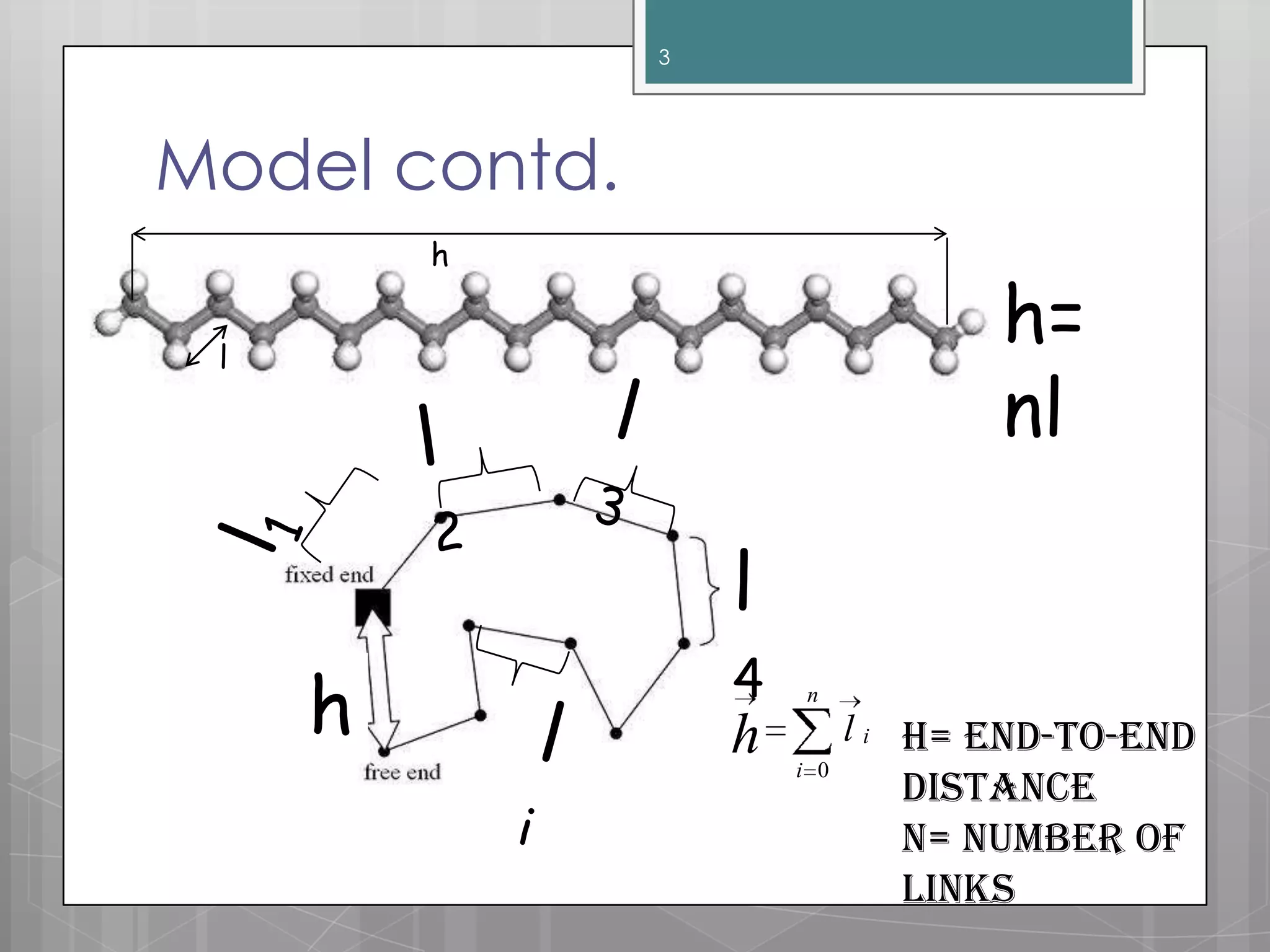
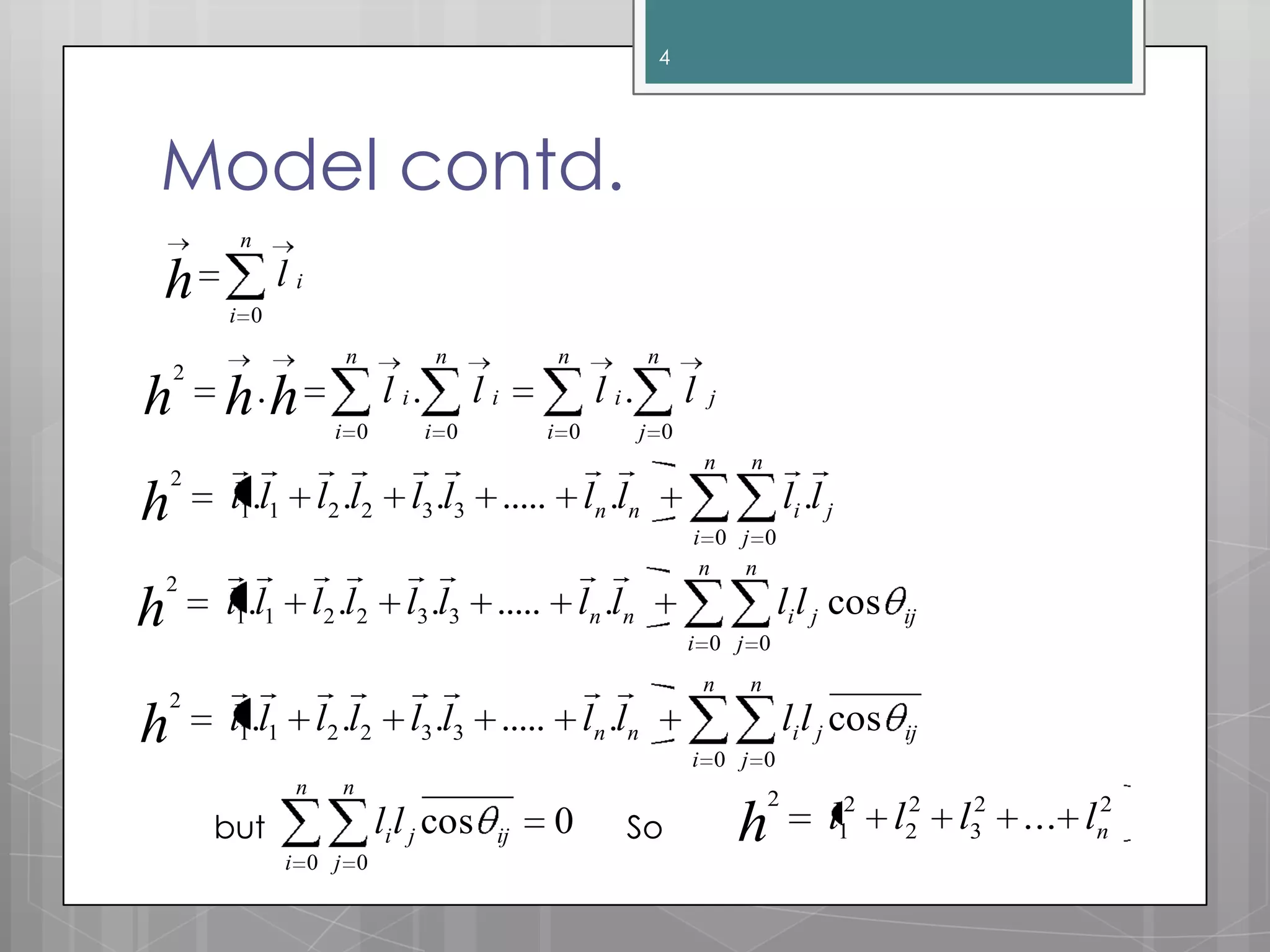
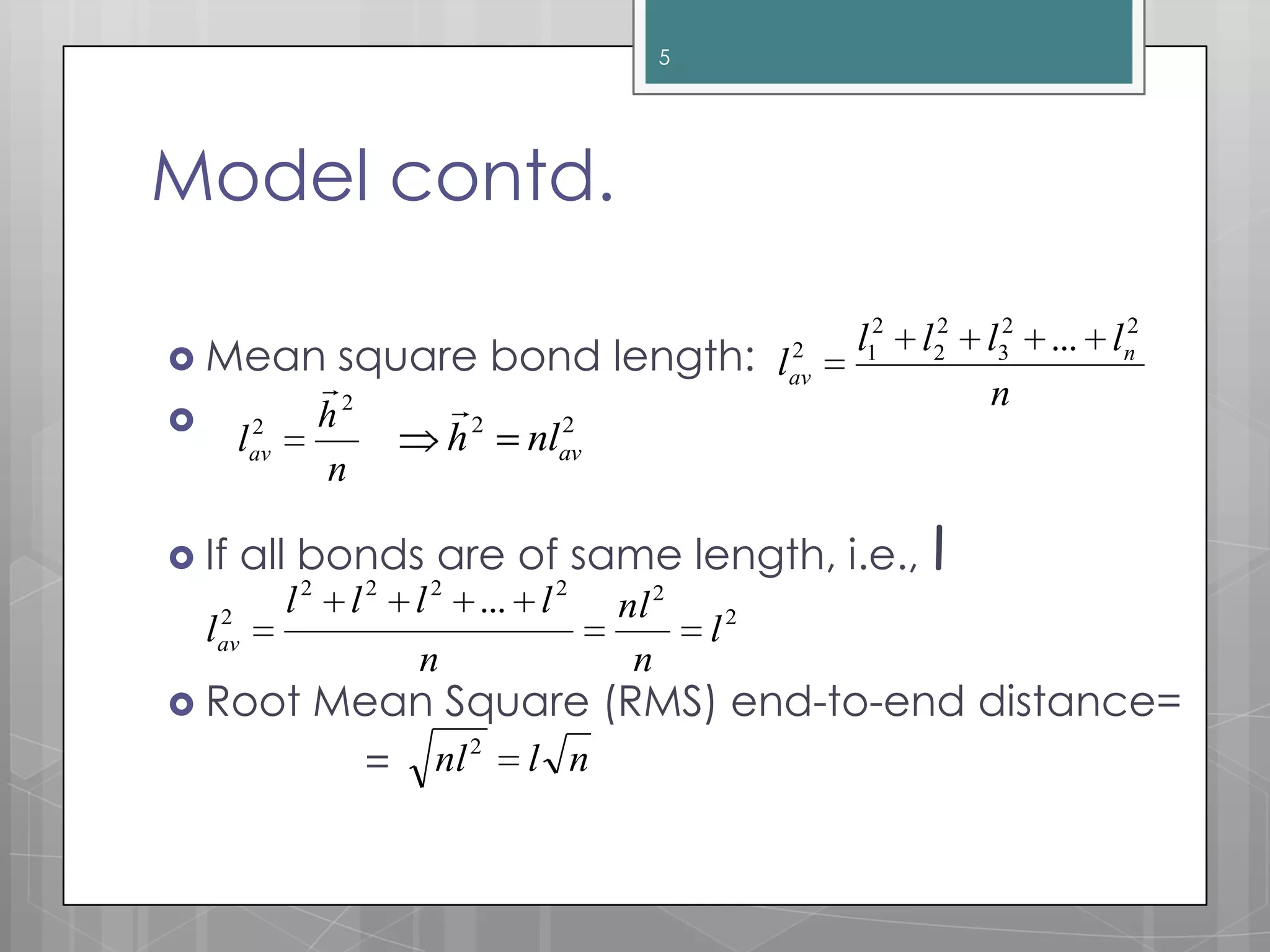
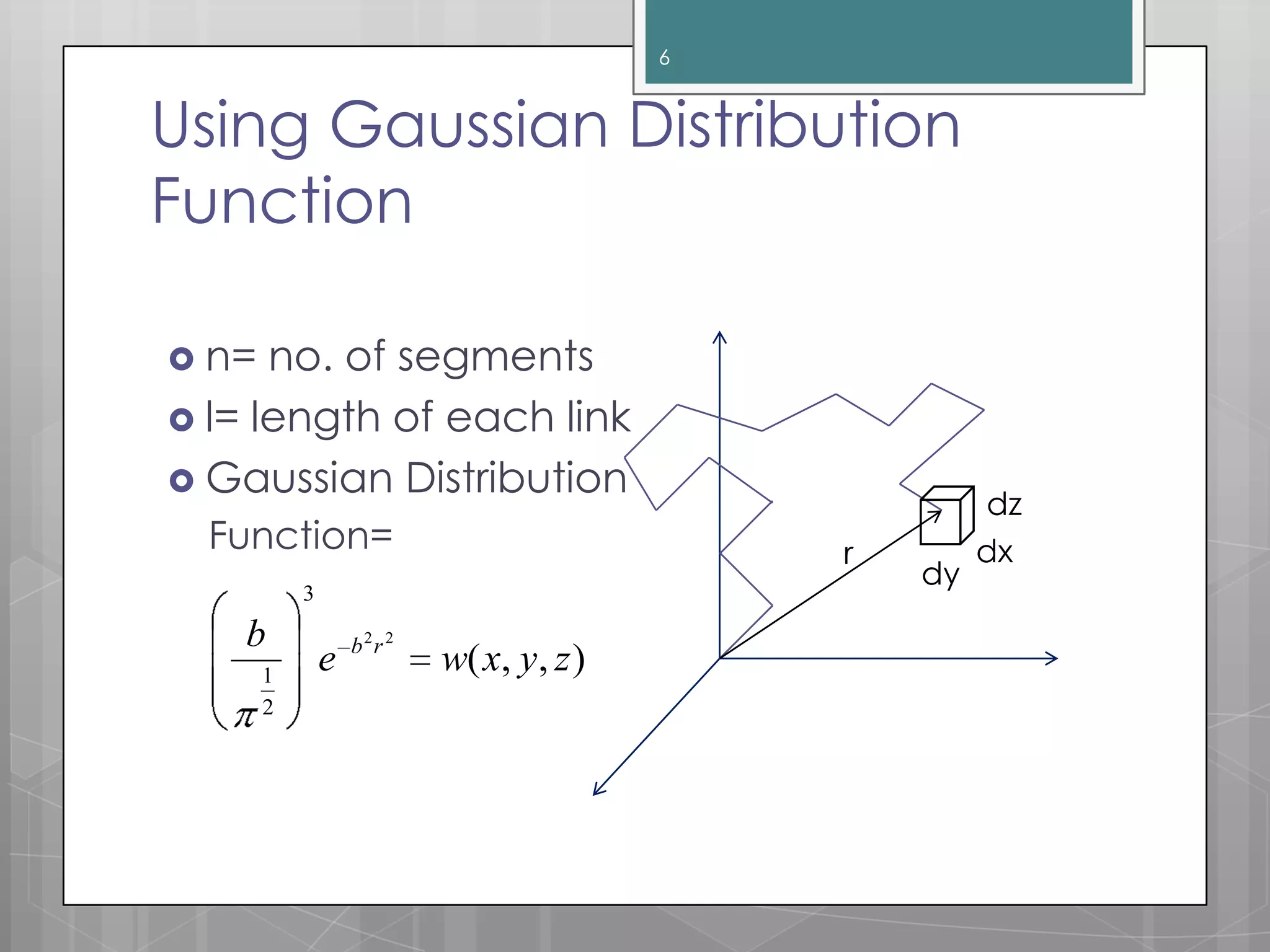
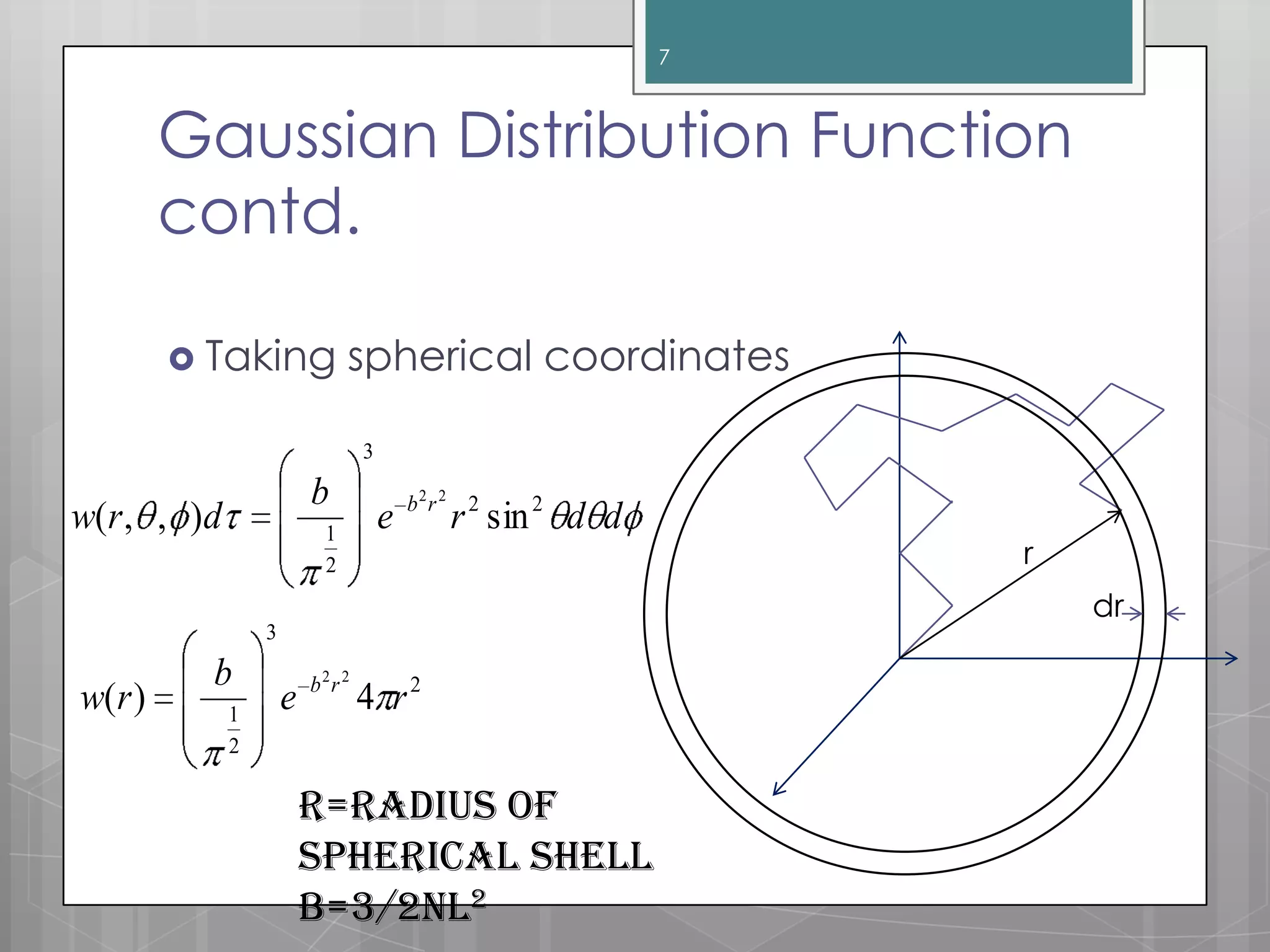
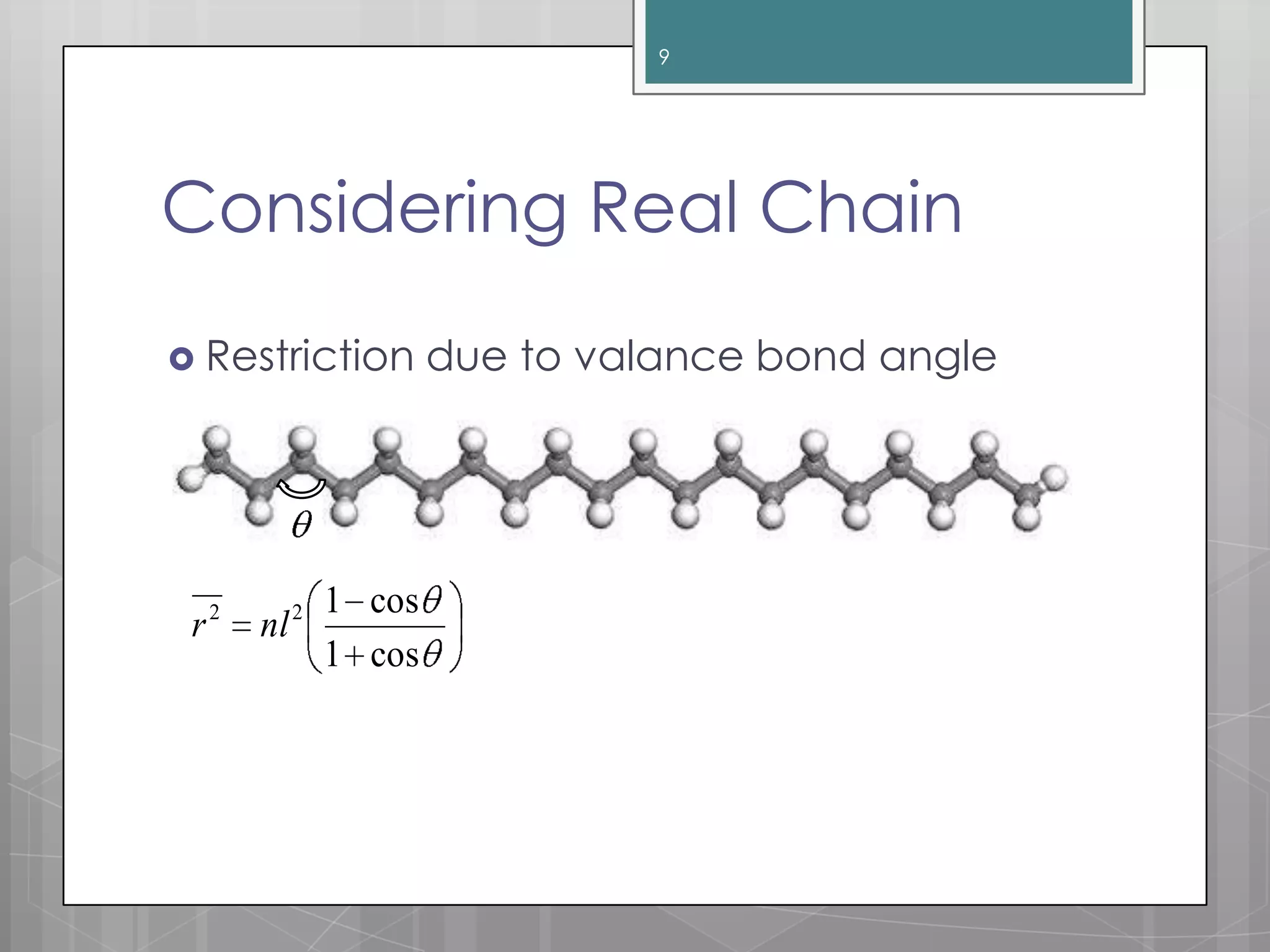
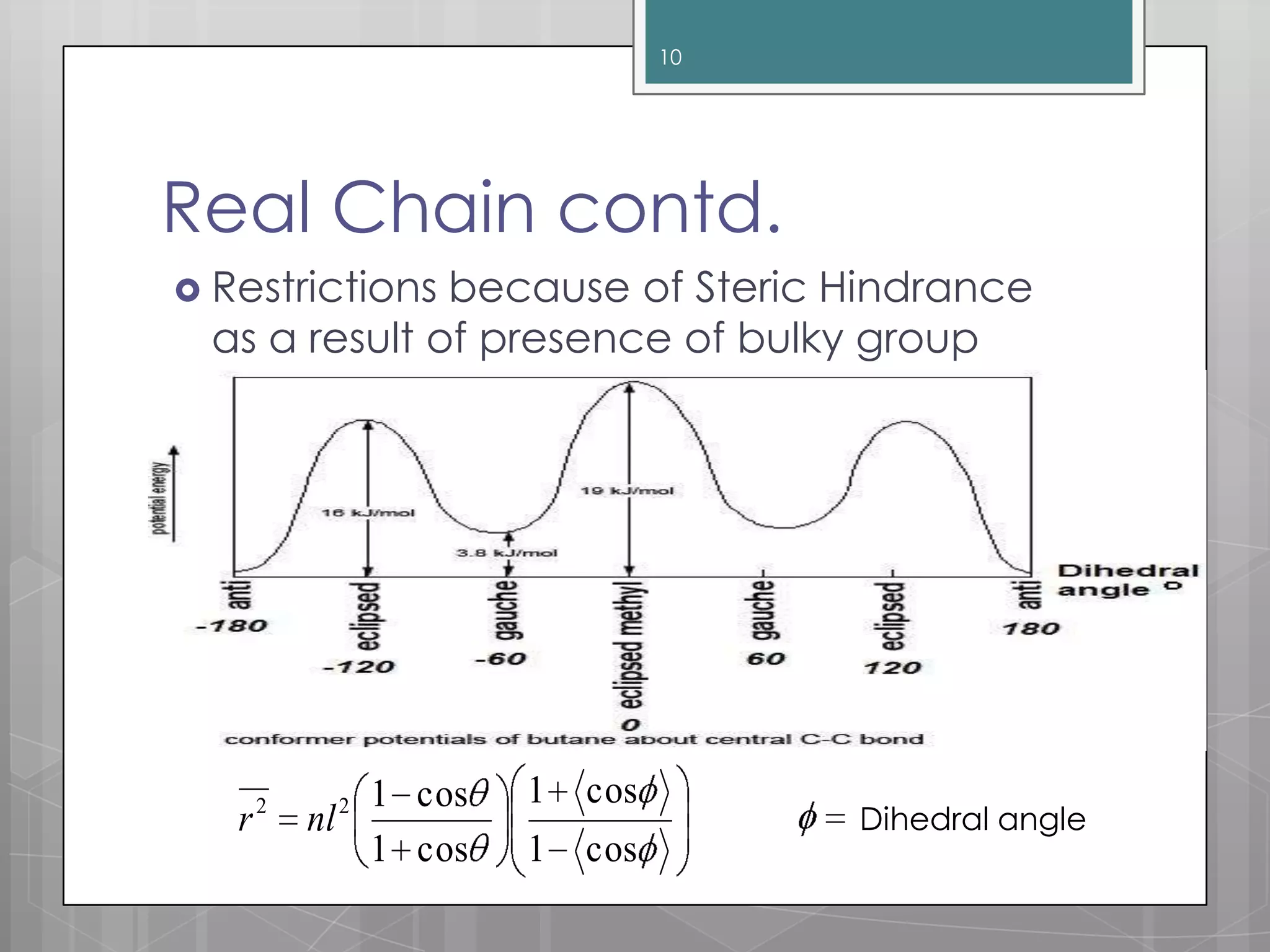
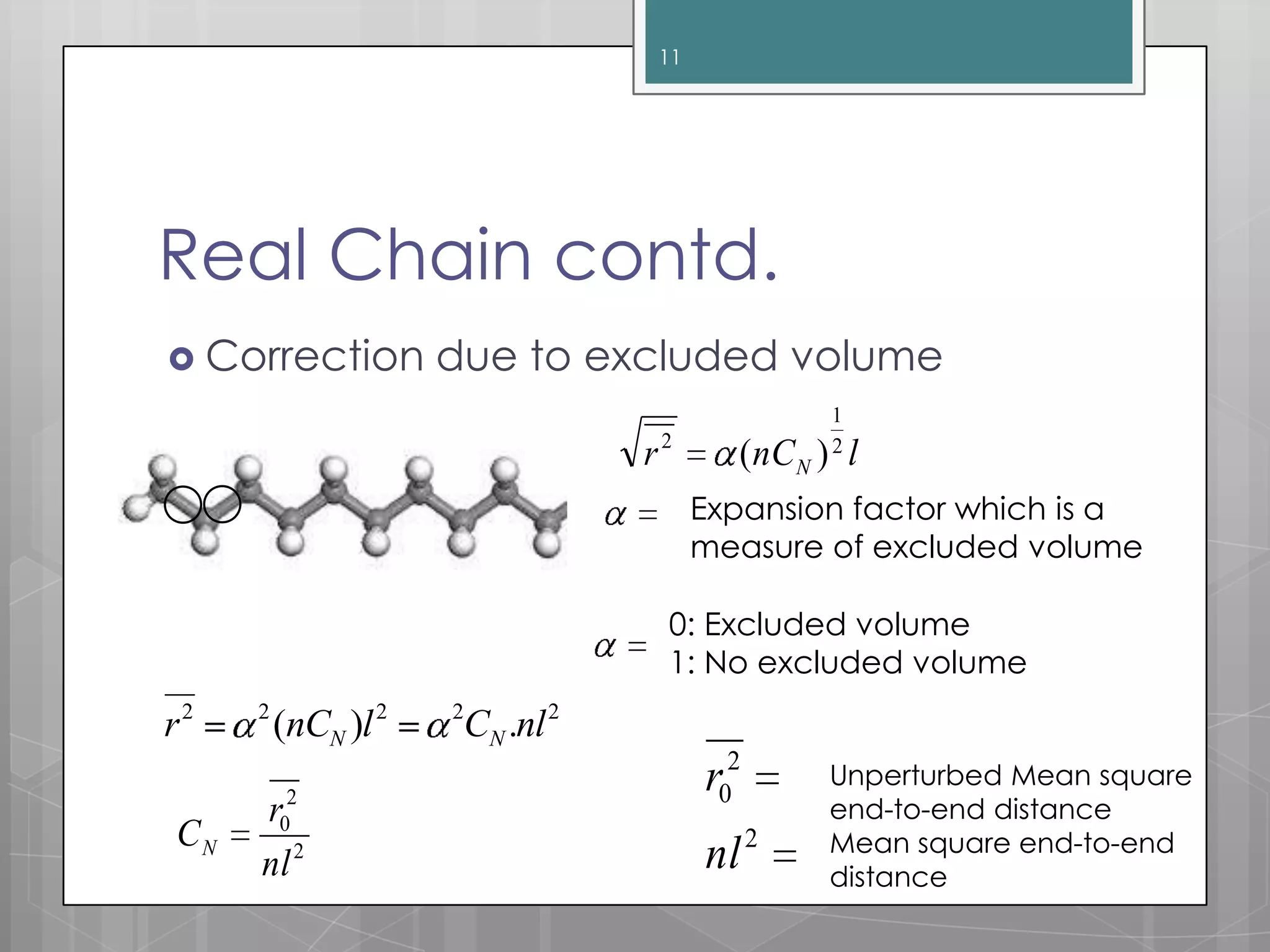
The document discusses polymer chain dimensions using the freely jointed chain model and Gaussian distribution function. It describes the freely jointed chain model, which assumes no restrictions on bond angles, rotations, or van der Waals volume. The model shows that the root mean square end-to-end distance of an ideal chain is proportional to the square root of the number of links. It then introduces the Gaussian distribution function and shows that it gives the same results as the freely jointed chain model for the average end-to-end distance. The document finally notes some corrections needed for real chains, which include restrictions due to bond angles, steric hindrance from bulky groups, and excluded volume effects.