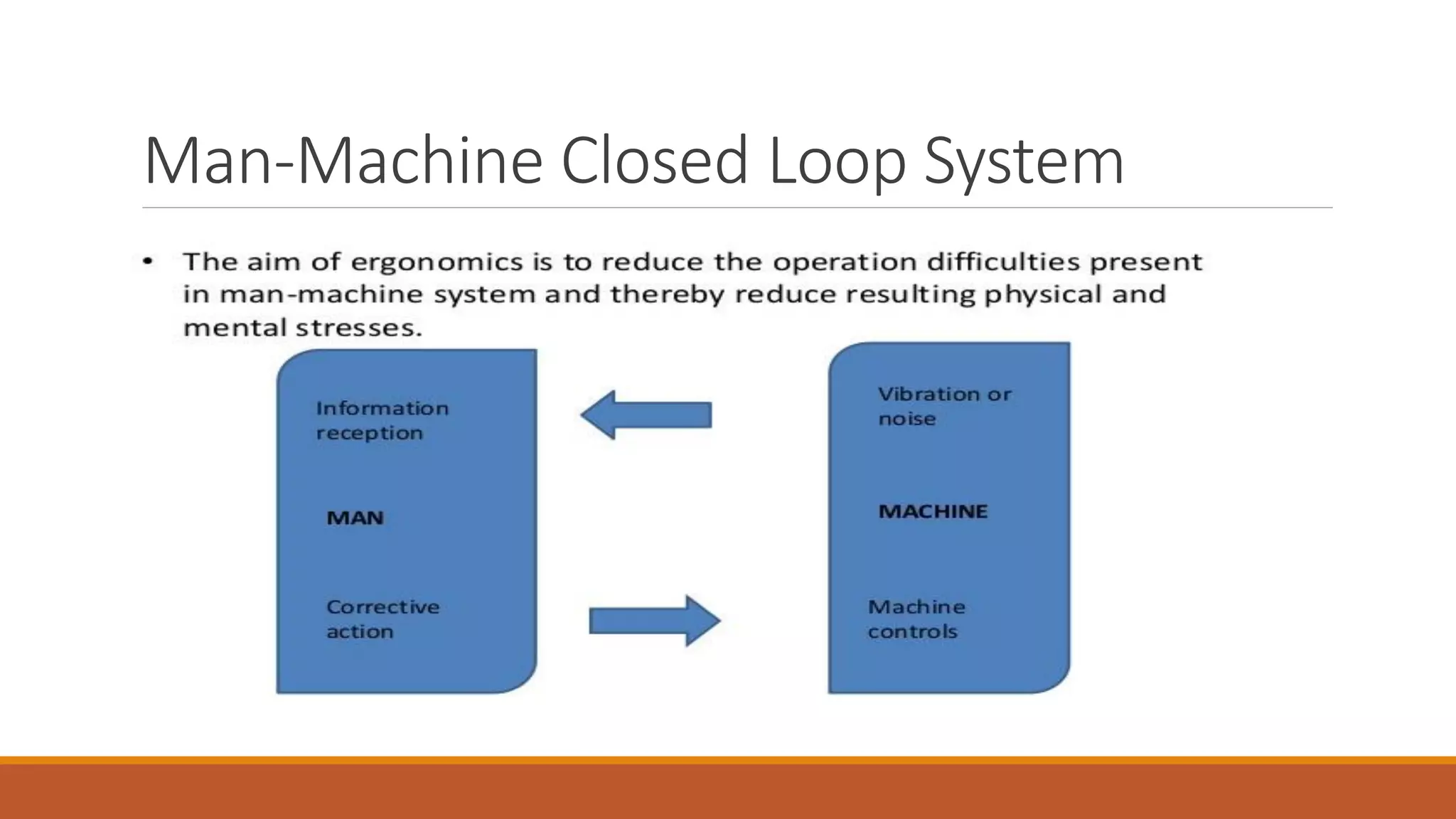
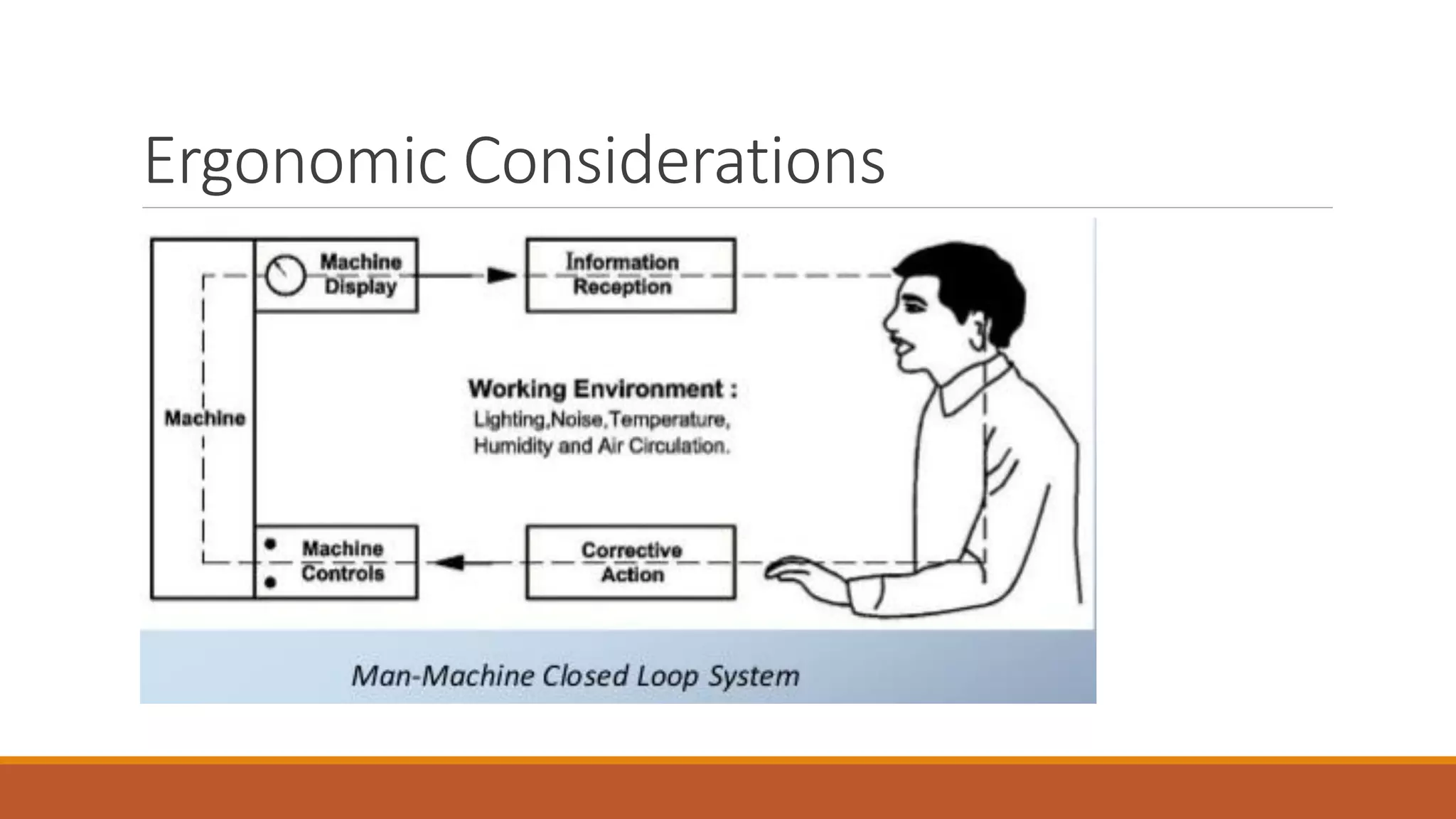
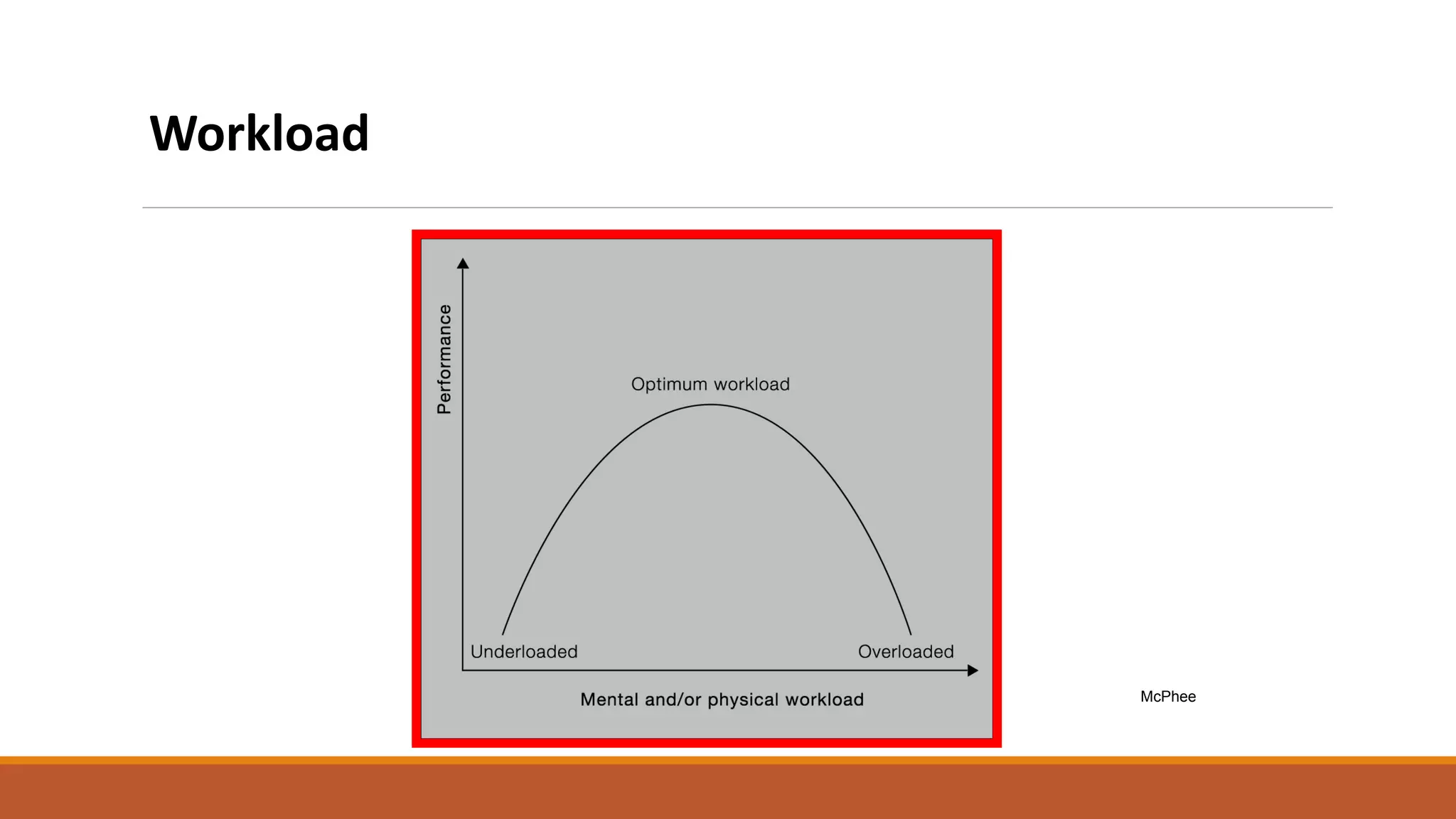
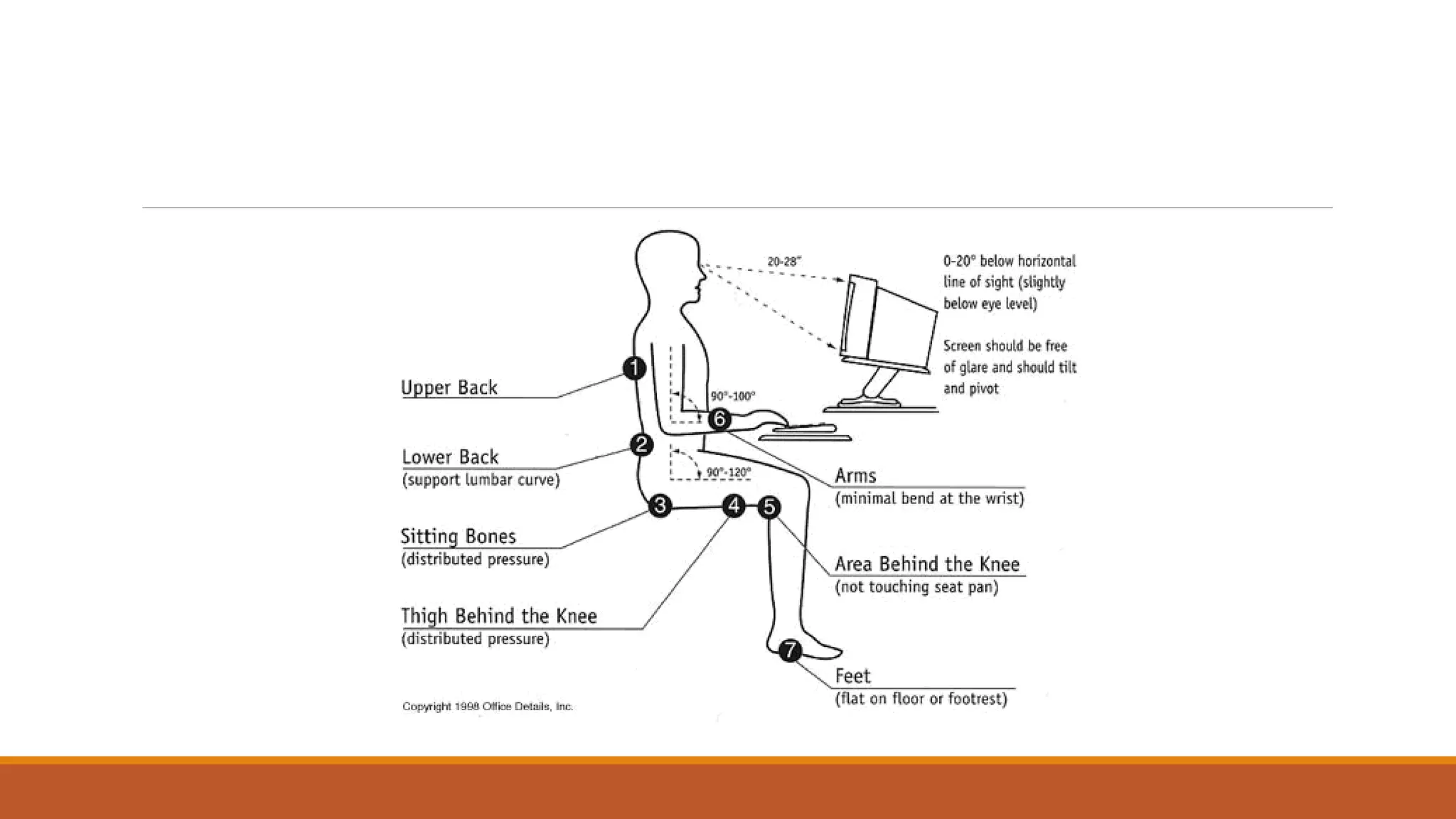
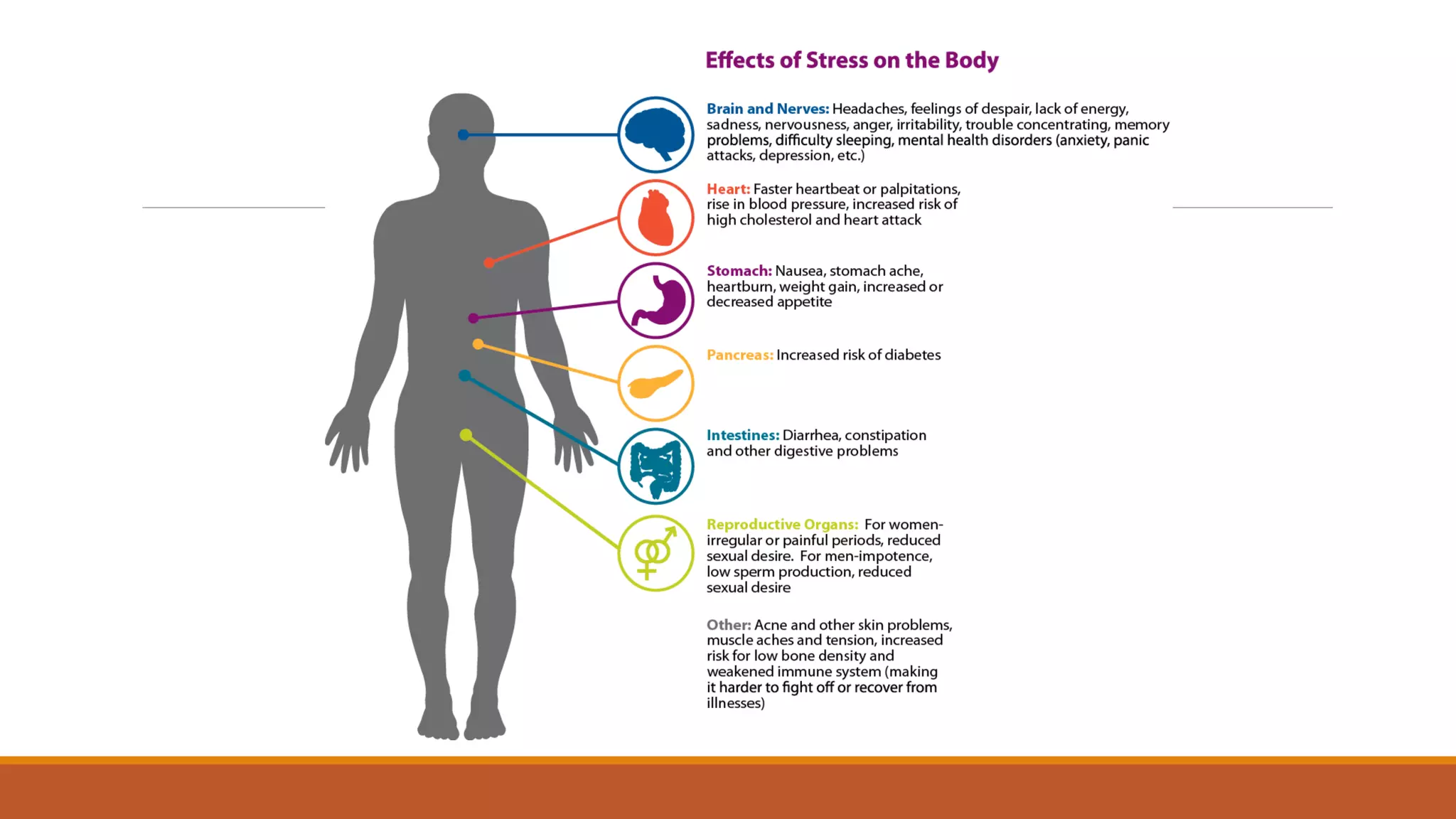
This document discusses ergonomics, including its definition as fitting the workplace to the worker to improve safety and efficiency. It covers major areas of study like anthropometry, biomechanics, and physiology. It describes the man-machine system model and components like the human, machine, and their interaction. It also discusses work capabilities and stresses on the human body, signs of stress, and managing work stress. Finally, it touches on computer ergonomics and ergonomic tips for computer users like correct sitting posture and an ideal ergonomic office setup.