The document summarizes key aspects of the respiratory system and gas exchange in three parts:
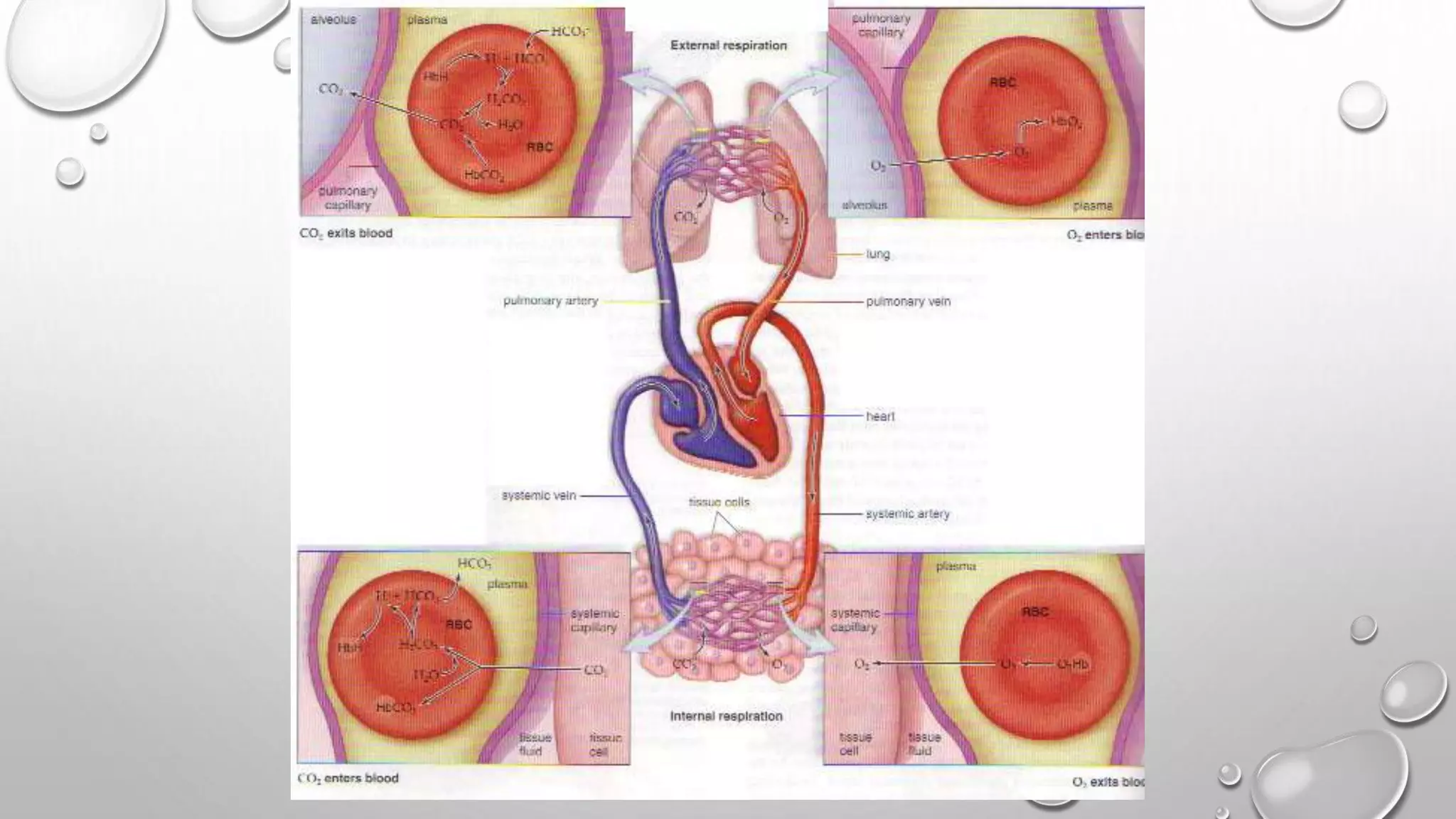
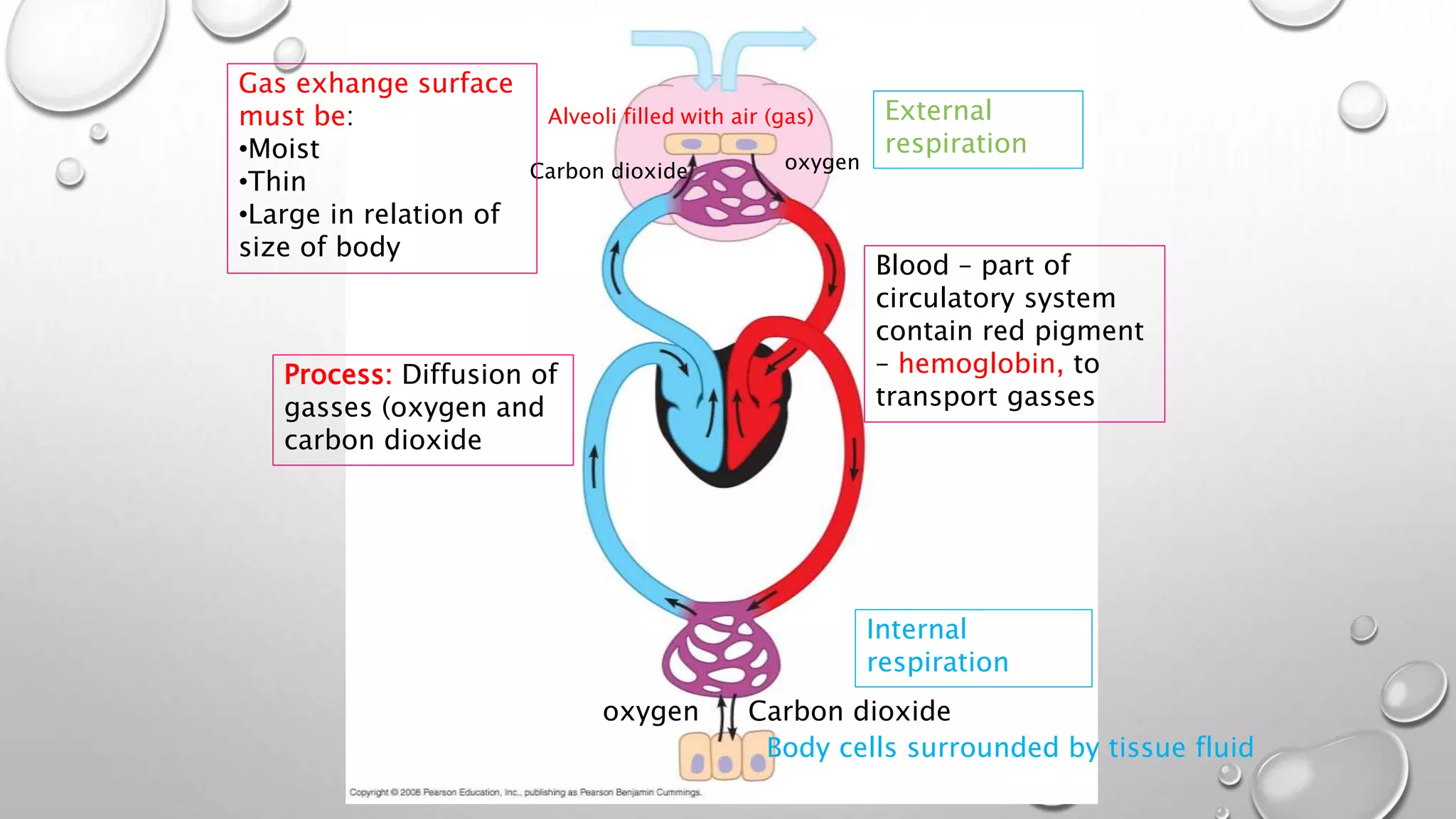
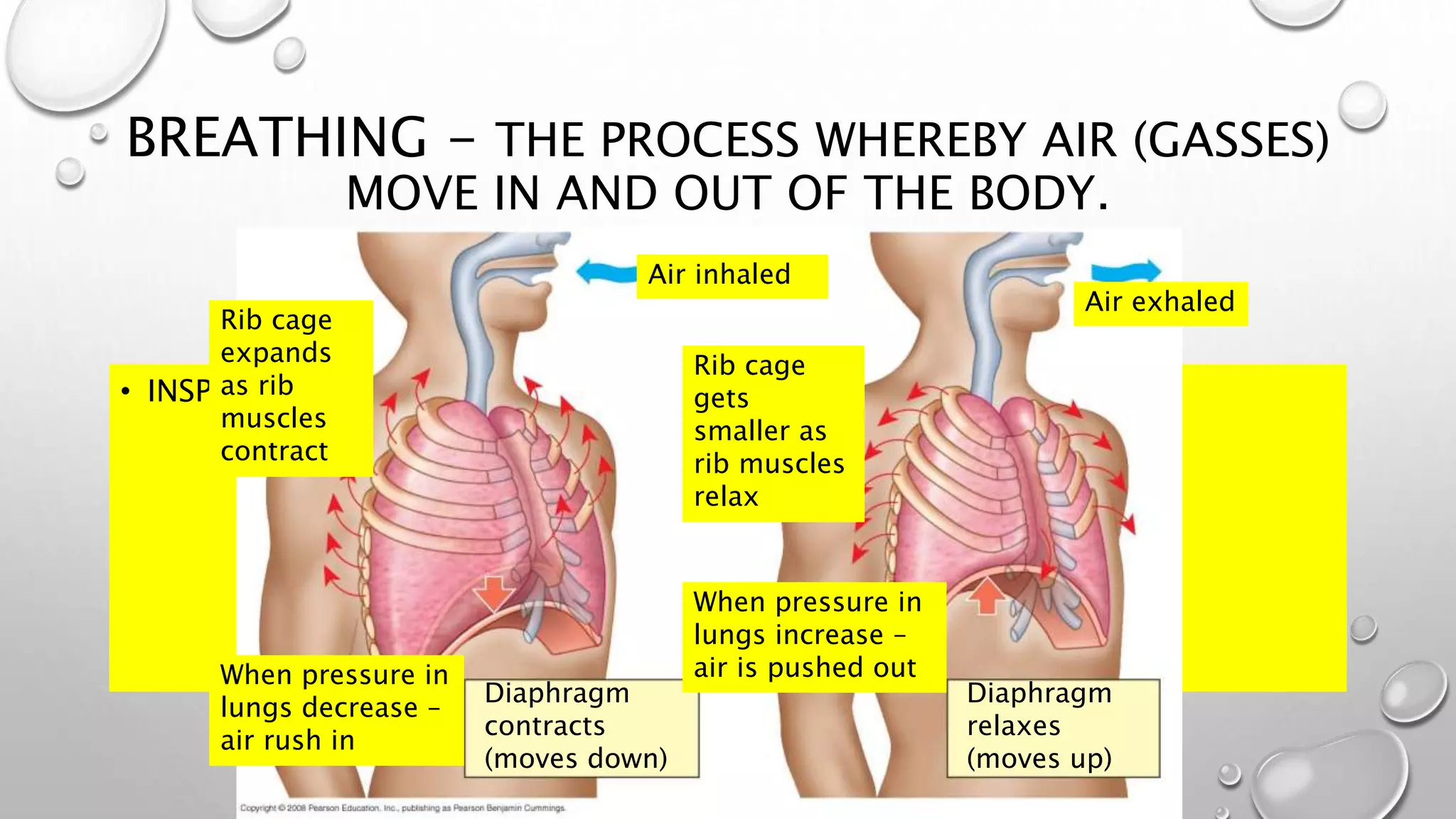
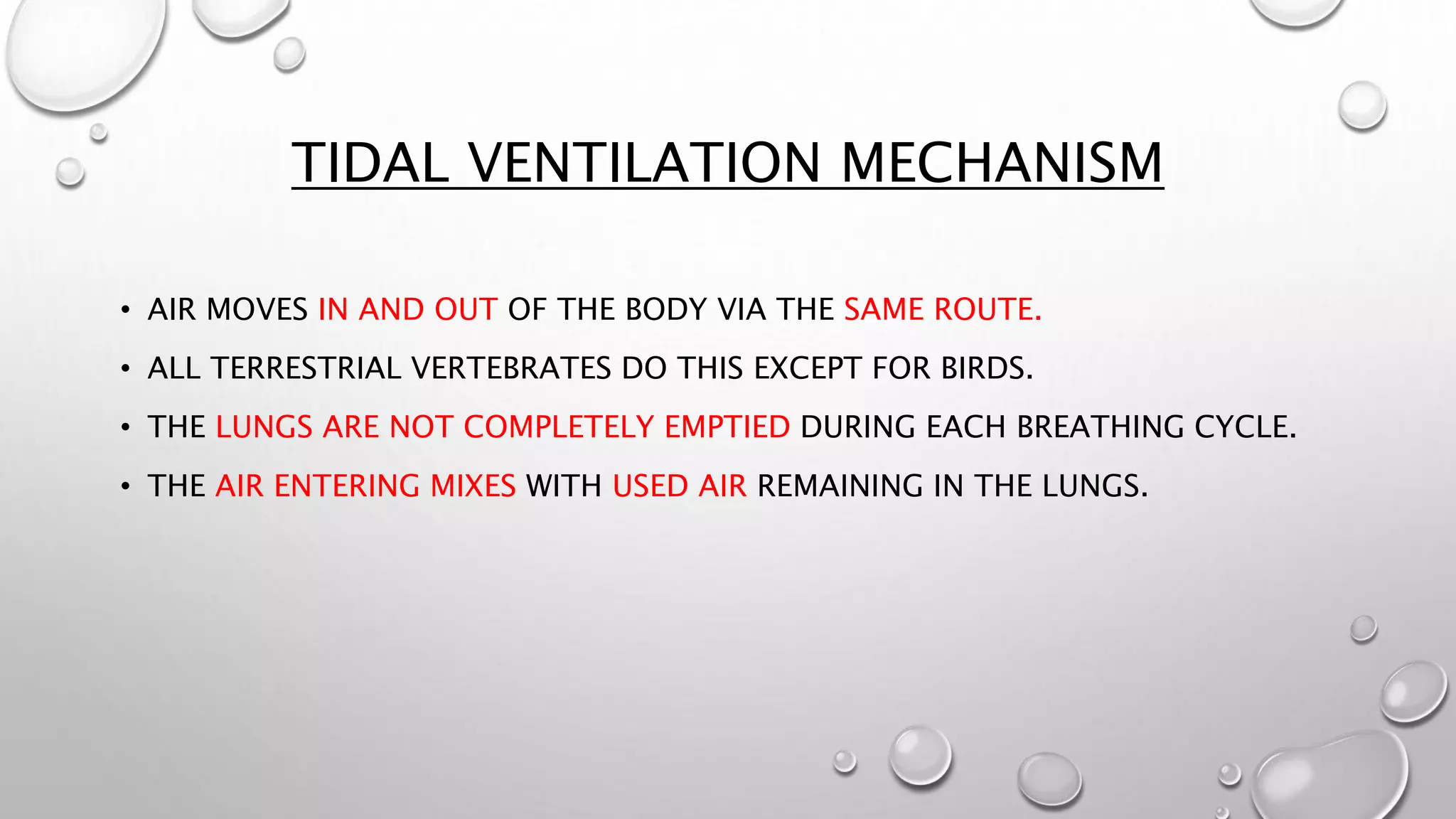
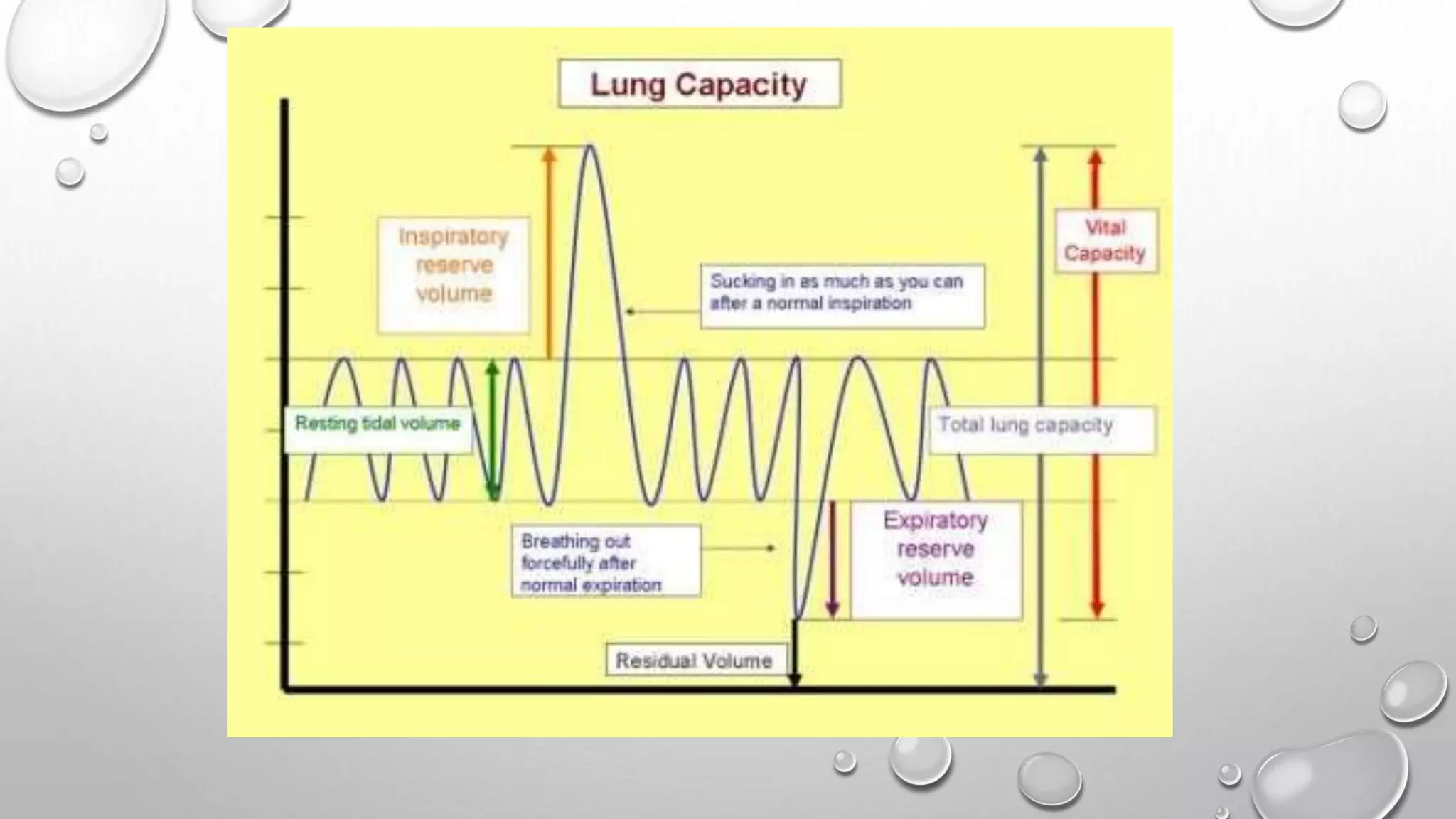
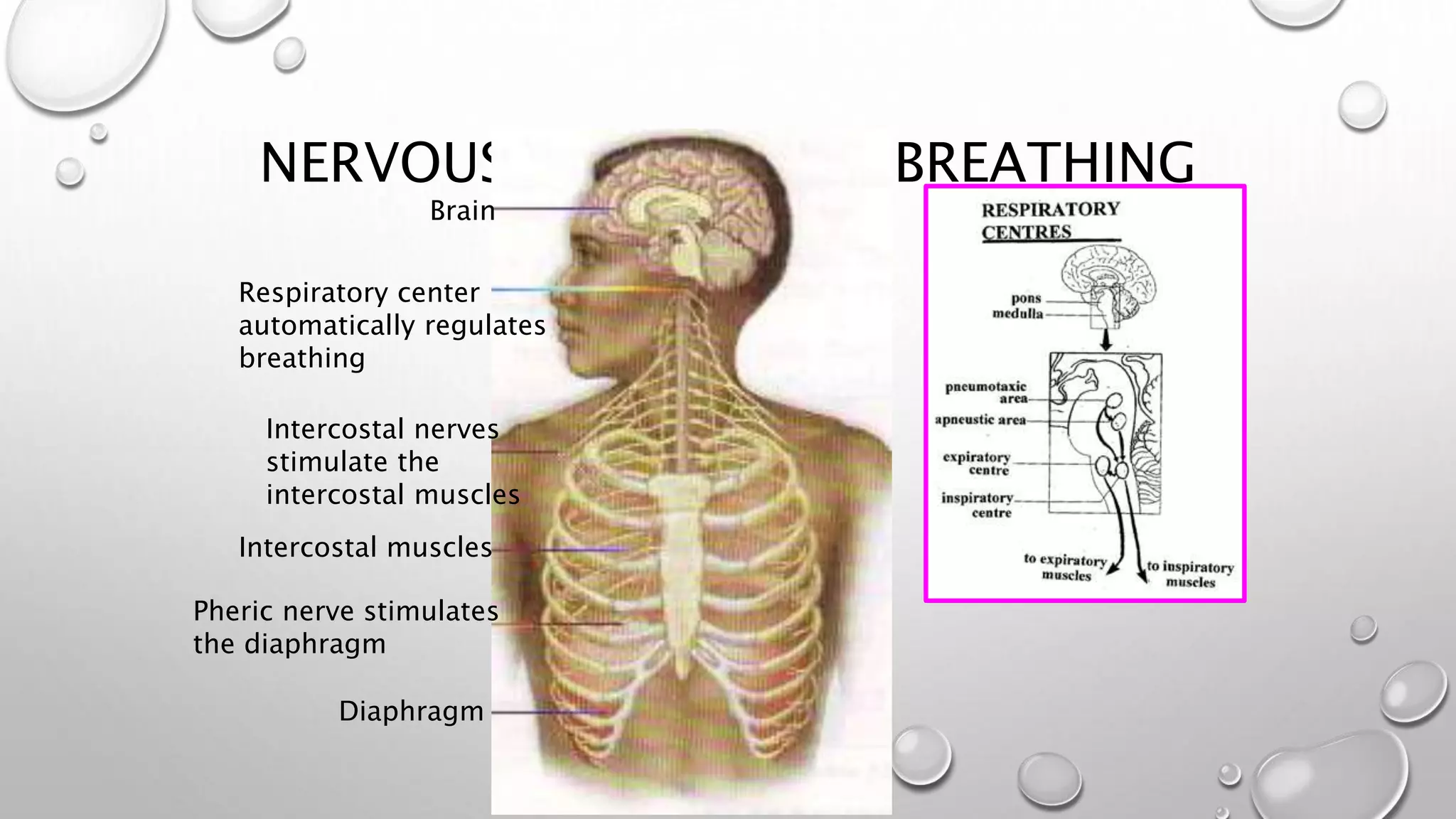
1. It describes the process of breathing, including inspiration, expiration, and the roles of the diaphragm and rib cage muscles. Gas exchange occurs through external respiration in the lungs and internal respiration in tissues.
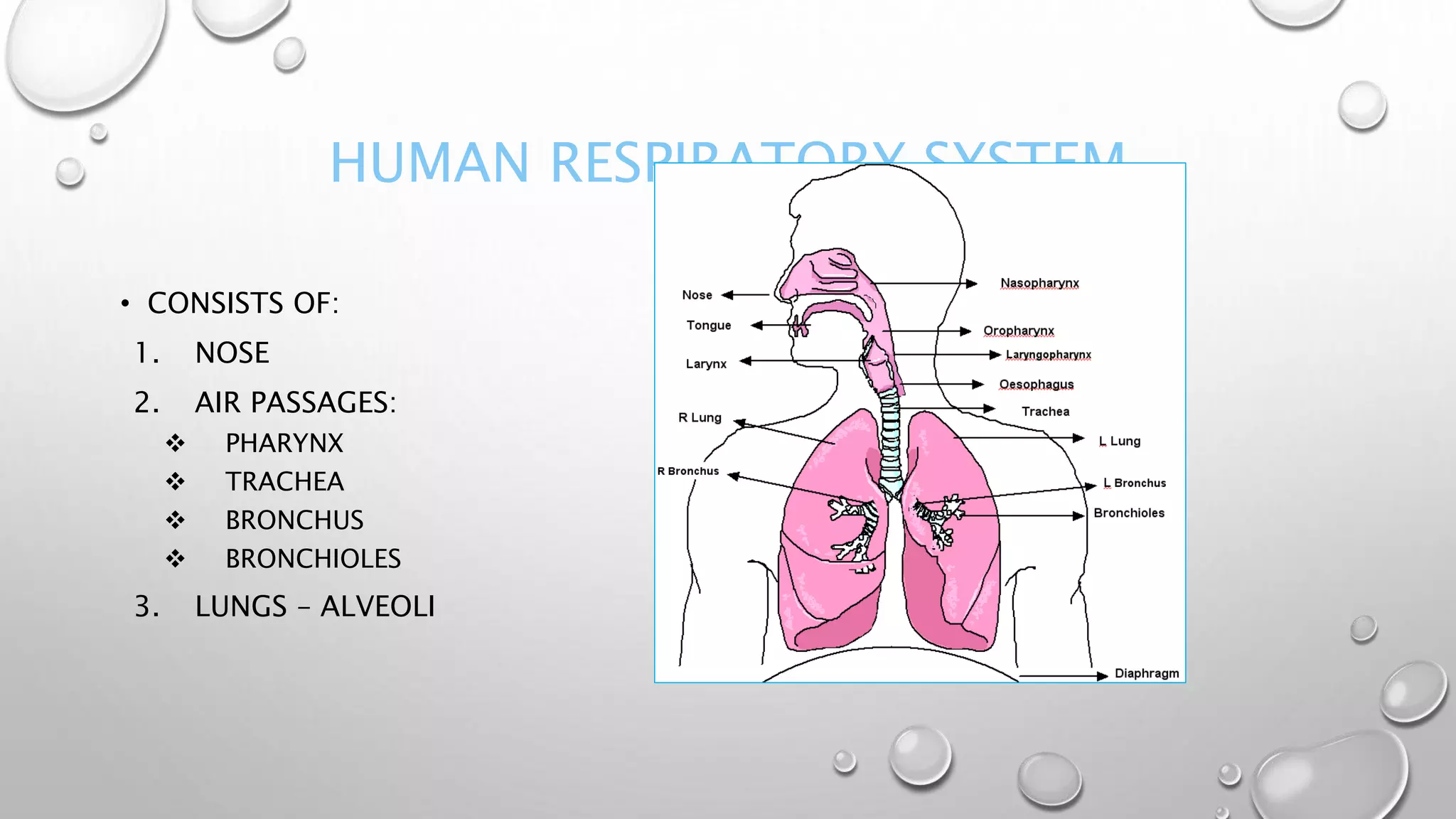
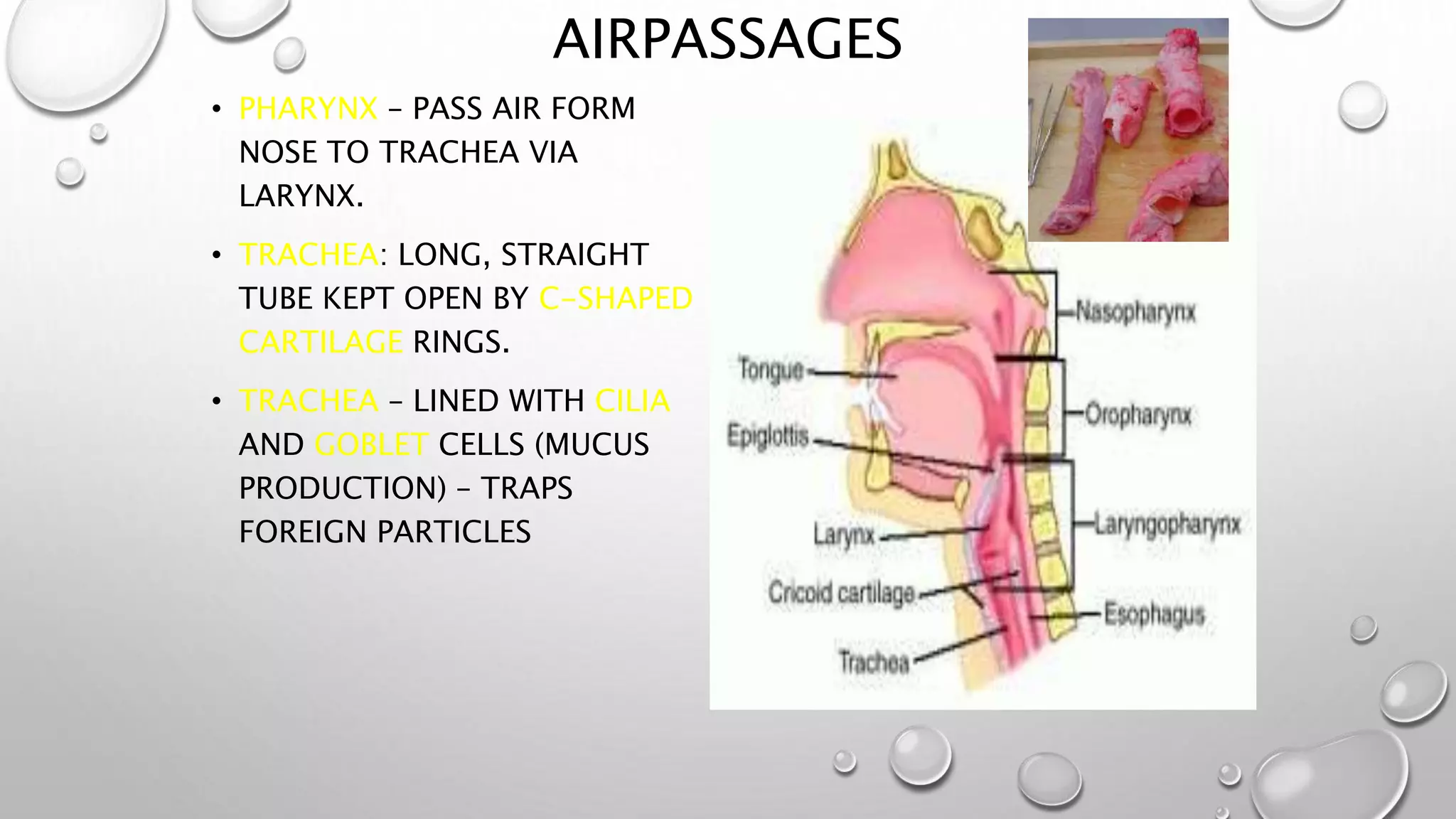
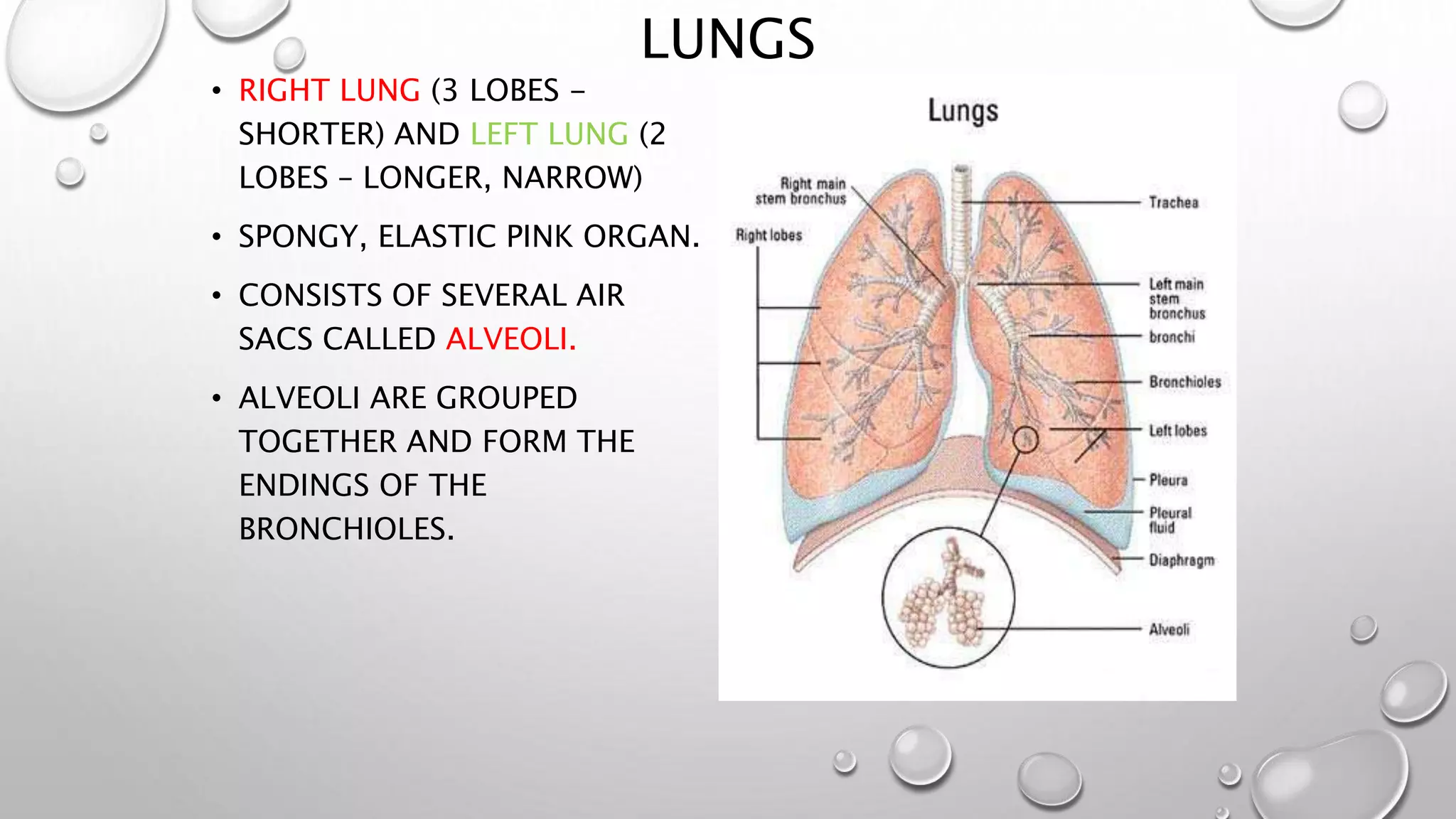
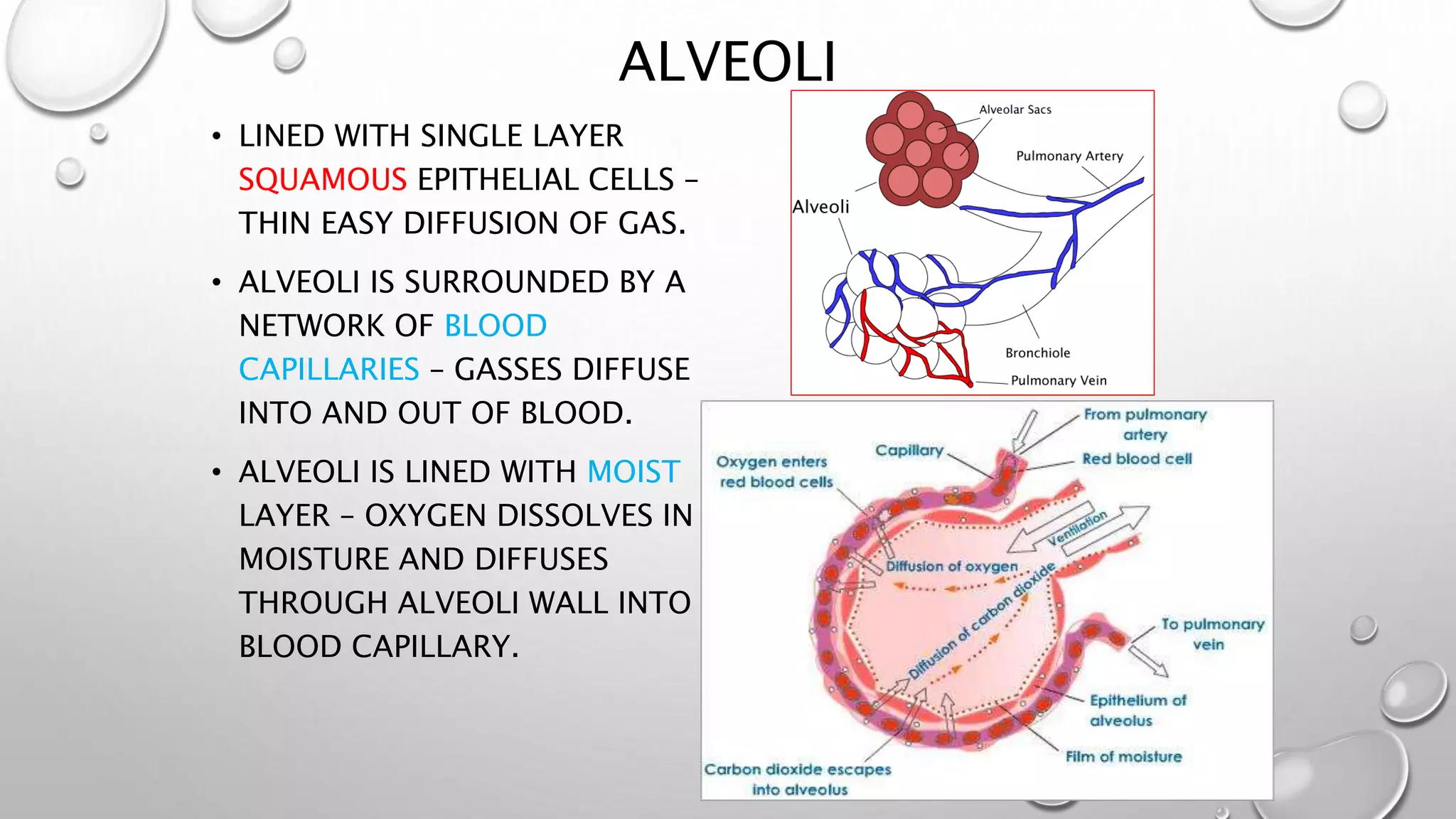
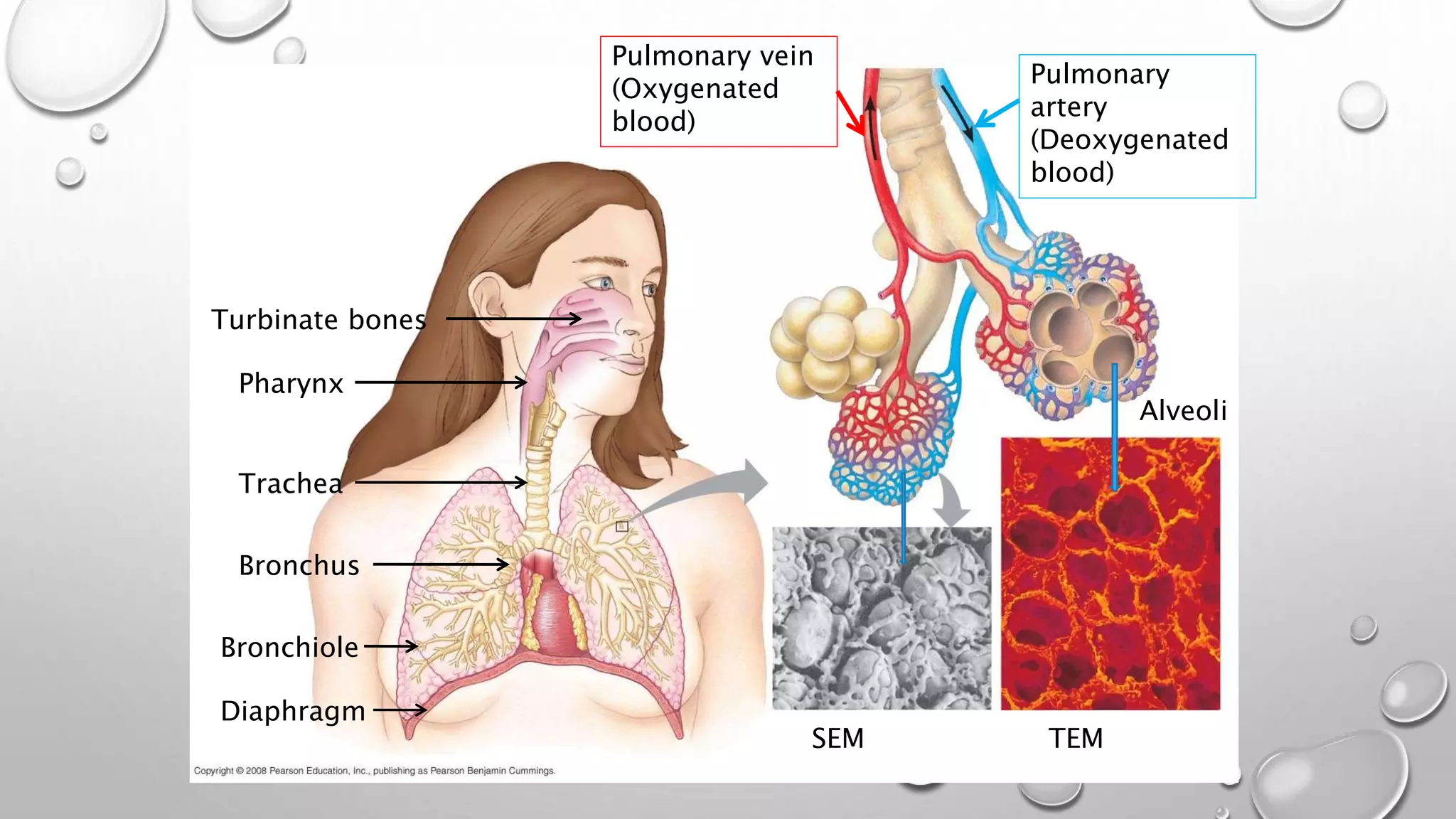
2. It explains the human respiratory system anatomy including the nose, air passages, lungs and alveoli where gaseous exchange takes place via diffusion.
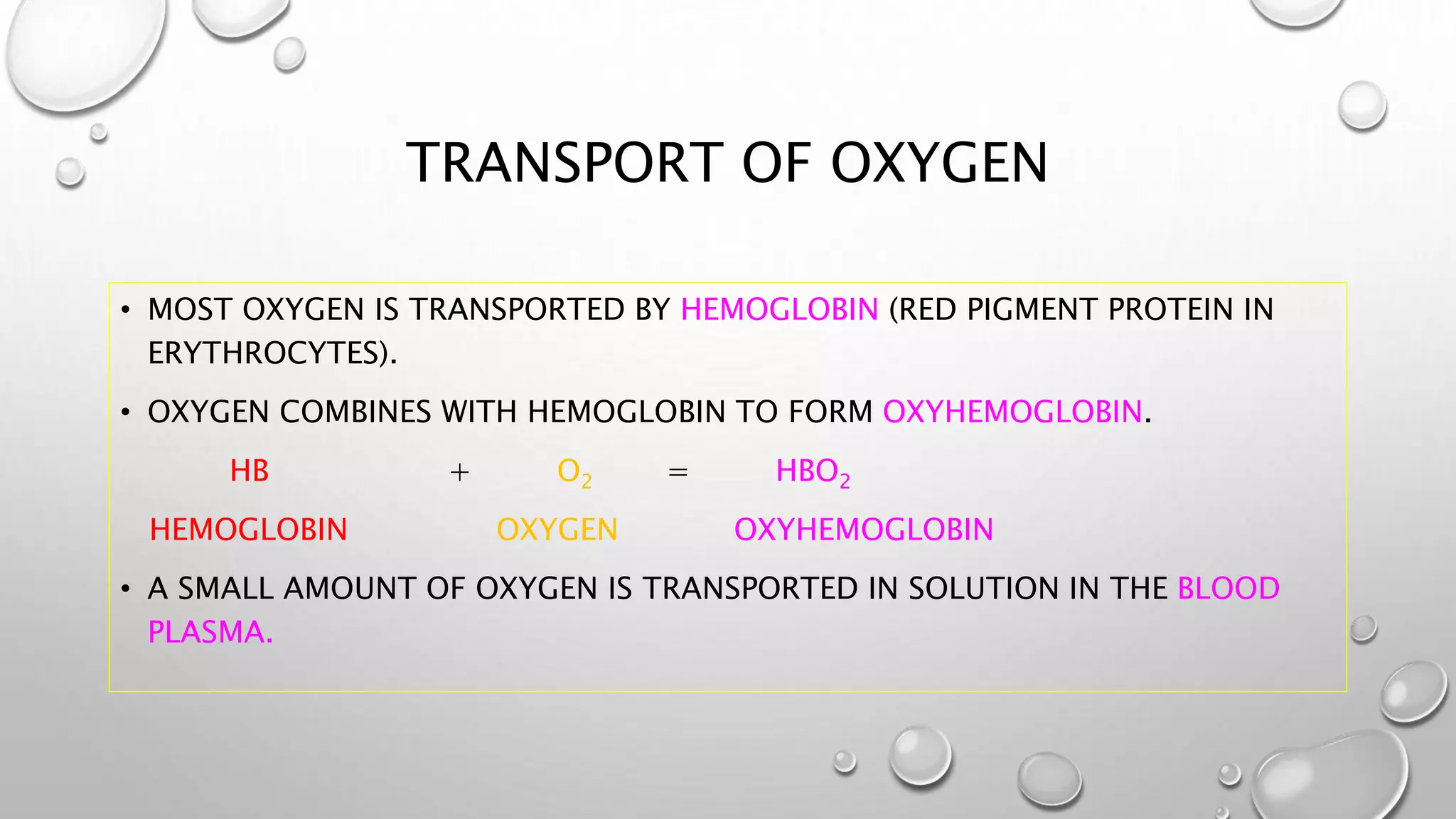
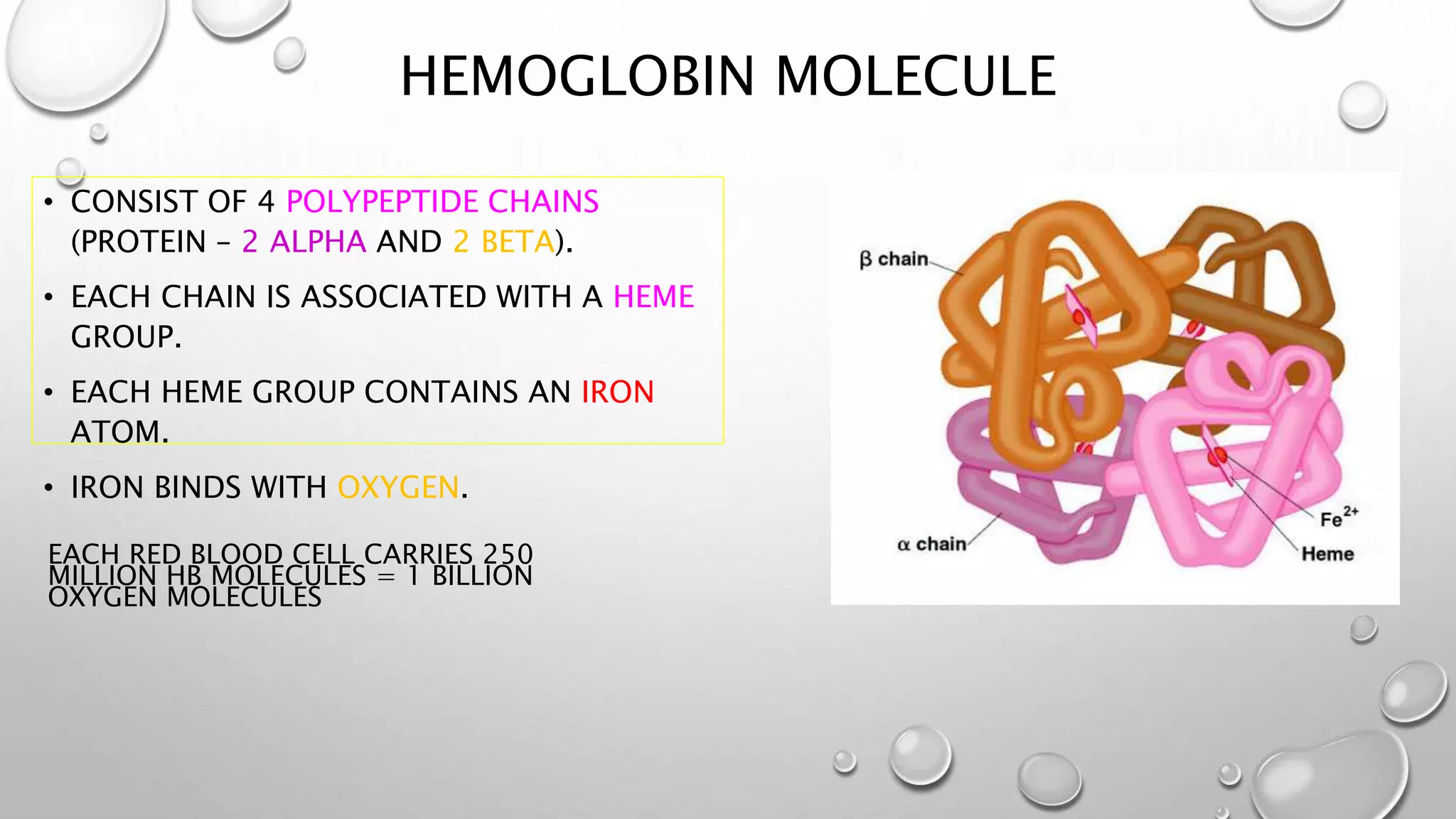
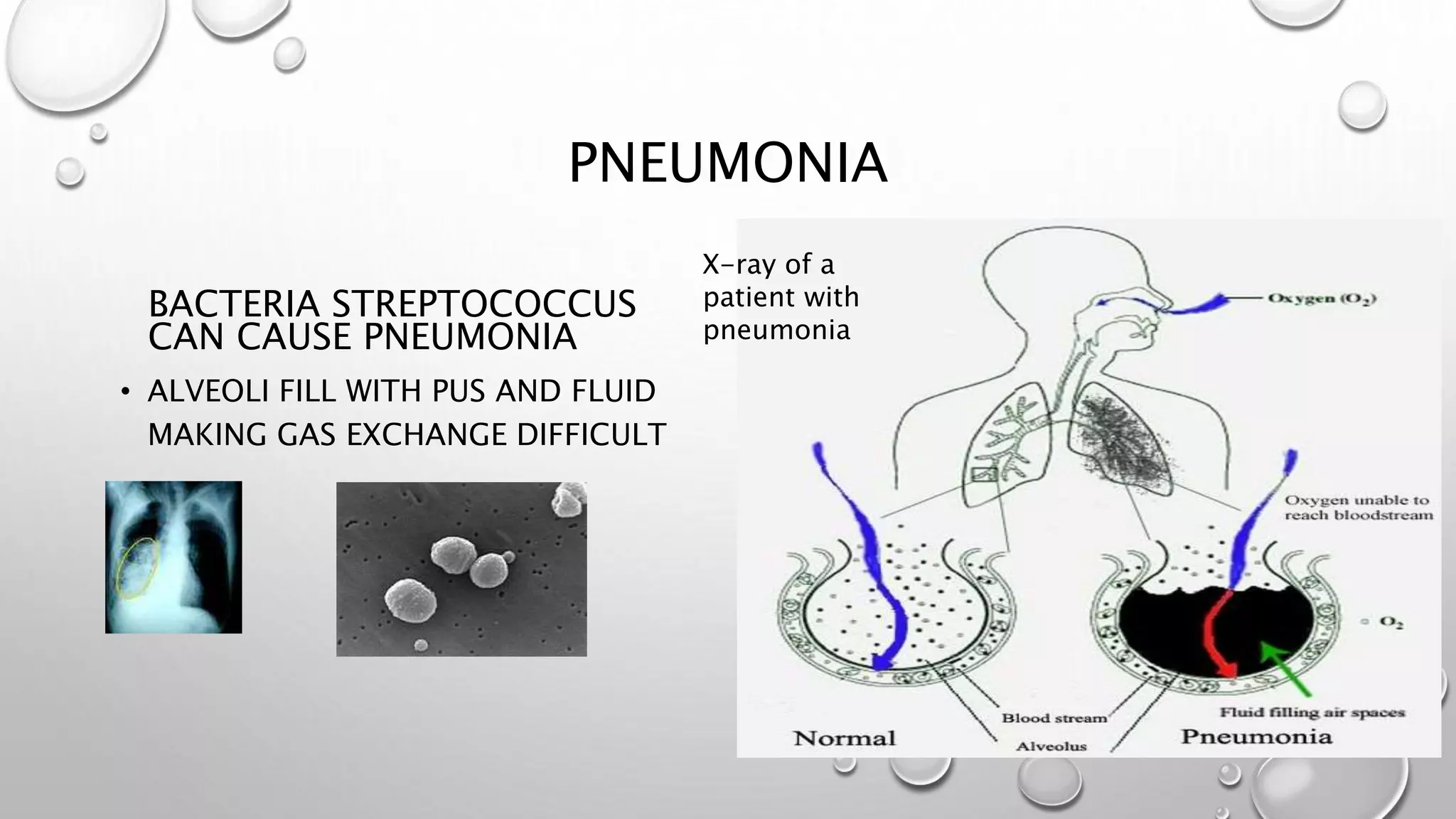
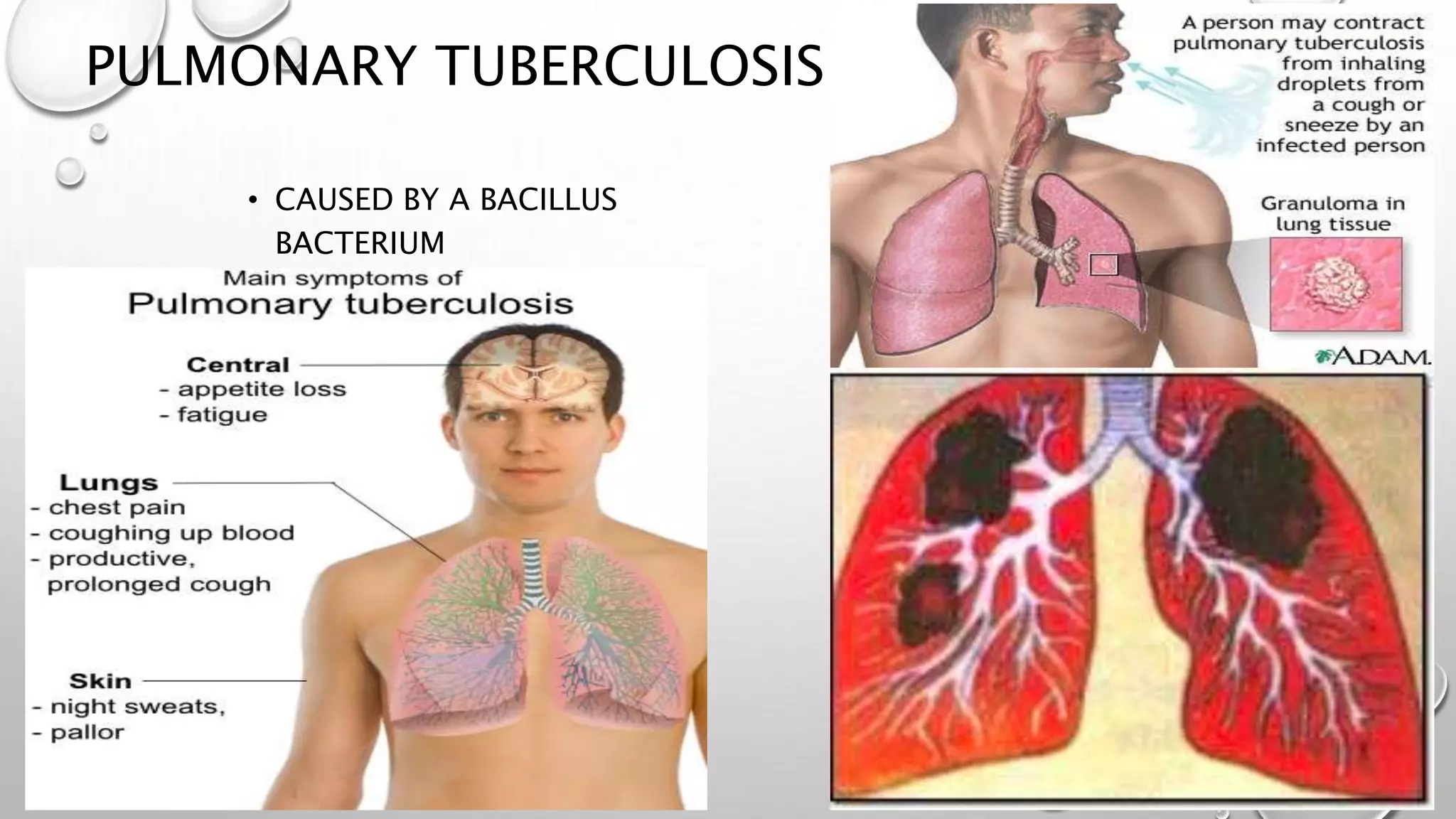
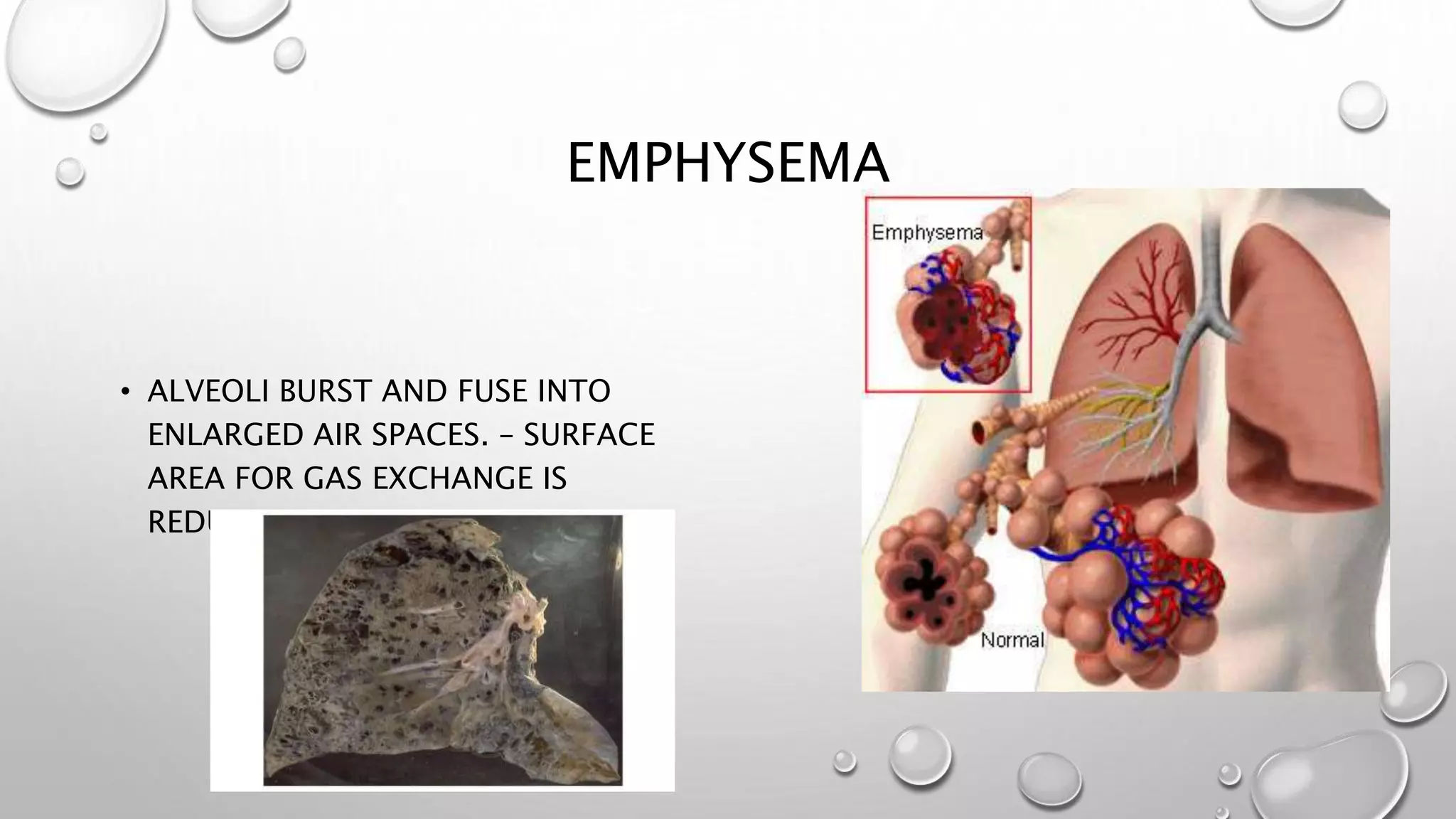
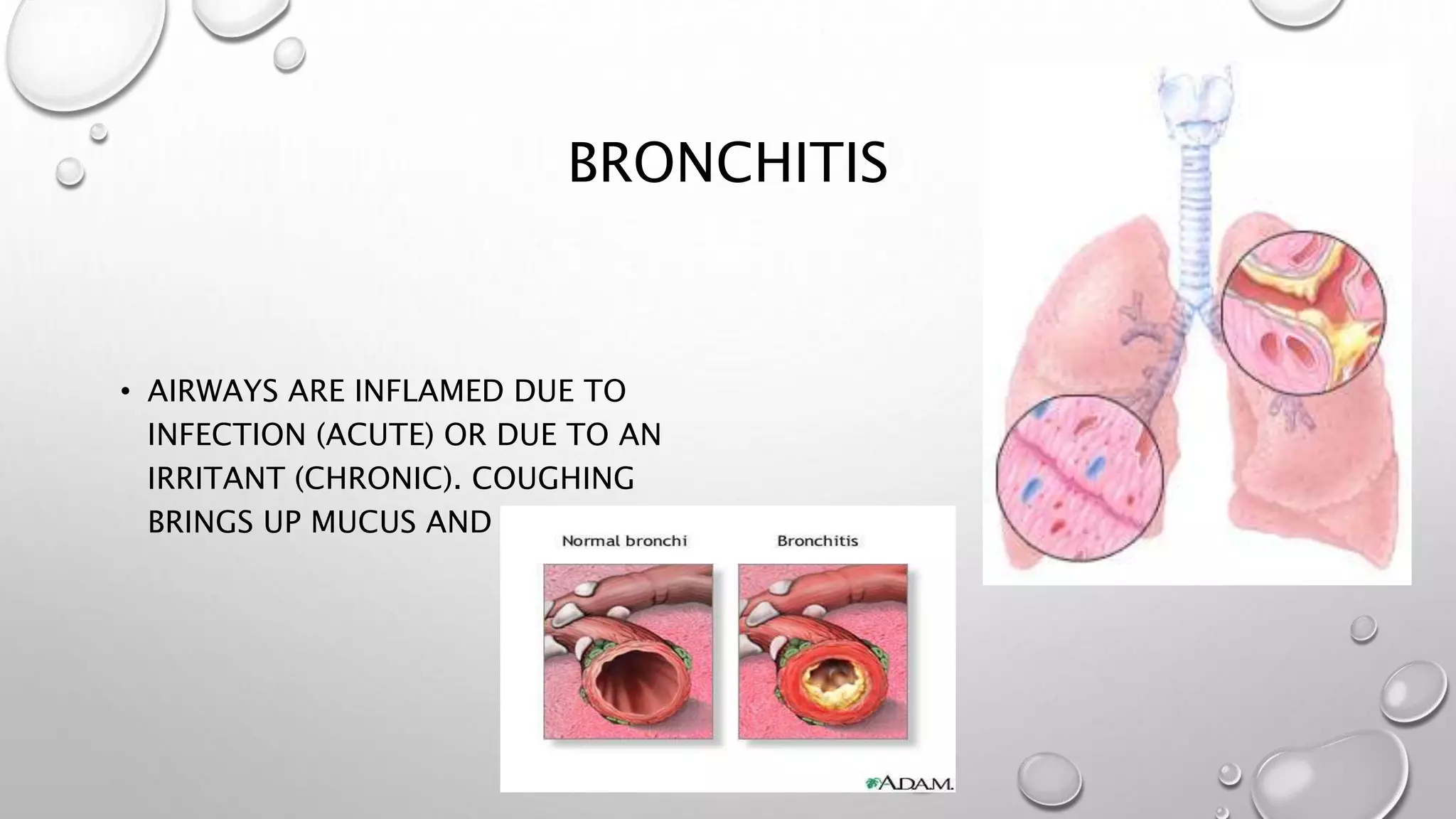
3. It covers the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, cellular respiration consuming oxygen to produce energy, and common respiratory diseases like pneumonia, tuberculosis, and effects of smoking.





![GAS EXCHANGE
EXTERNAL RESPIRATION
• GAS EXCHANGE BETWEEN AIR IN
LUNGS AND BLOOD
• MOVEMENT DRIVEN BY DIFFUSION
GRADIENT. ( [] TO [])
• GASSES EXERTS PRESSURE, THE
AMOUNT OF PRESSURE EACH GAS
EXERTS IS CALLED – PARTIAL
PRESSURE (PO2
AND PCO2
)
INTERNAL RESPIRATION
• GAS EXCHANGE BETWEEN BLOOD
AND TISSUE FLUID
• MOVEMENT DRIVEN BY DIFFUSION
GRADIENT. ( [] TO [])
• GASSES EXERTS PRESSURE, THE
AMOUNT OF PRESSURE EACH GAS
EXERTS IS CALLED – PARTIAL
PRESSURE (PO2
AND PCO2
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit3respiratorysystemandgasexchange2-181028120655/75/Unit-3-respiratory-system-and-gas-exchange-2-19-2048.jpg)