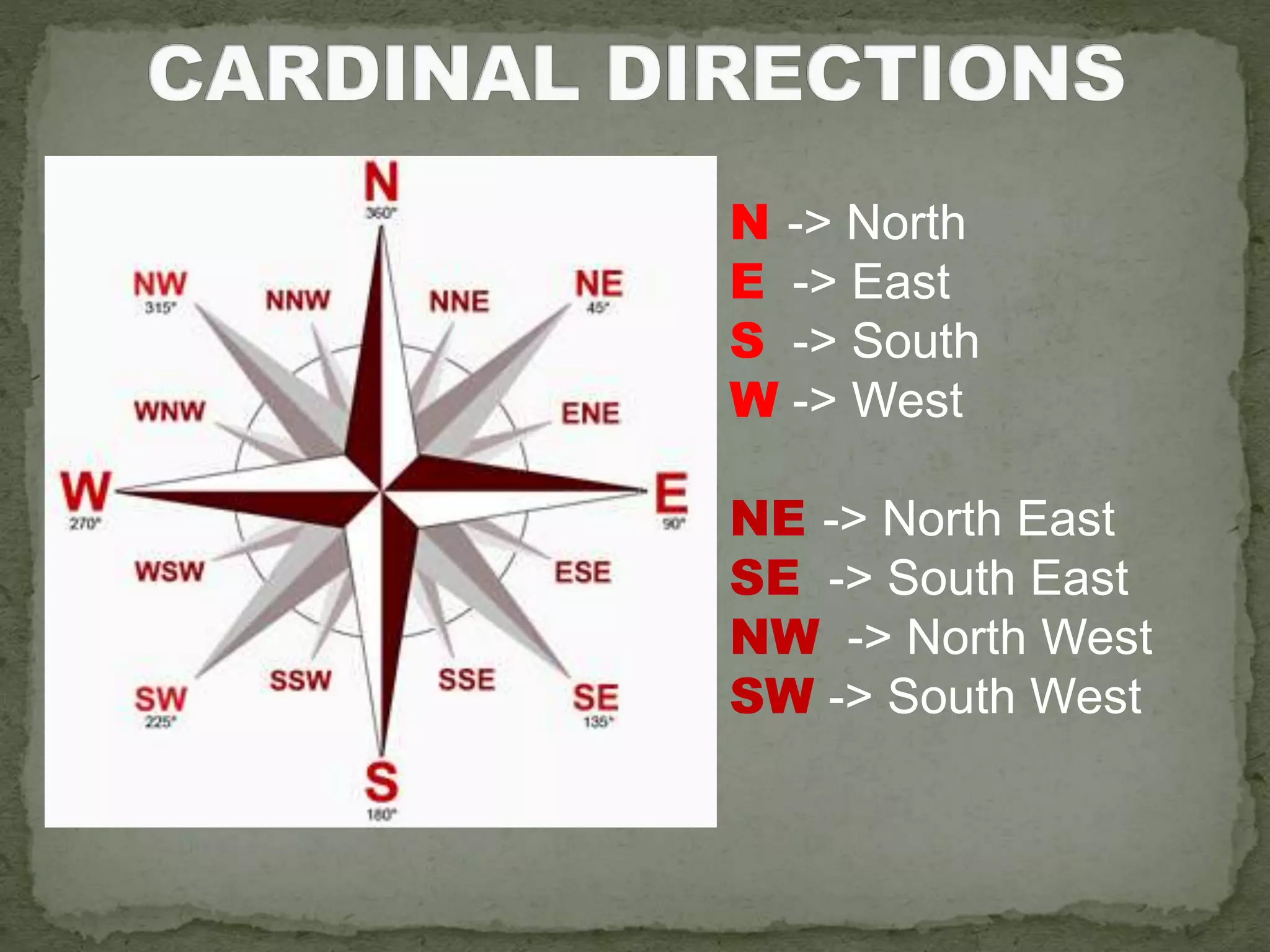
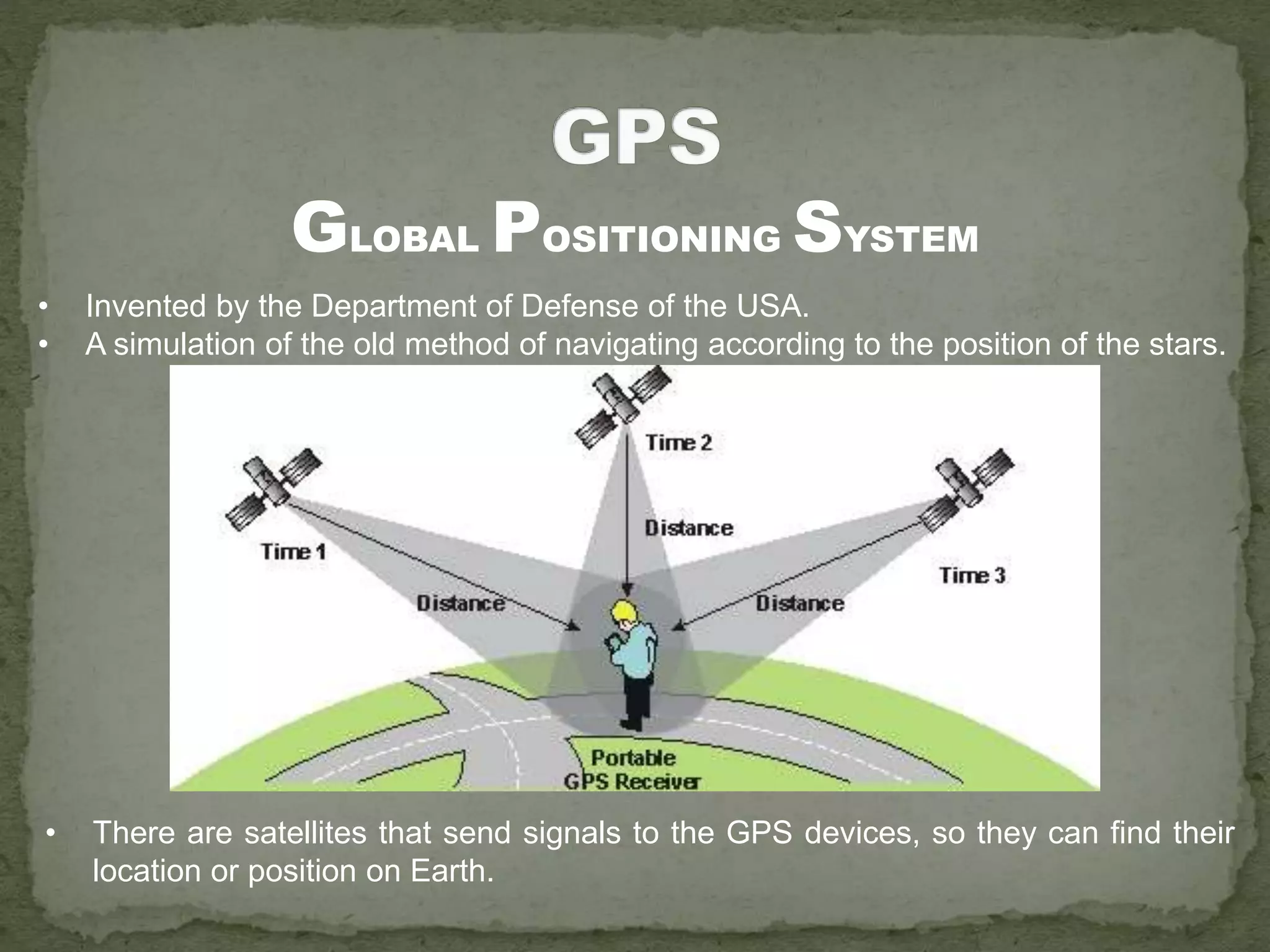
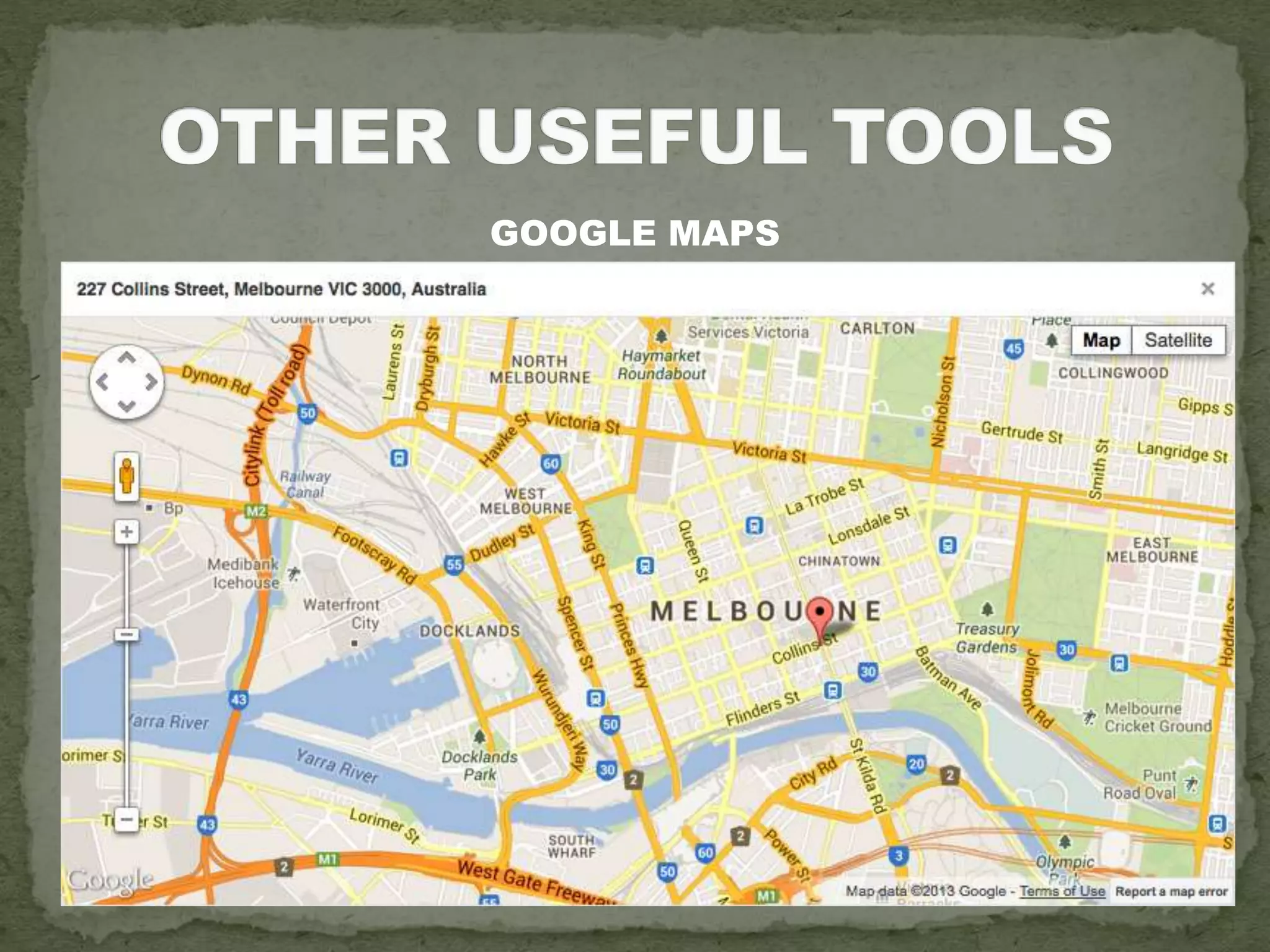
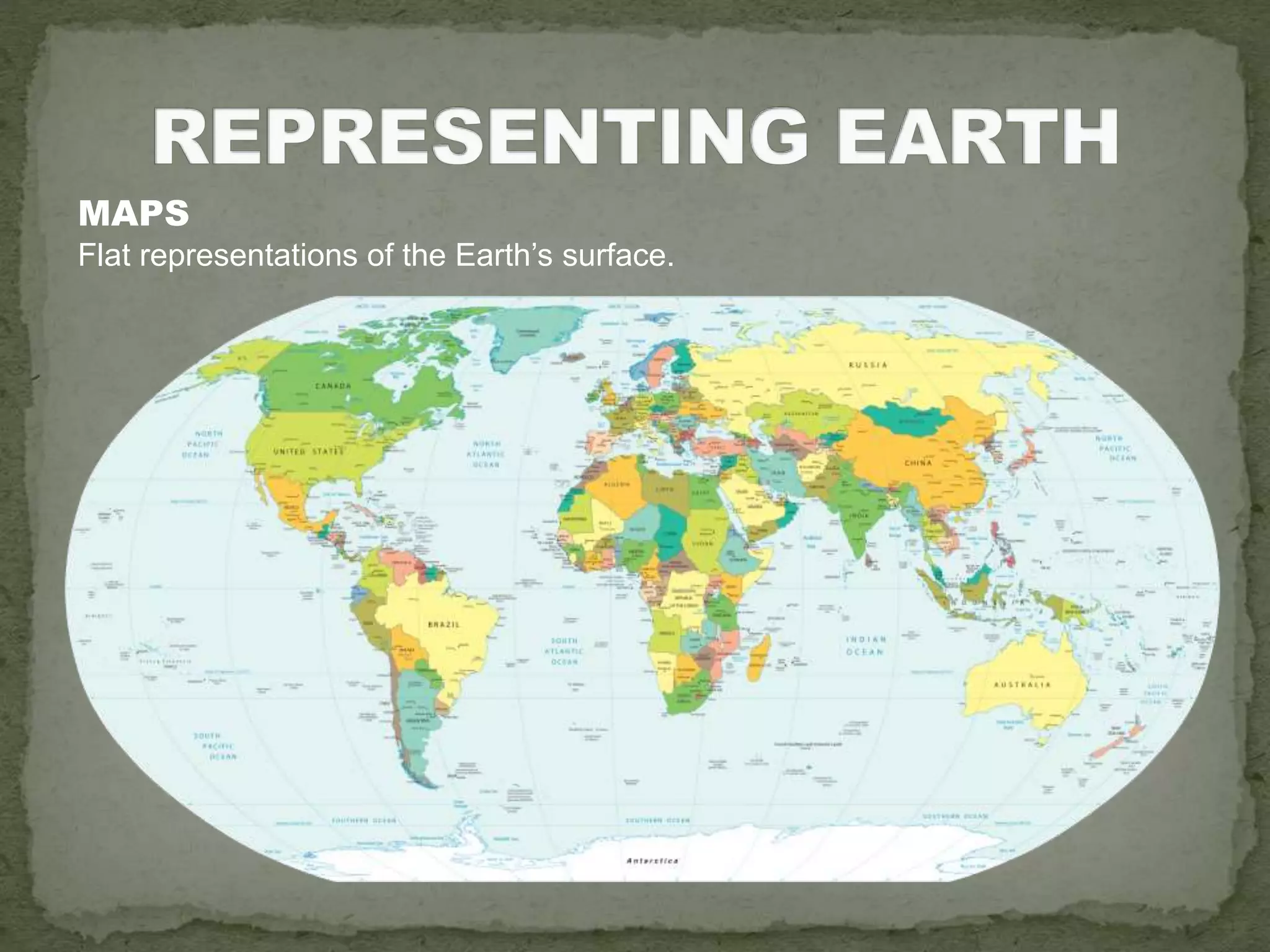
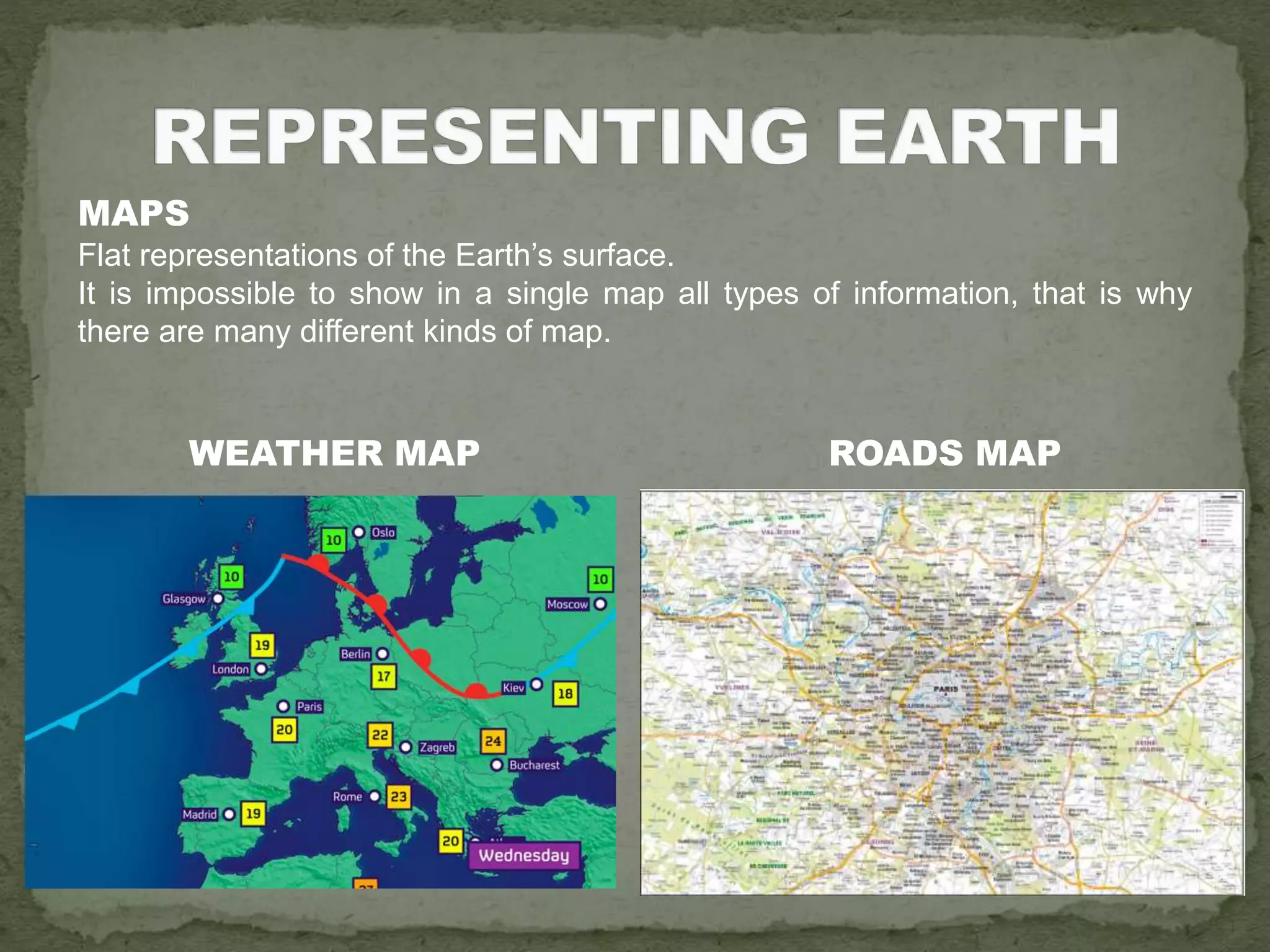
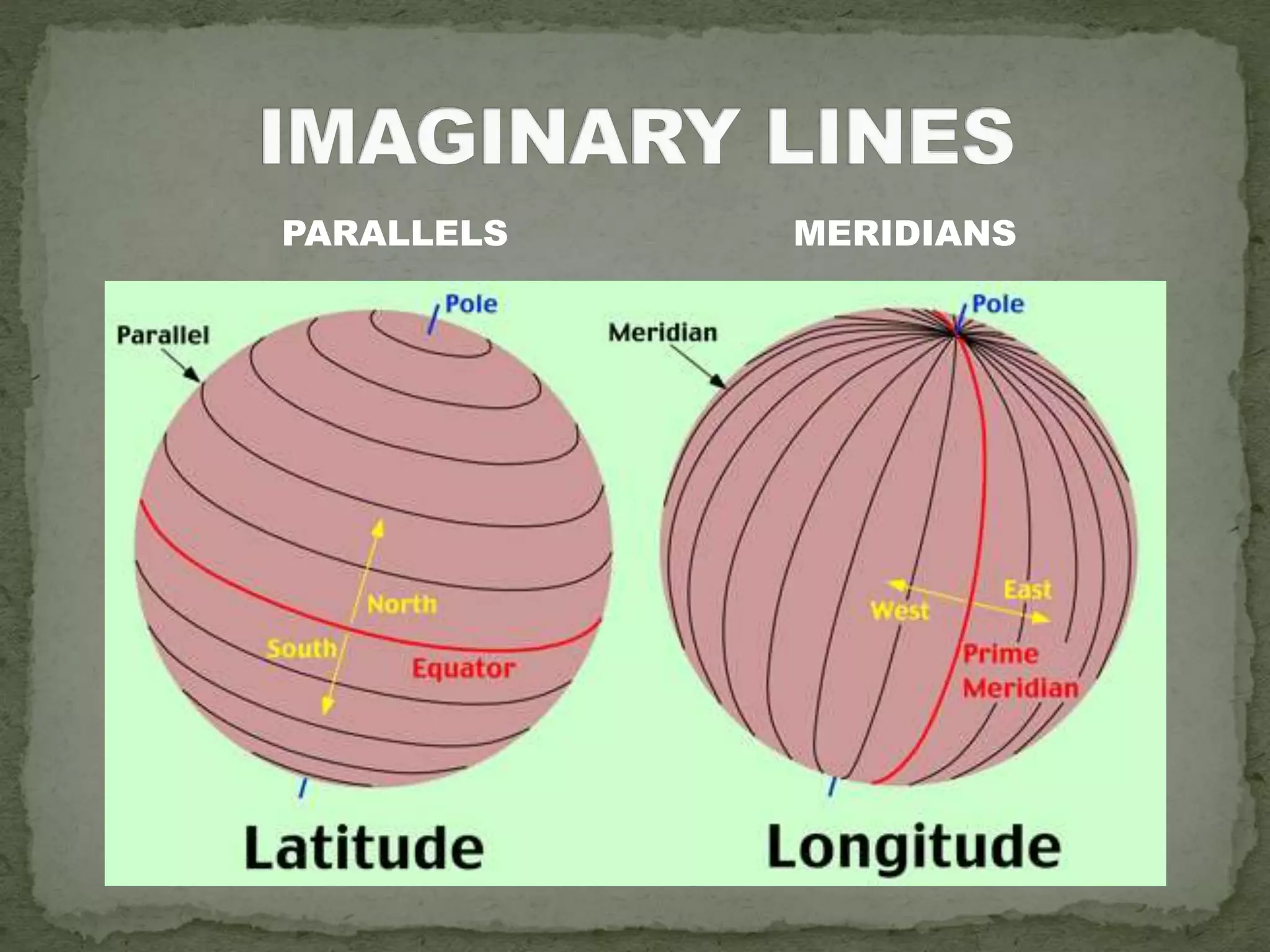
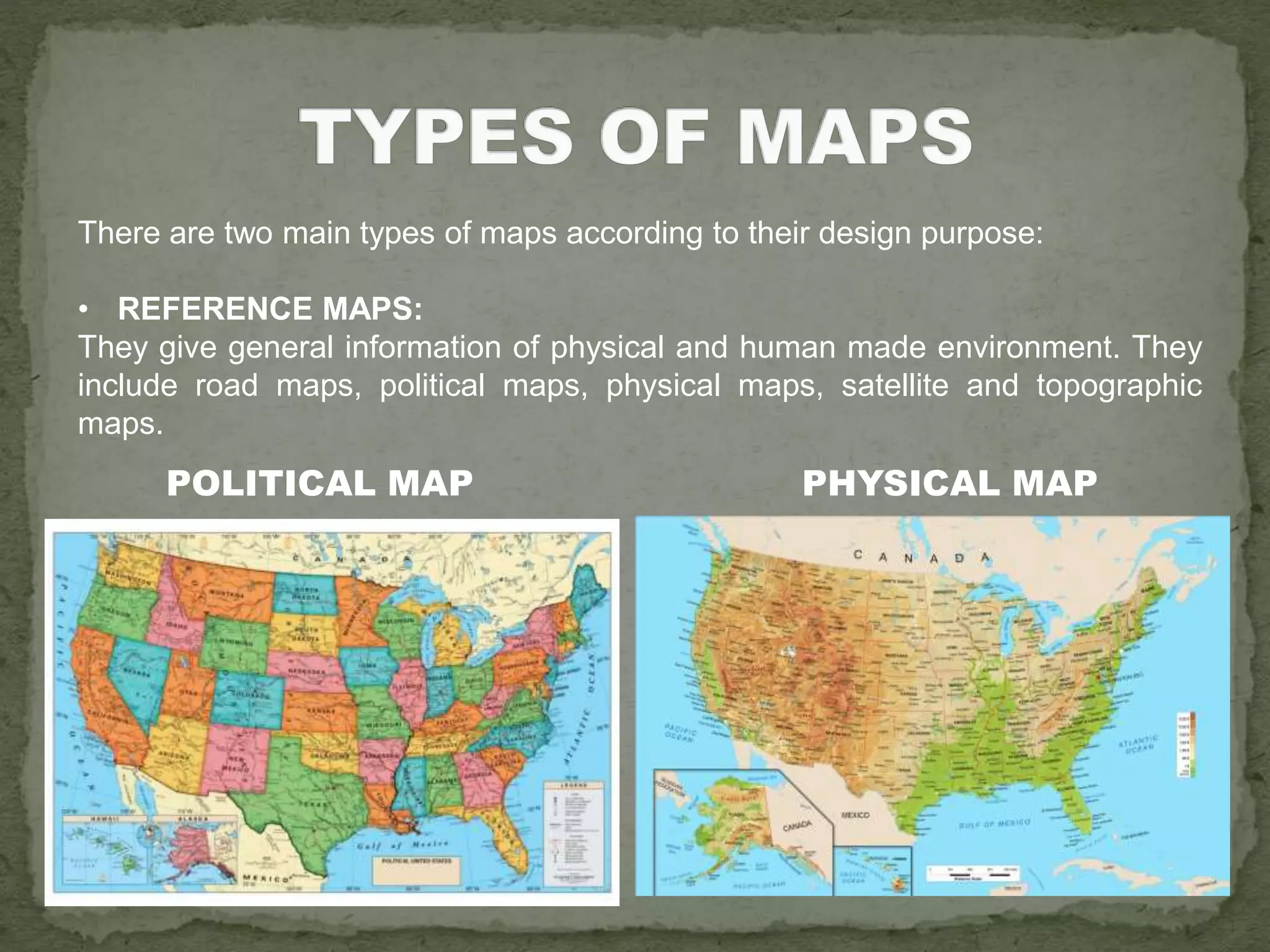
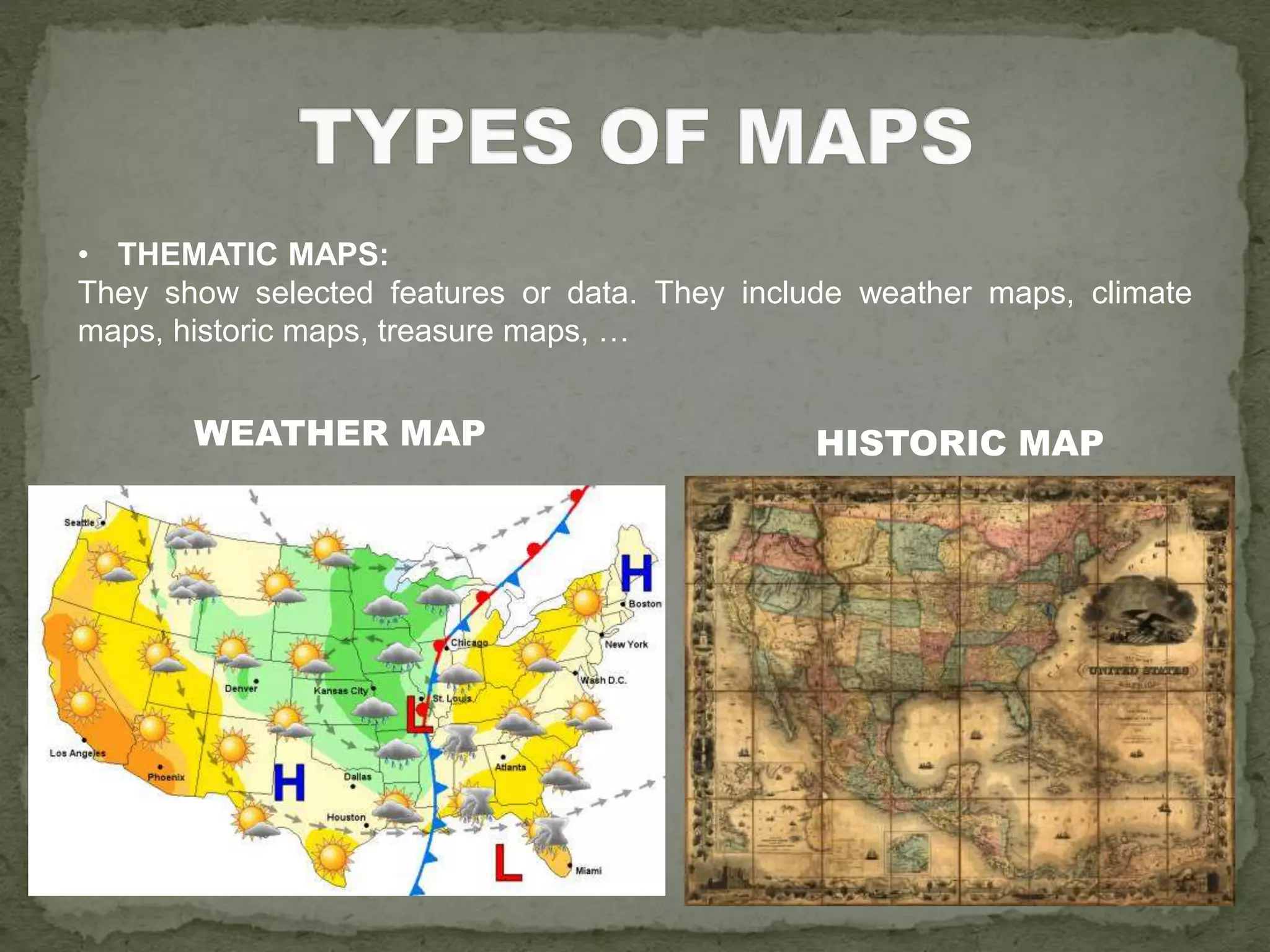
The document discusses the evolution of navigation tools, including GPS and traditional maps, and explains the essential elements of maps such as scales, types, and design principles. It highlights the role of cartographers and the credibility factors that enhance map reliability, summarized by the acronym 'DOGSTAILS'. Additionally, it outlines the differences between reference and thematic maps and provides guidelines for effective map creation.