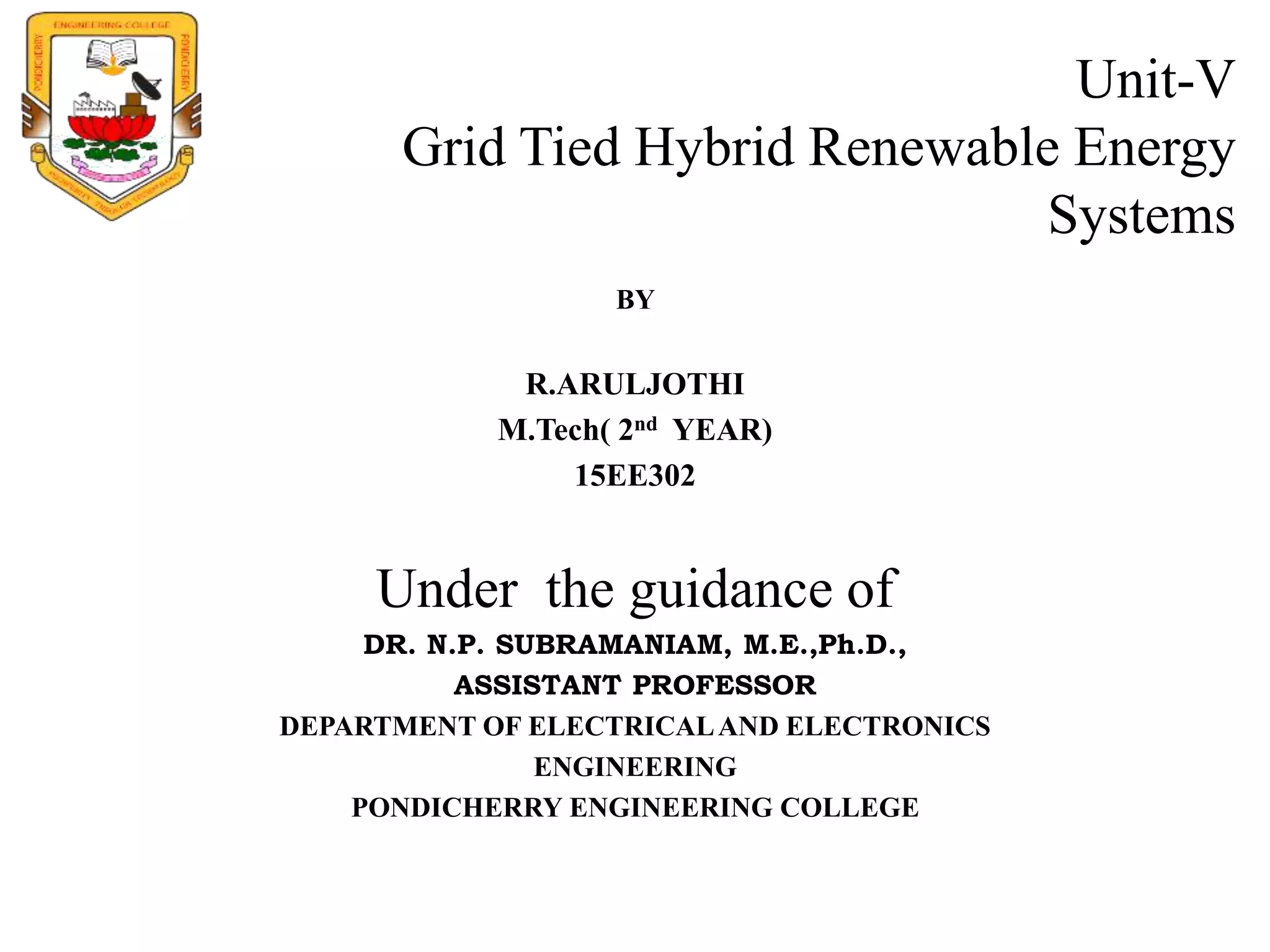
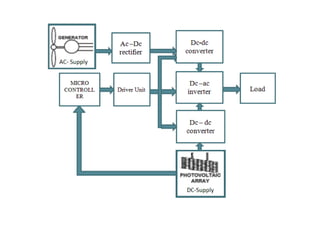
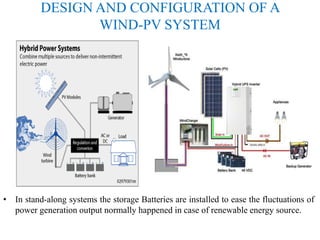
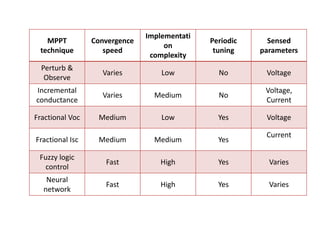
This document discusses grid-tied hybrid renewable energy systems. It provides details on how hybrid systems that combine sources like solar, wind and diesel generators can provide power to homes and businesses while also feeding excess electricity back to the main power grid. The key aspects covered include how grid-tied systems work, the components involved like inverters, the advantages of net metering arrangements, different hybrid configuration options, and maximum power point tracking technology to optimize renewable energy output.